The Co-Pilot features add design-time capabilities to accelerate your bot development process using tailored LLM features. By default, all the features are disabled. To enable the feature, select the model, prompt, and toggle the status to enable it. You can select another supported model for a feature if you have configured multiple models. You can also change the model, its prompts, and its settings.
Steps to enable the feature:
Change Settings for a Model
Choose the option below based on the model for which you want to change the settings:
Change Settings for a Pre-built Model
You can change the selected model’s settings if required. In most cases, the default settings work fine.
Follow these steps:
- Go to Build > Natural Language > Generative AI & LLM > Co-Pilot or Dynamic Conversation.
- Hover over the feature to view the Advance Setting (gear) icon.

- Click the Advance Setting. The Advance Settings dialog box is displayed.

Adjusting the settings allows you to fine-tune the model’s behavior to meet your needs. The default settings work fine for most cases. You can tweak the settings and find the right balance for your use case. A few settings are common in the features, and a few are feature-specific:
-
- Model: The selected model for which the settings are displayed.
- Instructions or Context: Add feature/use case-specific instructions or context to guide the model.
- Temperature: The setting controls the randomness of the model’s output. A higher temperature, like 0.8 or above, can result in unexpected, creative, and less relevant responses. On the other hand, a lower temperature, like 0.5 or below, makes the output more focused and relevant.
- Max Tokens: It indicates the total number of tokens used in the API call to the model. It affects the cost and the time taken to receive a response. A token can be as short as one character or as long as one word, depending on the text.
- Number of Previous User Inputs: Indicates how many previous user messages should be sent to the model as context for rephrasing the response sent through the respective node. For example, 5 means that the previous 5 responses are sent as context.
- Additional Instructions: Add specific instructions on how prompts should be rephrased. You can create a persona, ask it to rephrase in a particular tone, etc.
- Similarity Threshold: The Similarity Threshold is applicable for the Answer from Docs feature. This threshold refers to the similarity between the user utterance and the document chunks. The platform shortlists all chunks that are above the threshold and sends these chunks to the LLMs to auto-generate the responses. Define a suitable threshold that works best for your use case. Setting a higher threshold limits the number of chunks and may not generate any result. Setting a lower threshold might qualify too many chunks and might dilute the response.
Change Settings for a Custom Model
For a custom model, you can only change the post-processor script to adjust the actual response with the expected response.
Follow these steps:
- Go to Build > Natural Language > Generative AI & LLM > Co-Pilot.
- Hover over the feature to view the Setting (gear) icon.

- Click Edit. The Actual Response is displayed.

- Click Configure. The Post Processor Script is displayed.

- Modify the script and click Save & Test. The Response is displayed.

- Click Save.
Model and Feature Support Matrix
The following table displays the Co-Pilot features and the supported models.
(✅ Supported | ❌ Not supported)
| Model/Feature | Automatic Dialog Generation | Conversation Test Case Suggestions | Conversation Summary | NLP Batch Test Case Suggestions | Training Utterance Suggestions |
| Azure OpenAI –
GPT 3.5 Turbo, GPT 4 Turbo, GPT 4o, and GPT-4o mini* |
✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| OpenAI –
GPT 3.5 Turbo, GPT 4, GPT 4 Turbo, GPT 4o, and GPT-4o mini* |
✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Provider’s New LLM** | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Custom LLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Amazon Bedrock | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Kore.ai XO GPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
* The OpenAI GPT-4o mini and Azure OpenAI GPT-4o mini do not include system prompts, but they can be used with custom prompts.
** To use the Provider’s New LLM, you must create a custom prompt as system prompts are unavailable.
Feature Details
Automatic Dialog Generation
This feature auto-generates conversations and dialog flows in the selected language using the VA’s purpose and intent description provided (in English or the selected Non-English Bot Language) during the creation process. The Platform uses LLM and generative AI to create suitable Dialog Tasks for Conversation Design, Logic Building & Training by including the required nodes in the flow.
You must provide an intent description, and the Platform handles the Conversation Generation for the Dialog Flow.
You can preview the conversation flow, view the Bot Action taken, improvise the intent description, and regenerate the conversation to make it more human-like.
