To set up Syniverse as a channel, the developer needs to associate the bot with a Syniverse app, set up a subscription, and enable the delivery events for this app. This document explains the steps to add the Syniverse as a channel to your bot.
Create an App
To create the Syniverse app, follow the steps below:
- Log in to the Syniverse developer portal and navigate to the Applications section.
- Click Create New if you want to create your first app. If you want to access existing apps, click Your App.
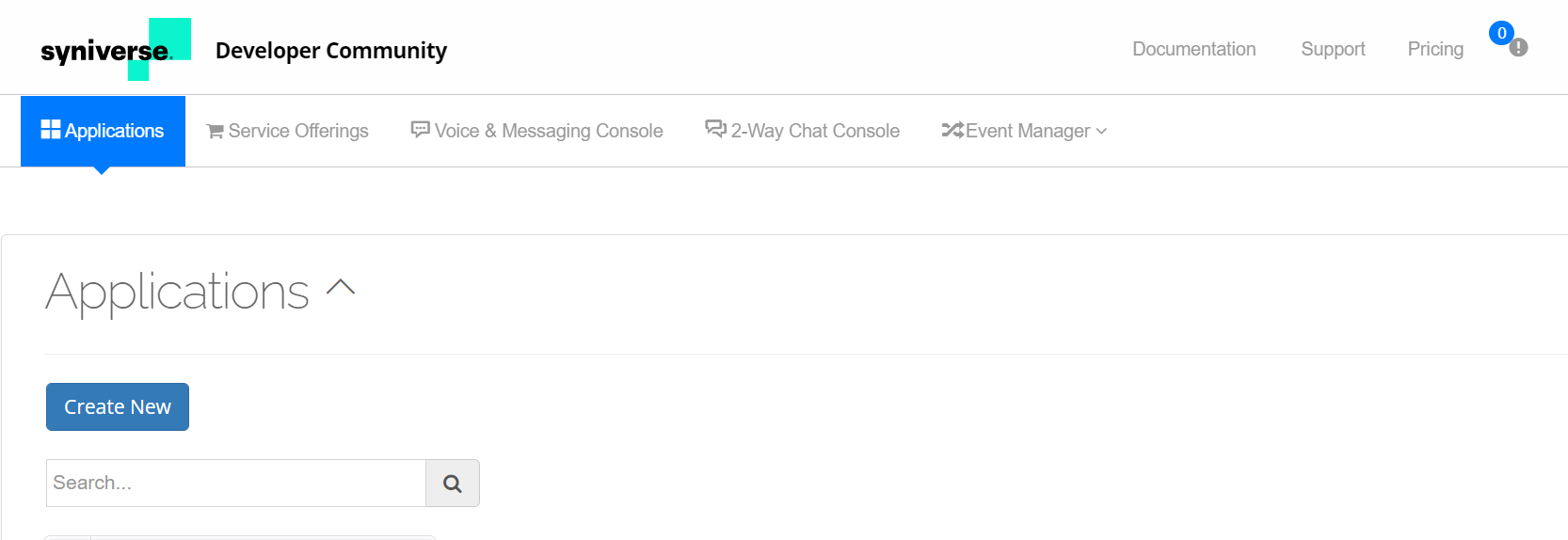
- In the Create App screen, enter the app name, description, select account, and click Save.
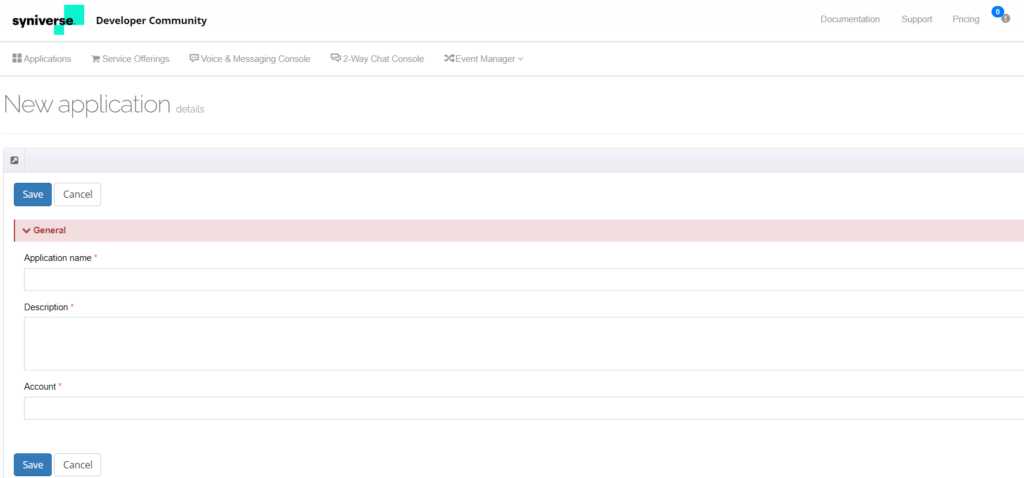
Capture Auth Keys
Once you create an app, to capture Auth keys, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to the created app in the Applications section and open the app.
