This article explains the terminology for building a Knowledge Graph within the XO Platform. This terminology applies to both the Few-Shot and the Ontology KG Models unless otherwise specified. Learn more about Knowledge Graph Types.
Terms or Nodes
Terms or Nodes are the building blocks of an ontology and are used to define the fundamental concepts and categories of a Knowledge Graph.
You can organize the terms in a hierarchical order to represent the flow of information in your graph. You can create, organize, edit, and delete terms and set term types to facilitate intent identification
The Knowledge graph is limited to 20 thousand nodes/terms and 50 thousand FAQs.
Node/Term Hierarchy
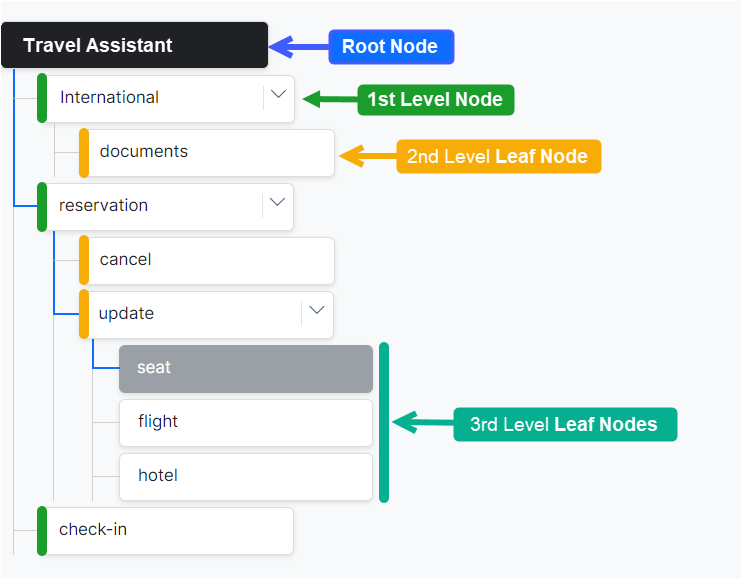
For easier representation, we identify node/term hierarchy using the following names:
Root Term/Node
The Root Term/Node forms the topmost term of your Ontology. A Knowledge Graph contains only one root node, and all other nodes in the ontology become its child nodes. The Root node takes the name of the VA by default, but you can change it as needed. In an Ontology-based KG, this node is not used for path qualification or processing. Path qualification starts from first-level nodes.
For Ontology-Based graphs, it is best to organize your FAQs into a clear structure, so we don’t recommend adding them at the Root node. You can, however, add a maximum of 100 FAQs if required.
First-level Term/Node
The immediate next-level nodes after the Root node are known as First-Level Term/Node. There can be any number of first-level nodes in a graph. We recommend using first-level nodes to represent high-level terms, such as the names of departments, functionalities, etc. For example, in a Travel Assistant, you might have a first-level node called Reservation, which can be structured by functionality into subnodes such as: Cancel and Update.
Leaf Term/Node
Any node at any level starting with the 2nd is called a Leaf Term/Node.
| Note: This hierarchical organization of nodes is for your convenience to keep related questions together. The Knowledge Graph Engine does not consider any parent-child relation while evaluating the questions for a match. The hierarchy does not influence the FAQ matching process since all the nodes are considered the same way, irrespective of their position. |
Term/Node Types
Functionally, there are three types of Terms/Nodes.
- Default: Default terms do not have any particular considerations in shortlisting qualified paths in Ontology-based KGs.
- Mandatory: When you mark a term as Mandatory, paths associated with it are shortlisted for ranking only if the user’s utterance includes the mandatory term or its synonyms.
- Organizer: This term type can be marked as part of the Knowledge Graph to organize the ontology and help qualify FAQs even when they don’t contain the specific terms.

Tags
For each term/node, you can add custom tags. Tags work exactly like terms but are not displayed in the Knowledge Graph ontology to avoid clutter. You can add synonyms and traits to tags as you do to terms.
Synonyms
The Knowledge Graph allows you to add Synonyms for terms to include all possible alternative forms. Adding synonyms reduces the need for training the VA with alternative questions.
For example, the reservation node in our previously-mentioned Travel Assistant may have the following synonyms added to it: booking, order, purchase, etc.
Synonym Types
When you add a synonym for a term or a tag in the Knowledge Graph, you can add it as a local or global synonym. Local synonyms (or Path Level Synonyms) apply to the term only in that particular path, whereas global synonyms (or Knowledge Graph Synonyms) apply to the term even if it appears on any other path in the ontology.
After v. 7.2 of the XO Platform, you can also use Bot Synonyms inside the Knowledge Graph engine for path qualification and question matching. With this setting, you need not recreate the same synonyms in Bot Synonyms and KG Synonyms.
Traits
A trait is a collection of typical end-user utterances that define the nature of a question. Learn more.
A trait is applied to multiple terms across your Bot Ontology.
| Note: Traits also help you filter nodes based on associated user utterances. So, if the user types an utterance that is present in a trait, the assistant only searches the nodes to which the trait is applied. If the utterance is present in any other node to which the trait is not applied, the node is ignored. |
Intents
A VA can respond to a given question with an FAQ or the execution of a Dialog Task.
- FAQ: The question-answer pairs must be added to relevant nodes in your ontology. A maximum of 50k FAQs is permissible. A question is asked differently by different users, and to support this, you must associate multiple alternate forms for each question. Preceding an alternate question with || will allow you to enter patterns for FAQs (after the v.7.2 release).

- Task: Linking a Dialog task to a KG Intent helps leverage the capabilities of the Knowledge Graph and Dialog tasks to handle FAQs that involve complex conversations.
Notes on the Few-Shot Knowledge Graph
|