The nodes and the flow for the Business Logic are automatically built for your conversation, and you only need to configure the flow transition.
The Platform auto-defines the Entities, Prompts, Error Prompts, Bot Action nodes, Service Tasks, Request Definition, Connection Rules, and other parameters.
Usage
Once you enable this feature:
- The Platform triggers the flow when you launch a task for the first time.
- The Platform presents the intent description and an option to generate conversation.
- You can preview the generated conversation, edit the description, and regenerate it.
- The Platform sends the updated description to Generative AI in the background to get the new conversation.
- Once you’re satisfied with the conversation, generate a dialog task.
If this feature is disabled, you will not have the option to auto-generate a dialog flow when first launching a Dialog Task.
| Note: The Platform uses the configured API Key to authorize and generate the suggestions from OpenAI. |
Conversation Test Cases Suggestions
This feature provides a regression tool or a Playbook that creates a conversation test suite for each intent (new and old) in English or Non-English Bot language to evaluate the impact of the change on the conversation execution.
You can view input/utterance suggestions at every conversation step simulating the various input types and scenarios. This feature helps check if the task/intent is robust enough to handle random user utterances.
This feature also helps you predict and simulate the end user’s behavior and check if the VA can execute all the defined flows by generating user responses and presenting any digressions from the specified intent.
Usage
- You can create a test suite by recording a live conversation with a VA by initiating the interaction or letting the VA initiate it.
- An icon displays to indicate the user input suggestions from Generative AI.
- The Platform triggers OpenAI or Anthropic Claude-1 based on your model selection to generate suggestions for user input where expected in English or a Non-English Bot Language.
- The Platform shares the following information with OpenAI/Anthropic to generate suggestions
- Randomly picked intents from the VA (Dialog, FAQ),
- Conversation flow,
- Current Intent, if any,
- Current node type:
- For an entity node, the system sends the following:
- Entity name,
- Entity type,
- Sample entity values.
- Types of user input scenarios:
- Entities,
- Without entities,
- Different entity combinations in the user input,
- Digression to another intent,
- Trigger error scenarios.
- For an entity node, the system sends the following:
- You can regenerate suggestions if required.
- You can accept the suggestions shown or type custom input at every step.
- Create a Test Suite after stopping the recording and validating the model.
If the feature is disabled, the Platform doesn’t display the Generative AI suggestions icon and the suggestions themselves. Learn more.
Conversation Summary
This feature generates concise, natural language summaries of interactions between the virtual assistant, users, and human agents. It distills the key intents, entities, decisions, and outcomes into an easy-to-read synopsis. Companies can leverage conversation summarization to boost agent productivity, ensure process compliance, and create better contextual recommendations – without having to read lengthy transaction histories. It is pre-integrated with Kore.ai’s Contact Center platform. It is also extensible to third-party applications via API integration.
Scenario 1
In a contact center environment, the customer interacting with a VA may request to transfer to a live agent. During agent handoff, the agent must have the necessary context information and interaction history to assist the customers efficiently. The system generates the conversation transcript and interaction summary and routes it to the agent for better understanding.
An example of the usage: When Conversation Summary is enabled and the conversation is transferred to an agent in SmartAssist, the Conversation Summary is displayed on the Agent Console, as shown in the screenshot below.
Usage
The Conversation Summary public API fetches the summary of the entire conversation included in the transcript. LLM and Generative AI are leveraged to provide a concise and informative conversation summary from the transcript.
Scenario 2
When closing a conversation request, contact centers require an agent to summarize the customer interaction and context in their closing notes to confirm that the issue has been resolved effectively. Closing notes help document the interactions, provide context for future interactions, support quality assurance efforts, and serve as references to deliver effective customer service.
Usage
The system uses the Conversation Summary public API to fetch the details of the entire conversation between the customer and the VA or agent. The API uses an open-source LLM to summarize conversations using a large number of sample conversation transcripts.
