The Kore.ai XO Platform offers multiple ways to train your virtual assistant for language understanding. One of the ways is to use translation services to translate the user input. In this approach, you can train the virtual assistant in a language (NLU Language) other than the interaction language. For example, you can enable Spanish as an interaction language but train the assistant using English language training data.
Translation services can also be used for translating the bot responses if they are defined in a language other than the conversation language. The Platform allows you to define language-specific responses for each of the languages enabled for the assistant. However, you may choose to write responses in a language other than the enabled language.
The Platform provides out-of-the-box support for Microsoft Translator and Google Translation APIs. You can also use the Custom Translation Engine feature to integrate with any other translation services or your in-house translation services.
Configuring Microsoft Translator Service
To enable automatic translation using Microsoft Translation Services, please follow the steps below:
- Go to Build > Configurations > Languages > Translation Configurations.
- Select Microsoft Translator.
- Provide the API Key of your Microsoft Translator API service. Learn More.
- Click Save to complete the setup.
Configuring Google Translation Service
To enable automatic translation using Google Translation Services, please follow the steps below:
- Go to Build > Configurations > Languages > Translation Configurations.
- Select Google Translator.
- Provide the API Key (Eg: AIzaXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXEpeW4xa0) of your Google Translation API service in the Access Key field. Learn More.
-
Note that the Platform does not validate the key. It is highly recommended that the key is validated beforehand and is active and working. A tool like Postman can be used to validate the key.
-
You can also save the translator key in an environment / content variable and provide that variable name enclosed in double curly braces while setting up the configuration.
-
- Click Save to complete the setup.
To know how to use the service, please visit KoreUtil Libraries – autoTranslate.
Configuring Custom Translation Service
The Custom Translation Service allows you to use translation services by integrating with other translation providers or to integrate with any in-house translation services you may have.
How it works
Here is how custom translation services work:
- Follow the instructions below to enable the Custom Translation Engine feature.
- You can set up the integration with your translation service APIs using the Get or Post method.
- Refer to your translation service documentation for the authentication mechanism, request payload, and response payload.
- This integration is used for translating both the user input as well as the bot responses. The platform will automatically make the following information available in the context during runtime.
- It will make use of the following functions while defining the request payload.
- koreUtil.conversation.sourceText()– This function will return the text to be translated.
- If the user’s input is being translated, then the function will return the user’s input.
- If the bot response is being translated, then the function will return the bot response.
- For translating user input, this function will return the user input. For translating the bot response, the function will return the bot response text.
- koreUtil.conversation.getSourceLanguage() – This function returns the current language of the text to be translated.
- If the user input is being translated, then the function will return the language in which the user is interacting.
- If the bot response is being translated, then the function will return the language in which the response is written.
- koreUtil.conversation.getTargetLanguage() – This function returns the language to which the text should be translated to.
- If the user input is being translated, then the function will return the language to which the input should be translated.
- If the bot response is being translated, then the function will return the language to which the response should be translated.The platform invokes the translation service using the defined configurations.
- koreUtil.conversation.sourceText()– This function will return the text to be translated.
- The translation engine should share the translated text as part of the API response.
- Map the relevant field from the response payload to be used as the translated text.
Enabling a Custom Translation Engine
- Go to Build > Configurations > Languages > Translation Configurations.
- Select Custom, and choose Add Custom Engine from the dropdown.

- Provide a name for the Custom Translation Engine.
- Define the request payload for sending the text to be translated. Refer to the details provided above for defining the request payload.
- Refer to the Service Node documentation to learn more about how to configure service integrations.
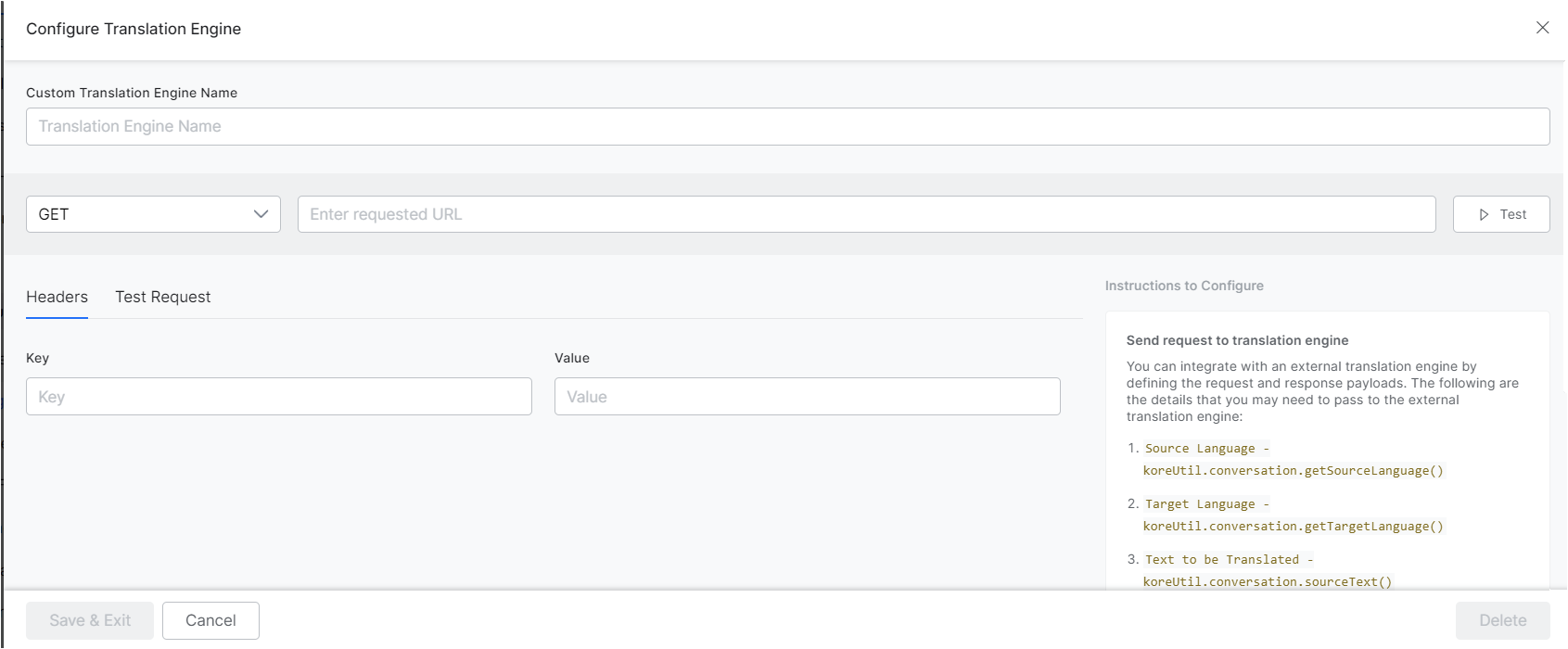
- After defining the request payload, you can test the integration by providing the required details from the Test Request tab. Provide the sample values for the variables shown under the Sample Context Values sections, click Test to verify if the custom translation connection is established.

- After a successful test, the platform displays the API response received from the translation service.
- Verify the response payload and map the translated text from the payload in the Translated Output field.

- Click the Extract button to verify if the translation output is correctly mapped.

- Click Save & Exit to return to the Languages page.
- Click Save to complete the configuration.