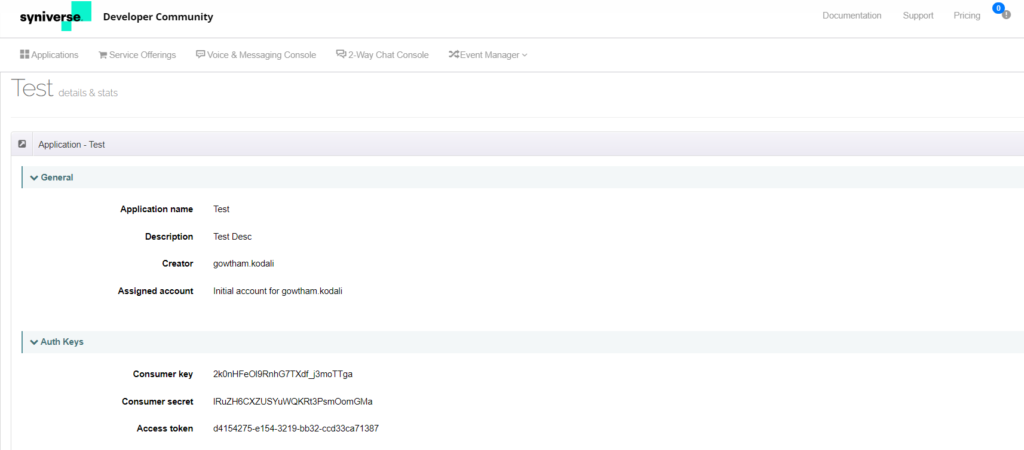
- Use the Auth Keys (see the following screenshot) to complete the configuration in the Kore.ai platform and send the SMS via bot.
Delivery Configurations
The next step is to configure how messages will be delivered via the Webhook URL configured on the XO Platform for Syniverse. To set up the delivery configurations, follow the steps below:
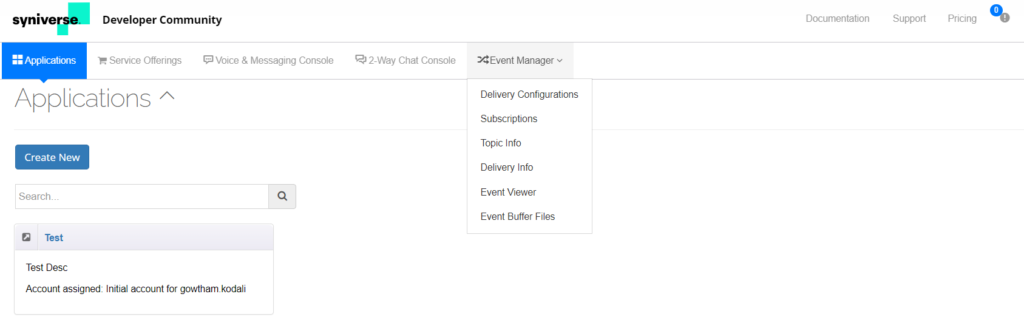
- Navigate to the Event Manager on the top menu bar and select Delivery Configurations.
