The following sections describe how you can test and debug your Virtual Assistant to validate the working of External NLU.
Talk to Bot
After completing the steps in Adapter Configuration and enabling the API, to check if the intent identification is done by External NLU adapter or not, you can follow these steps:
You can also analyze the Debug Log, NL Analysis, and Session Context & Variables to understand the intent detection mechanism.
Debug Log
If the external NLU is enabled, the Debug Log displays whether the intent is detected by External NLU or not before the ‘Intent node initiated’ debug log entry. In case of call failure, an error response is displayed in the debug log entry.
This is displayed only if an external NLU is enabled. If the API call fails, it is also indicated in the debug log statement.
-
- The debug logs display the request and response payload for the calls made to the LLM by the Dynamic Conversation features only.

- Hover over the information icon to view the KTraceid and XTraceid for each user interaction. The KTraceid helps track and debug activities. The XTraceid is a unique identifier for each message, included in the platform logs.

- Under Session Context & Variables, you can see the variables for intents and entities in detail as shown in the following screenshots.


- The debug logs display the request and response payload for the calls made to the LLM by the Dynamic Conversation features only.
NLP Analysis
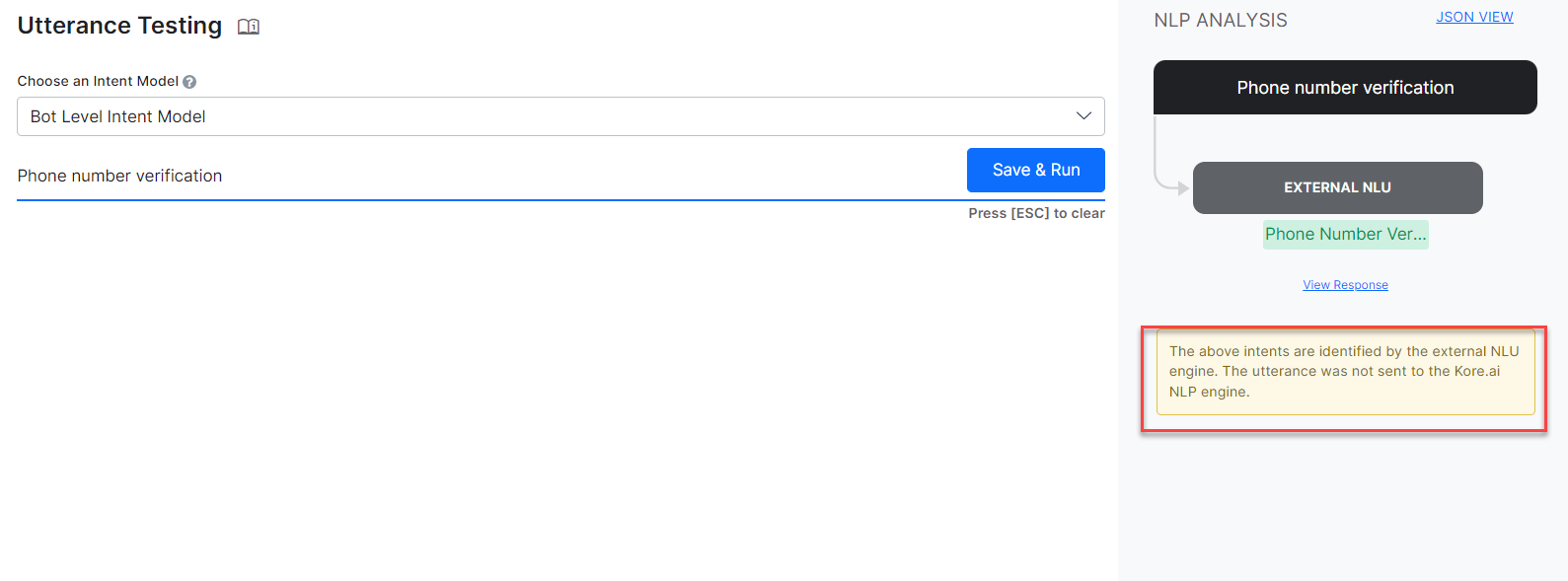
By using NL analysis, you can see whether the intent was identified or not by an external NLU engine. This works from all the workflows that provide the NLP analysis. For example – Talk to Bot, Utterance Testing, Batch Testing, Health and Monitoring, and NLP Insights.
