There are multiple places where the platform responds to user utterances without the developer having to code the details. Examples include:
- Intent Not Identified when the user intent is not found or understood by the bot. Click here to read more.
- Standard Responses to certain questions, greetings, error and warning scenarios, etc.
- Event Handlers for certain common bot events can be defined, click here for more.
Though these are set by default by the platform, you can customize them as per your business requirements. In this document, we look into such customizations.
Standard Responses
In the Kore.ai Bot Builder tool, you can view the default Natural Language Processing, or NLP interpreter responses to user inputs or events.
For example, a reply to a user input of Hi! The bot replies with one of the following responses, chosen randomly at runtime:
- Hi!
- Hello
- Hi there!
- Hey 🙂
The NLP interpreter displays pre-defined text responses to users based on an event, condition, trigger, or user input. Depending on your custom bot and users of that bot, you may want to modify the default responses to users displayed for an event or request for input.
Example
- User Input – When were you born?
- Event – Authorization Failure
- Trigger – Task canceled
You can define both standard bot responses, or if desired, add a channel override response that is displayed only in the specified channel the user is in, otherwise, one of the standard default responses is displayed. Click here for a comprehensive list of default standard responses.
For example, in the SMS channel, you may only want to use short bot responses to save data.
Default Responses
To access and manage the default responses in bot builder, follow the below steps:
For each standard response category tab, the event or user input is listed followed by one or more NLP interpreter standard responses. You can modify the default response, and if needed, add additional responses selected randomly by the NLP interpreter in response to user input or system event.
In the Standard Response section, the standard bot responses are categorized in the following tabs:
- Statements – Responses displayed to the user as the result of an action by the bot or user. For example, a user cancels a task, or a user gives an invalid response to your bot request.
- Queries – Statements from the bot to the user to ask for more information. For example, Which field do you want to change?
- Error & Warnings – Statements from the bot to the user when an error occurs during the scenario, such as the End date cannot be before or same as the start date!
- Questions – Questions the bot may pose to the user when not included in any other category.
- Choices – The bot is asking for Yes/No input. For example, Would you like to receive push notifications every time this task occurs?
Add and Edit Responses
Add a New Standard Response
Note: If the standard responses are updated at the conditions wherein an ambiguity is presented to the user, the bot response will not display the ambiguous choices to the user and you need to use the function getChoices() to present the ambiguity list (refer to point 6 below).
- Select a tab category for the standard response. For example, Greeting, and then hover the situation for which you want to add the response. Click Add Response:
- The Add Channel Overrides dialog is displayed.
- In the Choose a channel drop-down list, select a channel to create a channel-specific response. You can go with the Any Channel option to enable the response for all channels.
- In the case of channel-specific response, from the Choose a Task drop-down list, select Any Task to apply this channel-specific response to all tasks or select a specific task.
- When a specific task is selected, the Choose a Field is drop-down is displayed. Select Any Field or a specific field for this channel-specific response.
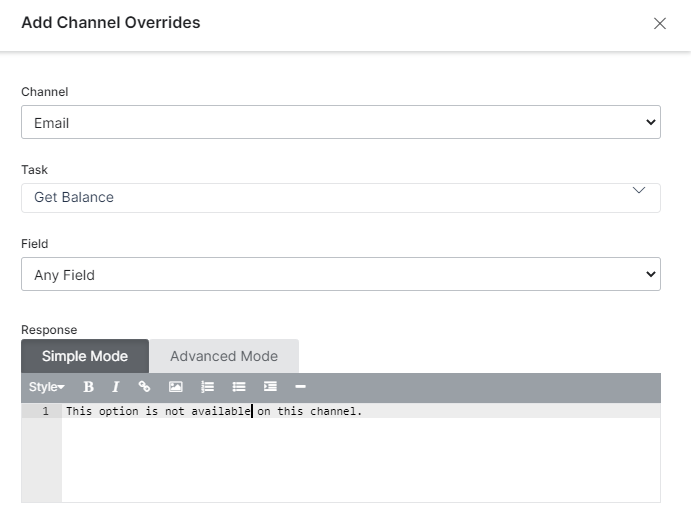
- In the bot Response editor, you can override the default Bot Response for this channel using basic editor controls on the Simple Mode tab, or write custom JavaScript for the response on the Advanced Mode tab. For the:
- Simple Mode tab – Enter the text for the default standard response. For example, *There* you are, I was ~hoping~ you would return soon! and then optionally, format the text using the formatting buttons for bold, italics, header styles, hyperlinks, ordered and unordered lists, and inserting a line. For more information, refer to Using the Prompt Editor.
- Advanced Mode tab – Enter JavaScript to override the channel message as described in the following code examples.
Note: Use the following keys to return default values for:
response.message – Returns the default message as a string.
response.choices – Returns the options choice or confirmation message types as an array.- Slack Channel Override Example
var message = {}; var attachments = []; var attachment = { 'text': "Exception occurred during API execution", 'color': '#FFCC00', 'attachment_type': 'default' }; attachments.push(attachment); message.attachments = attachments; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - FaceBook Channel Override Example
var message = { text: response.message }; var buttons = []; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices.length; i++) { var choiceItem = response.choices[i]; if (choiceItem.length > 20) { choiceItem = choiceItem.substring( 0, 18) + '..'; } var element = { content_type: 'text', title: choiceItem, payload: choiceItem }; buttons.push(element); } message.quick_replies = buttons; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - Email Channel Override Example
var message = {}; var text = response.message + ' <br> '; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices.length; i++) { text = text.concat( '<u> + response.choices[i] + ' < /u> <br>'); } message.text = text; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - SMS Channel Override Example
var message = {}; var indexArray = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z' ]; var text = response.message + '\\n'; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices .length; i++) { text = text.concat(indexArray[i] + ') ' + response.choices[ i] + '\\n'); } message.text = text; print(JSON.stringify(message));
- Slack Channel Override Example
- Using the getChoices() function, you can also customize the response display format using the message formatting templates. When the getChoices() function is called and there is an ambuguity, the platform returns the ambiguous choices information as an array which can be used to present the options to the end users.
For example, to display the standard response for Did you mean in a button format, you can use the following code:var info =getChoices() ; var message = { "type": "template", "payload": { "template_type": "button", "text": "Did you mean", "subText": "You can now customize response for did you mean", "buttons": [] } }; for (i = 0; i < info.length; i++) { var button = { "type": "postback", "title": info[i], "payload": "payload1" }; message.payload.buttons.push(button); } print(JSON.stringify(message)); - Click Done to save and close the Edit Response dialog and apply the new standard response.

