Kore.ai has one of the best NLP engines in the market including the unique Multiengine NLP capability. However, to provide integration flexibility and let the customers use the NLU engine of their preference with other features of the platform, Kore.ai provides an ability to make an external NLU engine co-exist with our built-in NLP engines.
Overview
The Kore.ai XO Platform provides an option to configure and enable an external NLU adapter for your Virtual Assistant so that you can easily use the NLU models built and trained on the other engine. Integration with external NLU engines is provided on the platform as an additional helpful feature for Intent and Entity detection. All other functionalities are managed on the Kore.ai XO Platform. When the adapter is enabled, the external engine’s intent or entity detection takes precedence. However, Kore.ai proprietary NLU acts as a fallback, in case the external engine fails to detect an intent or entity. Additionally, you have the option to continue training intents on the XO Platform while also utilizing previously trained intents from the external engine.
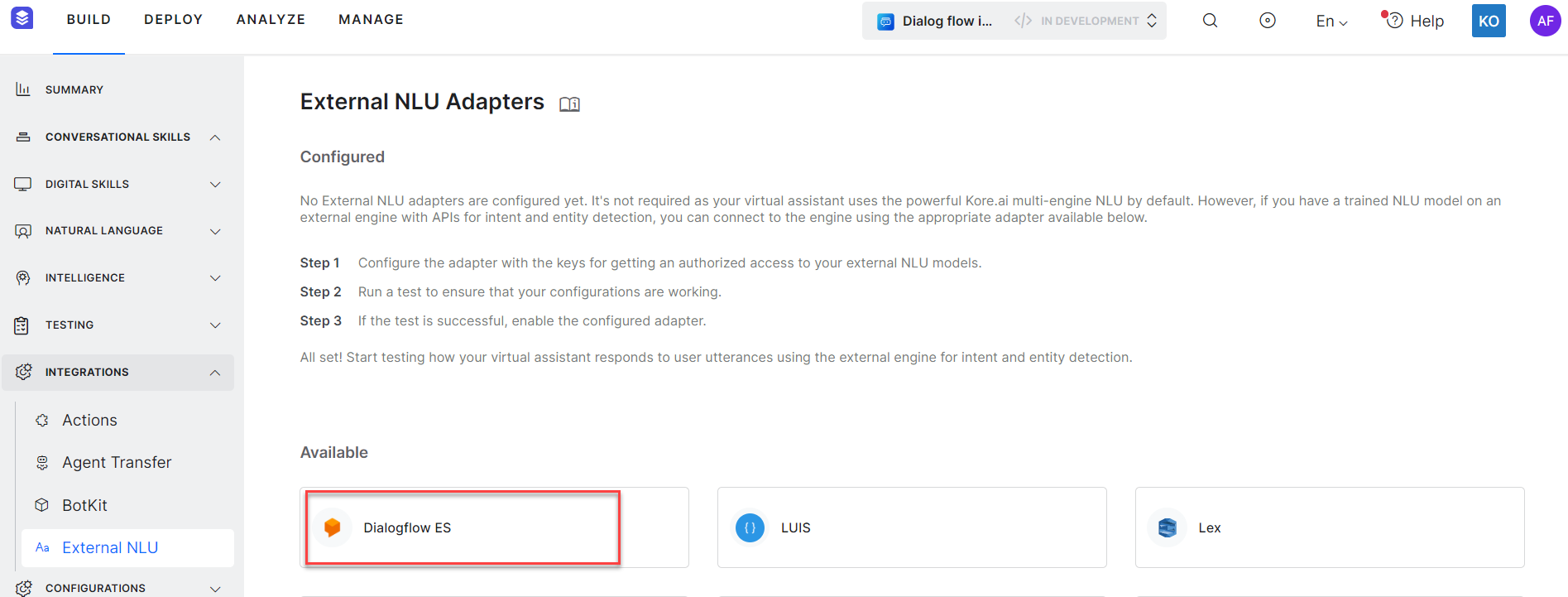
The Build → Integration → External NLU page has the list of available adapters
Adapter Configuration
Steps to configure an external NLU adapter:
- Click on the External NLU adapter corresponding to the engine you want to use for intent and entity detection, to configure the settings.