Refer to the following sections for more details.
Utterance Testing
Utterance Testing also provides NLP Analysis. The Matched Intents and Fields/Entities tables that provide an easy way to update training data like synonyms, patterns, etc are not displayed if the Intent is identified on the external NLU engine.
-
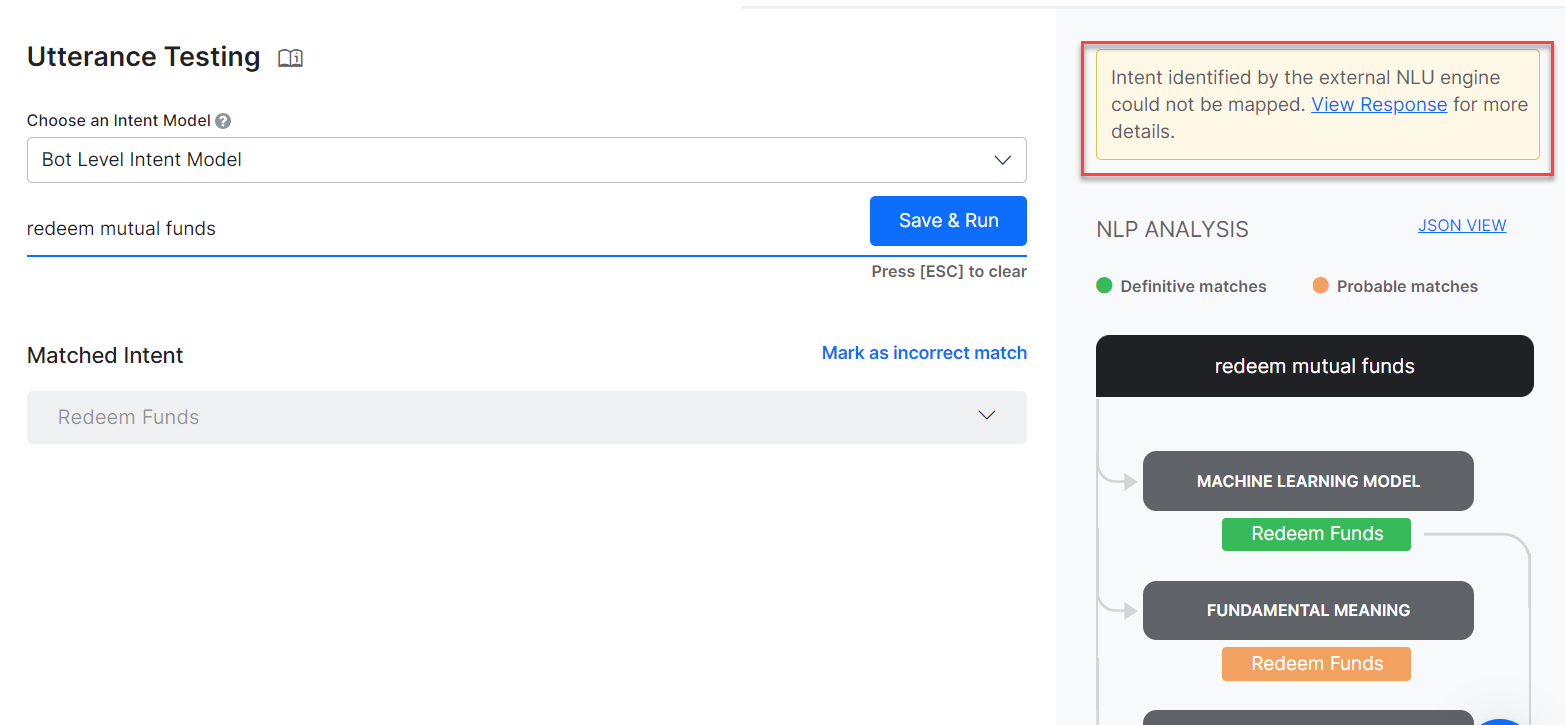
- If the intent is not detected by the external engine, the Kore.ai NLU engine acts as a fallback. So, in this case, the NLP analysis shows the analysis of intent detection results from our three engines along with the ranking and resolver. For more information, see Ranking and Resolver.