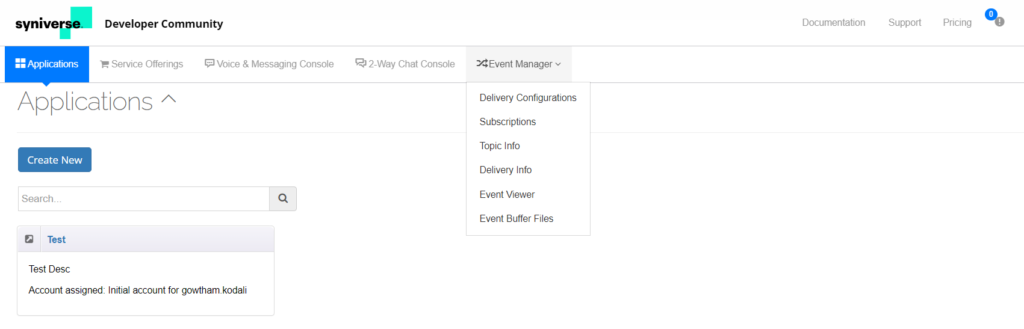
- If you want to use an existing delivery configuration to set up the bot’s webhook URL, select one of the configurations from the displayed table (see the following screenshot), else, click New Delivery Configuration.
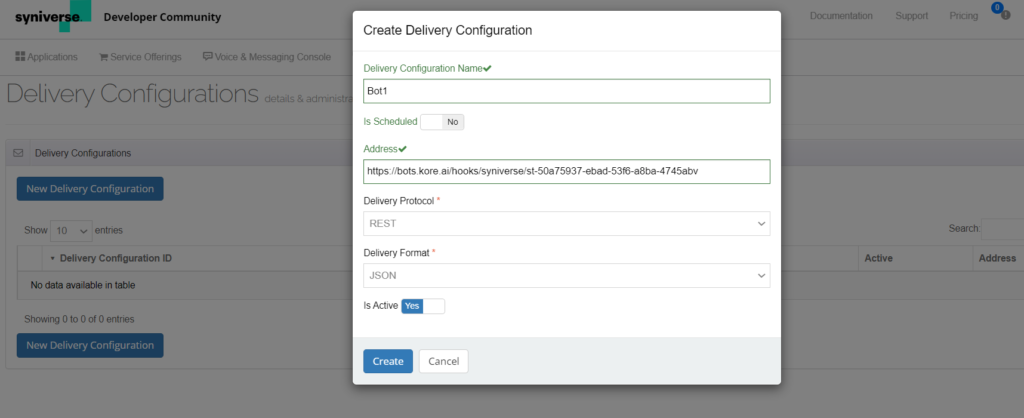
- In the Create Delivery Configuration pop-up, enter the following values:
- Provide a Delivery Configuration Name.
- Address: Copy and paste the webhook URL value from the XO Platform’s Syniverse Channel Configuration section.
- Set Is Active: to Yes.
- Click Create.
Subscriptions
To set up subscriptions, follow the steps below:
- Navigate to the Event Manager on the top menu bar and select Subscriptions.
- If there are existing subscriptions, select one from the table to set up the event subscription (see the following screenshot), else, click New Subscription.
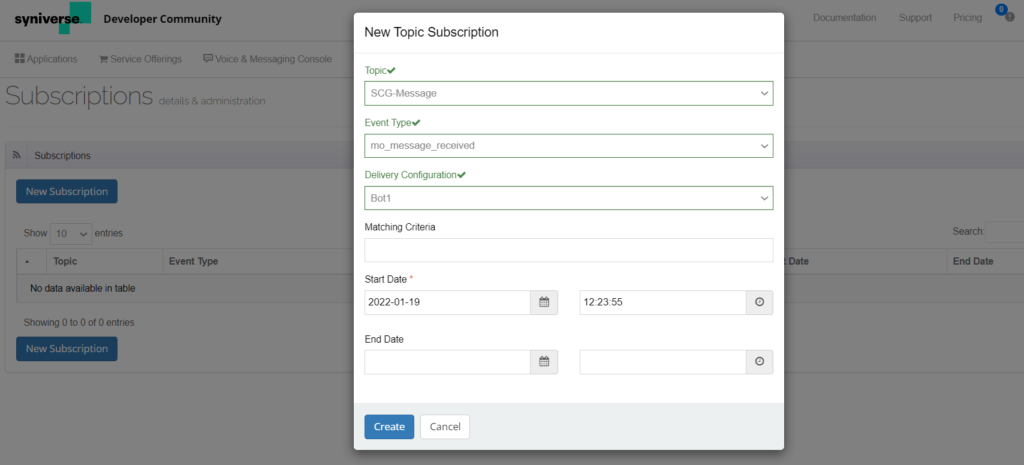
- In the New Topic Subscription pop-up, enter the following values:
- Topic: Select SCG Message from the drop-down.