- Provide the configuration details required for establishing authorized connection between the Kore.ai and the external engine.
Note: Authorization keys and other parameters configured here are required by the external engine to allow APIs access.
- In the platform specific settings, by default De-identification of PII data is selected as No as shown in the preceding screenshot.
Note: De Identification of PII data means removing or masking PII data in order to reduce the risk of disclosure of user’s sensitive information that is connected with the data. If the de-identification of PII is disabled for the External NLU Adapter, any API call being made to the external NLU will send the masked PII data in the payload. If you select the option – do not de-identify PII data from the user input, intent or entity detection may not work properly. To know more about PII data, see Redacting Personally Identifiable Information.
- Click Save, to save the configurations.
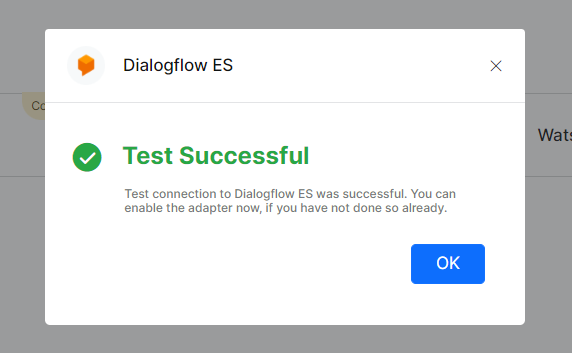
- You can check the External NLU connectivity by clicking TEST. On successful completion of the test, the following message is displayed.
 Note: You can configure multiple external adapters but you can enable only one external NLU adapter at a time. You can test the connection for an adapter that has all the mandatory fields configured. The test can be executed even if the adapter is not enabled.
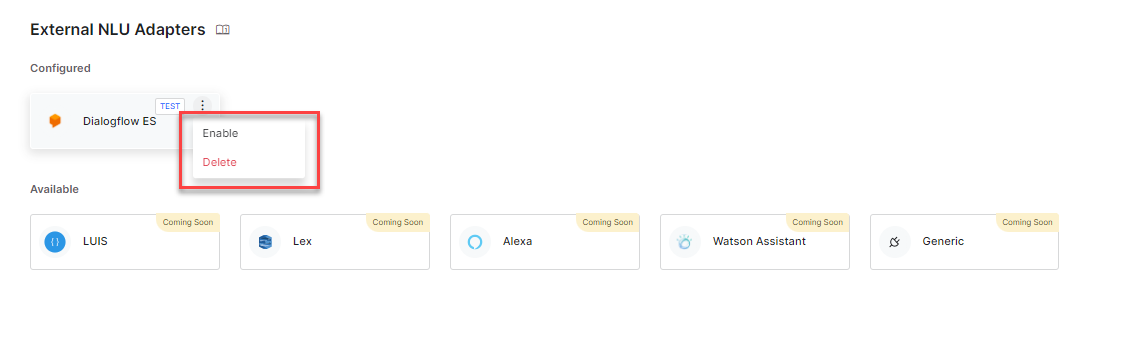
Note: You can configure multiple external adapters but you can enable only one external NLU adapter at a time. You can test the connection for an adapter that has all the mandatory fields configured. The test can be executed even if the adapter is not enabled. - External NLU can be enabled either by updating the configuration setting to Yes under the Enable External NLU Adapter option in the configuration panel, or by using the Enable/Disable option that is displayed on clicking the ellipsis icon.
Note: Starting from 10.1 released on 16-April-2023, the Universal Bots (UB) allows you to link bots that are using external NLU alongside other bots using built-in NLP. However, the UB dialog tasks and linked bot qualification always use Platform’s built-in NLP.
See Dialogflow Engine to understand the Dialogflow usage. See Test and Debug to know how to test your virtual assistant to validate the external NLU and to understand the conversation behavior.