- If the intent is not detected by the external engine, the Kore.ai NLU engine acts as a fallback. So, in this case, the NLP analysis shows the analysis of intent detection results from our three engines along with the ranking and resolver. For more information, see Ranking and Resolver.
Batch Testing
The test case result for True positive, False Positive, True Negative, and False Negative(TP, FP, TN, FN) scenarios is generated based on the net outcome of a combined result of External NLU and Kore.ai NLU engine.
For example, irrespective of whether the expected intent is detected by the External NLU or Kore.ai engine, the test result is TP. If the net result is a wrong intent identified, the test result should be FP. In case of no intent detected by any of the engines, it is classified as TN, when no intent was expected but some intent was detected, then it is FN.
| Note: There is no common base to compare the scores of all the engines, hence scores sent by the external NLU are not considered. |
For any intent detected by the external NLU, it should be considered that the thresholds have been met and in the ‘Matched Intent Score’ column, this is indicated as ExtNLU (without any score against it) in place of ML, FM, or KG scores. This can be viewed in the downloaded CSV under NLU of Batch Testing. To know more, see Batch Testing.
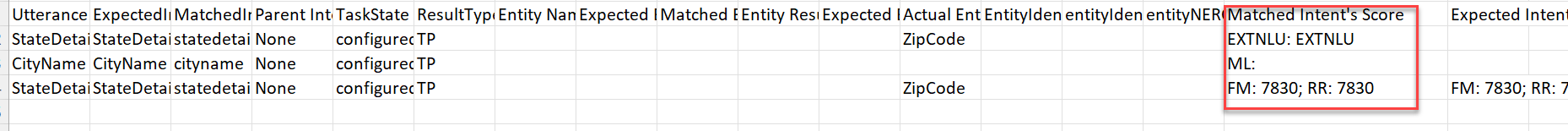
If the ExtNLU returns multiple intents, the thresholds met for all those intents are considered and accordingly the test result is concluded.
Health and Monitoring
In Health and Monitoring go to Test Cases —> Detailed Analysis to see the Intents and Entities identified by External NLU, without any scores. The Traits engine is not dependent on the external NLU.
| Note: If the external NLU is enabled, some of the recommendations may not be relevant because they are for the Kore.ai NLU engines. The recommendations are displayed based on the training done on the Kore.ai Platform. |

For more information, see Virtual Assistant Health and Monitoring.
NLP Insights
NLP Insights have Intent Identified, Intent Not Identified utterances and their NLP analysis details captured. You can view the details of all the failed External NLU API calls in the debug logs of NLP Insights.
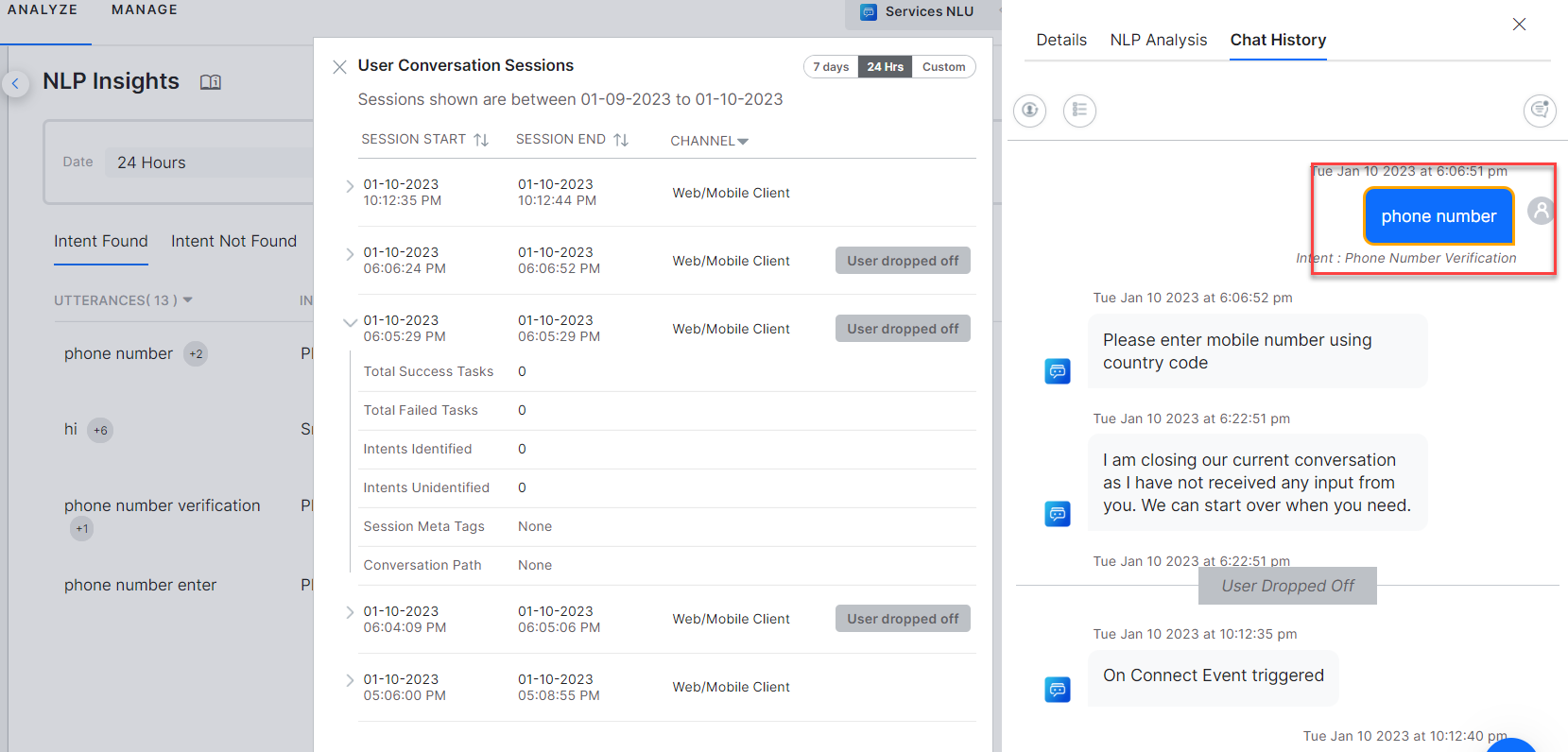
For more information, see NLP Insights.
Conversation Behavior
This list describes the conversation behavior while using external NLU adapter:
- When an intent is identified by the external engine, the corresponding task on the Kore.ai Platform is triggered based on the name mapping.
- Quality of the intent, entity, or FAQ detection depends on the training and capabilities of the external engine
- All the other conversation flow behaviors are handled by the Platform. For e.g.:
- Re-prompts, error prompts, message responses, widgets, supported channels, channel-specific experience customizations, authorization for service calls, alerts, small talk
- Language Detection
- Sentiment Analysis
- Traits identification
- Decisions to scan for sub-intent, follow-up intents
- Interruption handling as per settings
- Entity over Intent or Intent over Entity as per settings
- PII Masking/Redaction
- Execution of all the nodes of a Dialogue Task
- Context Object construction
- Response messages and fulfillment
- Logical flows
Note: Information like the response messages and fulfillment from the external engine is ignored. - When external NLU is enabled, in the interruption handling only one behavior, “Switch to a new task without any notification to the user and discard the current task”, is supported. To know more information, see Interruption Management Settings.
- If the external NLU API returns an error or the API cannot be reached, a fallback intent gets activated with the standard response as, Error in continuing the conversation due to incorrect bot definition. To know more information, see Standard Responses.
-
Note: The Intent and entity mapping work based on a case insensitive comparison of the names defined on the two platforms. - For the entity identification to work properly, it is recommended to define the entity nodes in the same sequence on the XO Platform and the external engine.
- If the external NLU fails to detect the entity, then as a fallback, an attempt is made to detect the same on the Kore.ai NLP engine.
Follow-up and Sub-Intents Identification
- If all the required parameters are available in the context, the Follow-up intent scope gets activated on the External NLU. Once the follow-up intent scope gets active on the Platform, the utterance is sent to External NLU for intent identification.
- Similarly, when the scope for sub-intent is active on the Kore.ai Platform, the utterances should be sent to the external NLU for intent detection along with the parent intent context.