NLP Batch Test Cases Suggestions
This feature lets you generate test cases based on the NLU Language selected, and add them to the test suite with minimum or no errors. You can give instructions in English or any Non-English bot language you’ve selected. Additionally, in case of a Multilingual NLU, the system generates utterances in the language prompted by the user. For instance, if your instructions are in Hindi, the utterances are generated in Hindi.
Usage
- When creating a New Test Suite, select Add Manually or Upload Test Cases File to add test cases.
- Add Manually creates an empty test suite where you can generate test cases and do the following:
- Select a Dialog Task.
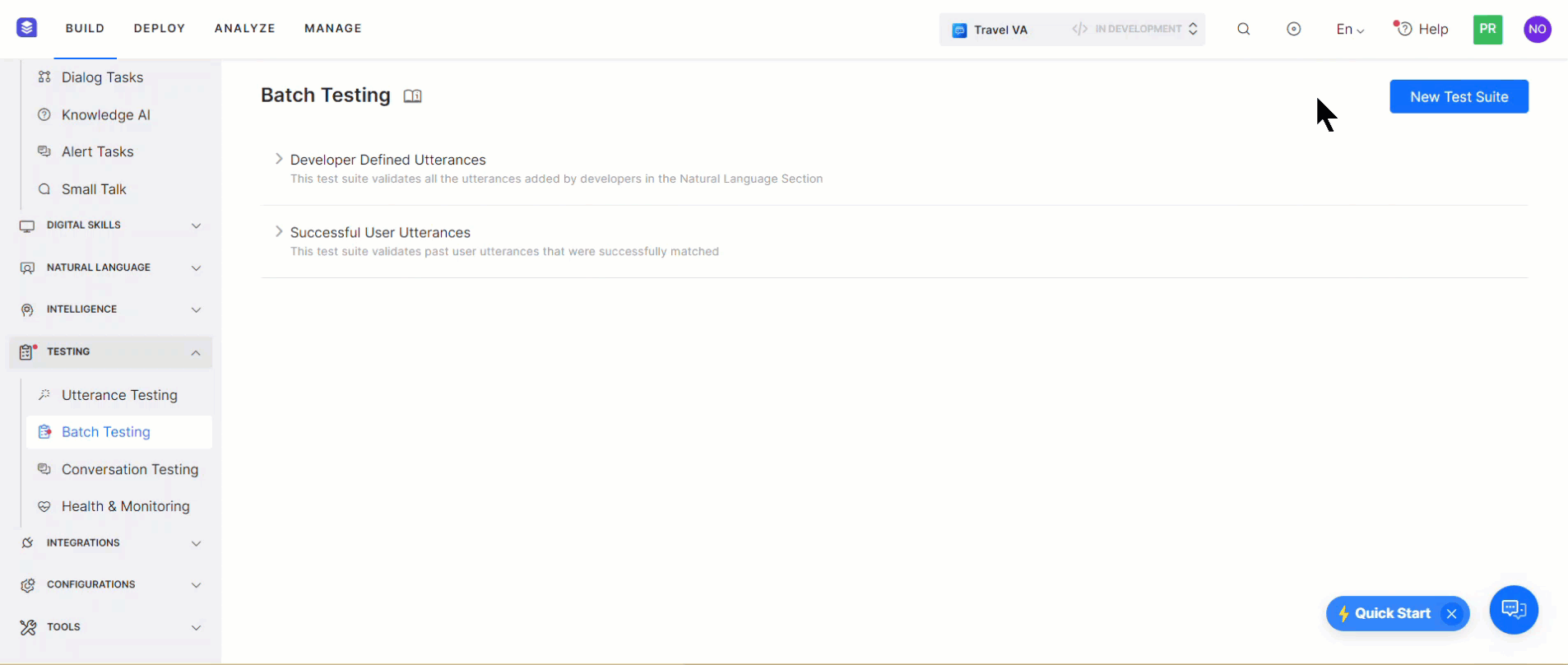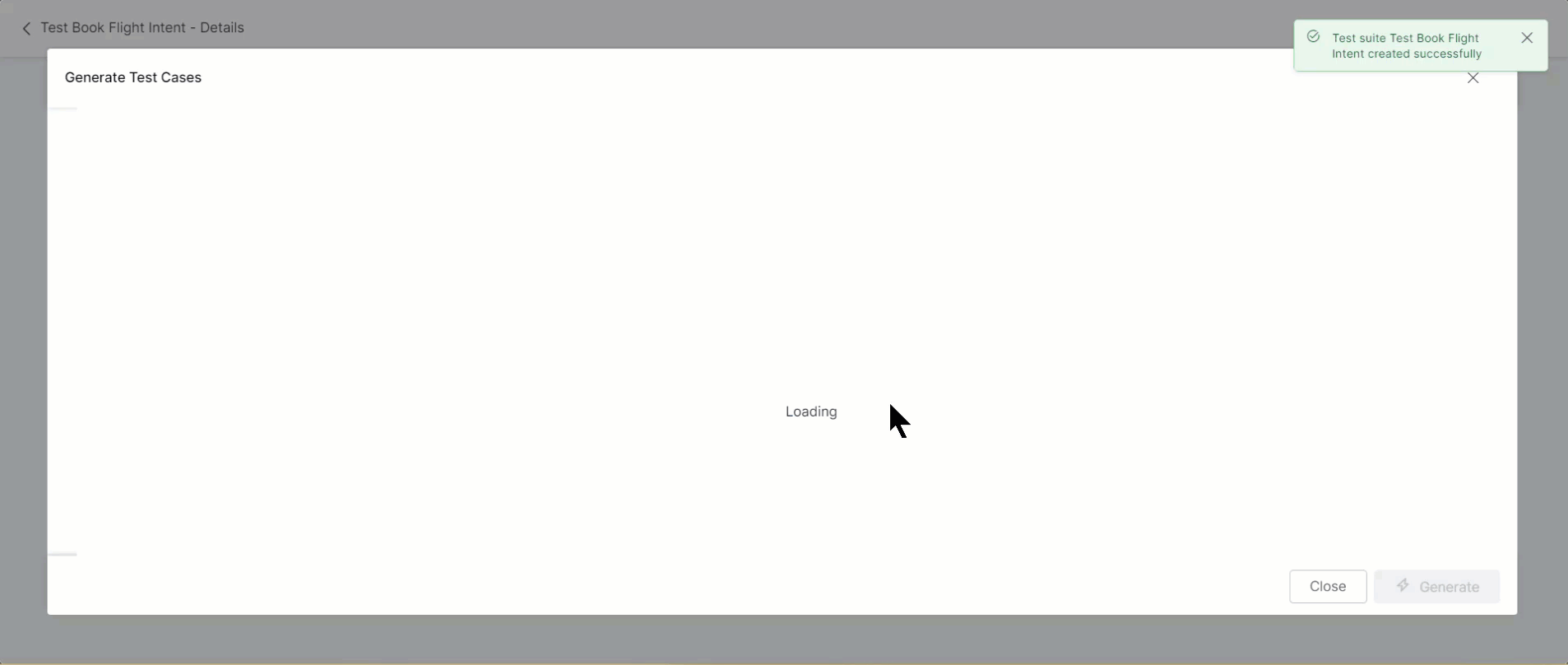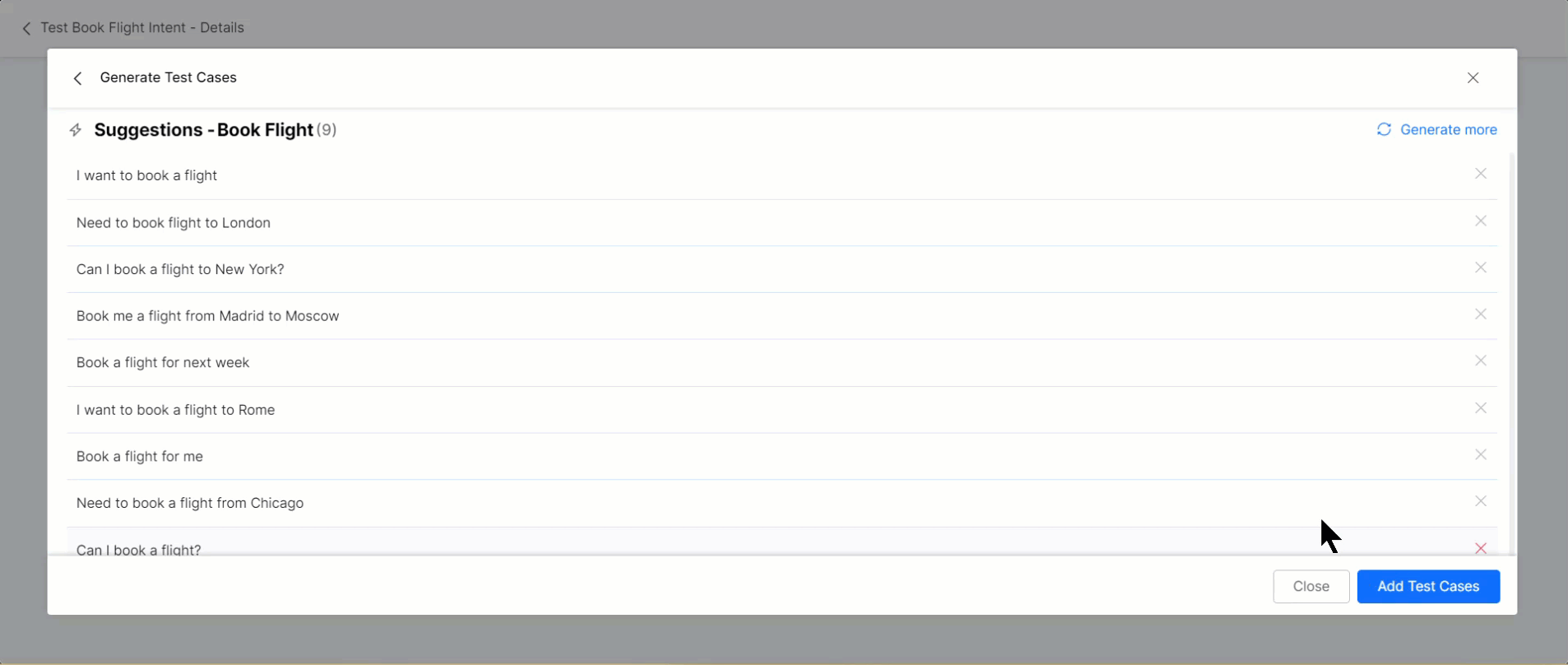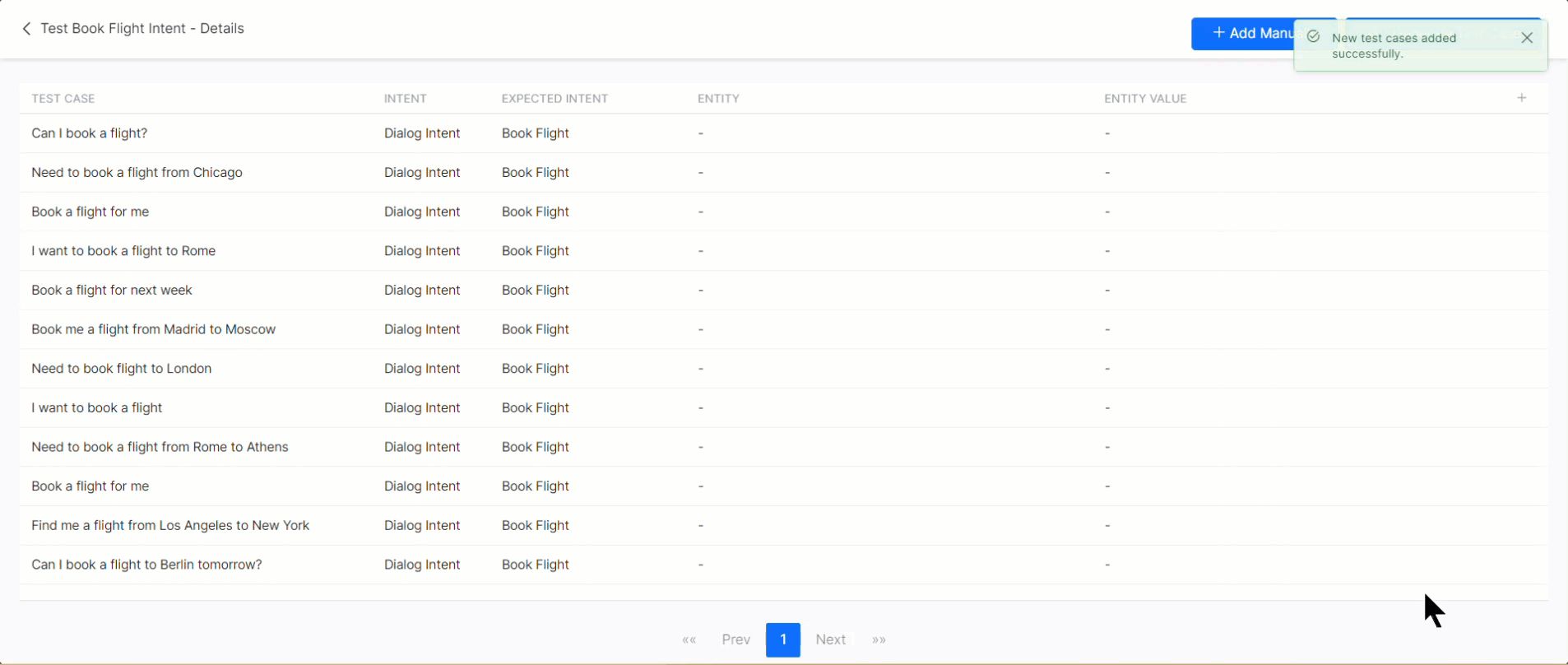
- Based on the intent context, the Generative AI generates test cases you can review and add to or remove from the Test Suite.