- Event Type: Select mo_message_received from the drop-down.
- Delivery Configuration: Select delivery configuration configured in the Delivery Configurations section.
- Start Date: Select a date from when this subscription has to be active.
- End Date: Select an end date. Leave it blank if you want this event subscription to work for a lifetime.
- Click Create.
Capture Sender ID
To ensure that messages flow between the two systems, you should obtain the Sender ID from Syniverse, and provide it on the XO Platform. To obtain the Sender ID, follow the steps below:
-
- Navigate to the Voice and Messaging Console on the top menu bar of your Syniverse Developer Portal account, and double click Sender ID from the Messaging Accounts in left Navigation Menu. Click +Purchase or Migrate Sender Address button to purchase a new Sender ID.
- Scroll down to Alias, and copy the value.
-
- Paste this value in the Syniverse Configurations panel of the Kore.ai platform.
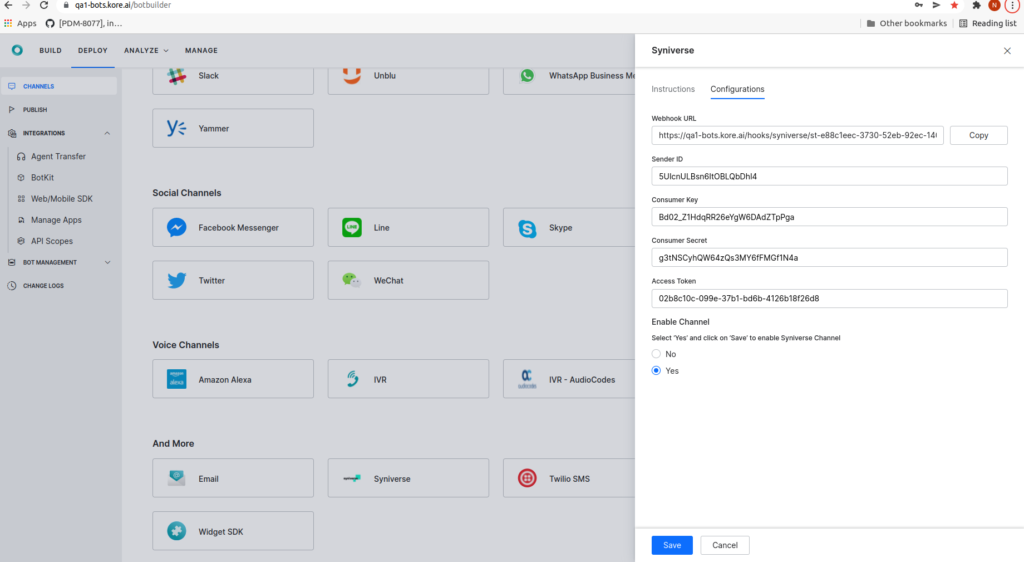
- Select Yes for Enable Channel.
- Click Save.
Configuring the Request and Response
- Internally, the XO Platform integration extracts and uses the
sender_id_aliasvalue (from Syniverse) in the API call to send the messages. - To identify the source channel, the system trims the
sender_id_aliasfrom the formatChannel type_Channel ID (if present)_sending number, and considers Channel Type as the source. - To identify whether the request came through Channel Id or Sender Id, and also respond to Syniverse accordingly, the following is considered:
- If the
sender_id_aliashas the formatChannel type_Channel ID_sending number, then the request is from the Channel. This information is used to reply to the Channel. In this case, thesender_id_idfield which contains the value of sender id is not used to respond. - If the
sender_id_aliashas the formatChannel type_sending number, then the request is from the Sender Id. This information is used to reply to the Sender Id. In this case, thesender_id_idfield is used to respond.
- If the