- When you click Generate Test Cases, the Platform sends Generative AI (OpenAI or Anthropic Claude-1 model based on your selection) the following information to generate test cases:
- Intent
- Entities
- Probable entity value
- Different scenarios to simulate end-user utterances,
- Random training utterances and test cases that are generated to avoid duplicate test cases from Generative AI.
If this feature is disabled, you will not have the option to generate test cases during batch testing. Learn more.
Training Utterance Suggestions
This feature generates a list of suggested training utterances and NER annotations based on the selected NLU language for each intent description and Dialog Flow, eliminating the need for manual creation.
Usage
The Platform can generate utterances in the NLU language to train your VA.
Once you request to generate utterances for a given intent, the Platform provides utterance suggestions (in the selected NLU language) based on the following information:
- Intent
- Entities and Entity Types
- Probable entity values
- Different scenarios for training utterances based on entities, a combination of entities, structurally different utterances, etc.
You can add/delete the suggested training utterances from the list or generate more suggestions.
If this feature is disabled, you won’t see the Suggestions tab on the training page. Learn more.
Use Case Suggestions
In the standard Virtual Assistant creation journey, use case suggestions help link the standard bot to a business scenario. Based on the selected use case, the system identifies and creates specific dialog tasks or interactions that the virtual assistant should be able to handle.
Generating Use Cases automatically creates up to 30 customizable Dialog Tasks tailored to specific use cases. This streamlines the development process, as developers won’t need to manually create each interaction from scratch.
LLM and Generative AI help generate accurate suggestions automatically without configuring any LLM settings for this feature. Providing a detailed bot description is crucial for the effective functioning of this feature. The more information you provide about the virtual assistant’s intended purpose and capabilities, the better the generated use case suggestions will be.
Usage
- The user initiates a new standard virtual assistant creation on the XO Platform.
- The user provides the Bot Name and selects the following:
- Purpose
- Standard Bot for Bot Type.
- English for Default Language.
- When adding the short Bot description, the user must include specific details on the high-level scenarios the Bot needs to handle.
- The user generates use case suggestions by clicking Get Use Cases.
- Based on the user’s description, the system generates improved use case suggestions with the help of the OpenAI Model.
- The user selects the relevant use cases from the suggestions to create and configure the VA accordingly.
If you select Create without use cases when creating a bot, the system won’t provide use case suggestions for VA creation. Only the default Dialogs for Welcome and Fallback tasks are created for the VA. Learn more.