The Kore.ai XO Platform offers a Custom Integration using the BotKit to configure agent transfer integrations for any system.
NOTE: The Agent Transfer and BotKit features are moved from Deploy > Integrations menu to Build > Integrations > Agent Transfer menu. Kore.ai’s Botkit is now renamed to Custom Integration.
Custom Agent Transfer Integration refers to the process of integrating a custom-built agent (such as a virtual assistant) into a larger system or workflow. This typically involves connecting the agent to external APIs or databases and configuring it to interact with other systems or users in a specific way. The custom integration allows the custom agent to seamlessly interact with other components of the system and to provide a more complete and efficient solution for the end user.
This post provides the configuration steps to enable the Custom Agent integration. Use the configurations provided below as general guidelines as there could be some differences based on the version of the Intercom that you are using.
The source code for the Agent Transfer is available at Kore.ai GitHub repo: https://github.com/Koredotcom/BotKit.
Overview
Let’s understand how the custom agent can be integrated and how it can improve business processes by providing a more efficient and seamless user experience.
Prerequisites
- A fully functional Bot (we will be using a Banking Bot).
- Download BotKit SDK from Kore’s GitHub.
- Download and Install the Node.js(version 10 or above). The BotKit SDK requires node.js to run on the same server where the SDK is installed.
- Go to
https://nodejs.org/en/download/and select your OS as a .pkg file type for Mac and .msi file type for Windows. - In a Terminal window, run the
node -vcommand to verify installation and version, for example, v6.10.2.
- Go to
- A test callback server application. We will be using NGROK from https://dl.equinox.io/ngrok/ngrok/stable to simulate the callback server application. Following are the steps to install NGROK:
- Open https://dl.equinox.io/ngrok/ngrok/stable.
- Download and install the ngrok file for your operating system.
- To download NGROK on Windows:
- Download the zip file for your Windows machine 32-bit or 64-bit.
- Unzip and run the
ngrok.exefile to install ngrok.
- To download NGROK on mac:
- Press
Command+Space, type Terminal, and press enter/return key. - Run in Terminal app:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" < /dev/null 2> /dev/nulland press enter/return key.
If the screen prompts you to enter a password, enter your Mac’s user password to continue. When you type the password, it won’t be displayed on the screen, but the system would accept it. So just type your password and press ENTER/RETURN key. Then wait for the command to finish. - Run
brew cask install ngrok.
- Press
- To download NGROK on Windows:
- A live agent software. We will be using LiveChatInc.com. You can use your LiveChat subscription or set up a free 30-day trial account at LiveChatInc.com by entering your business email in the Start using LiveChat now! Sign up and create an account.
Design and Configuration
- As a Bot developer, open Kore.ai Bot Builder – https://bots.kore.ai/botbuilder.
- Select the Bot for which Agent Transfer needs to be configured.
- Open or create a dialog task (Support Call Back) and add an Agent transfer node.
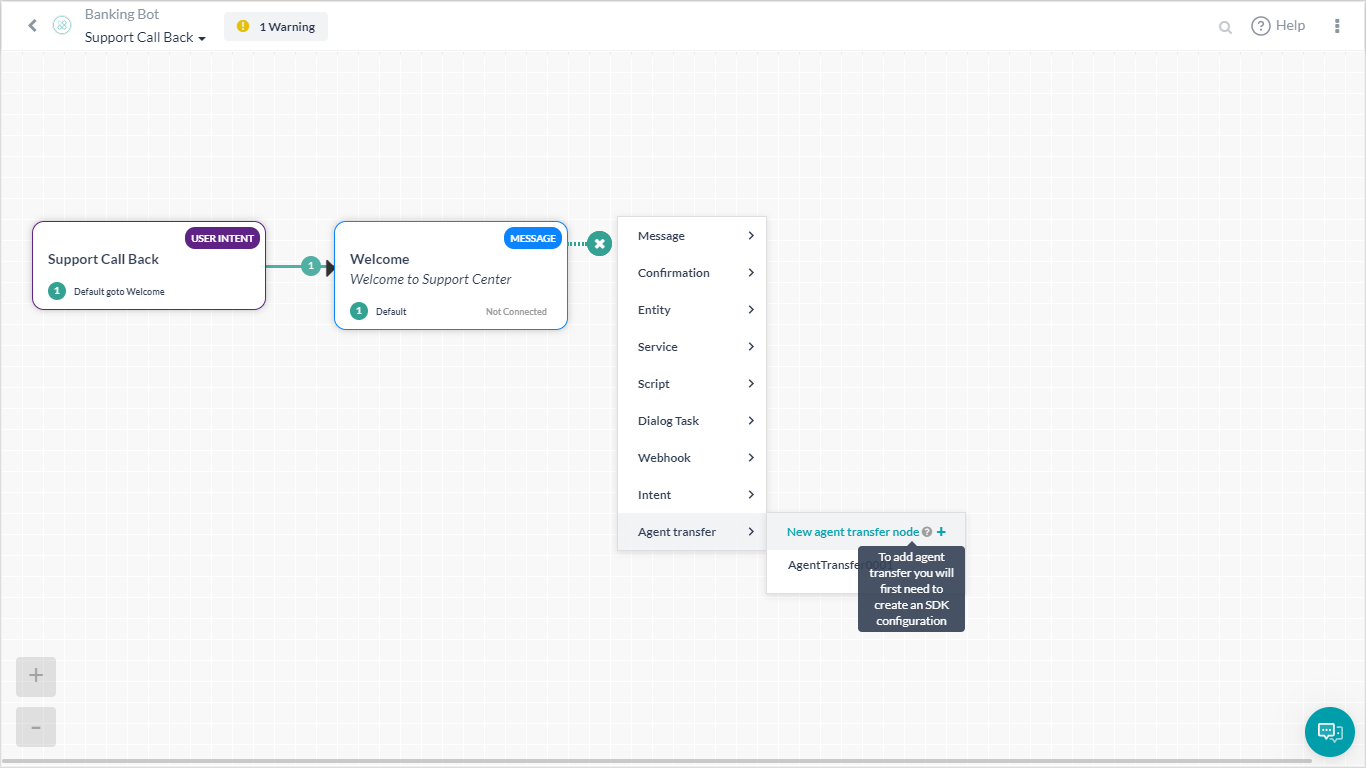 .
. - Enter a Name (LiveChat) and Description and Save.
- You will see a message ‘SDK is not currently configured/Subscribed. Please go to API Extensions to configure the SDK.’. For now ignore this message as we will see how to configure SDK later in this article.
- From the Bot Builder screen, go to Build > Integrations > Agent Transfer > Custom (BotKit).
- In the App Name section, select an existing app from the list or use the Create App option to create a new app.
Note: The Bot ID Client ID and Client Secret keys.
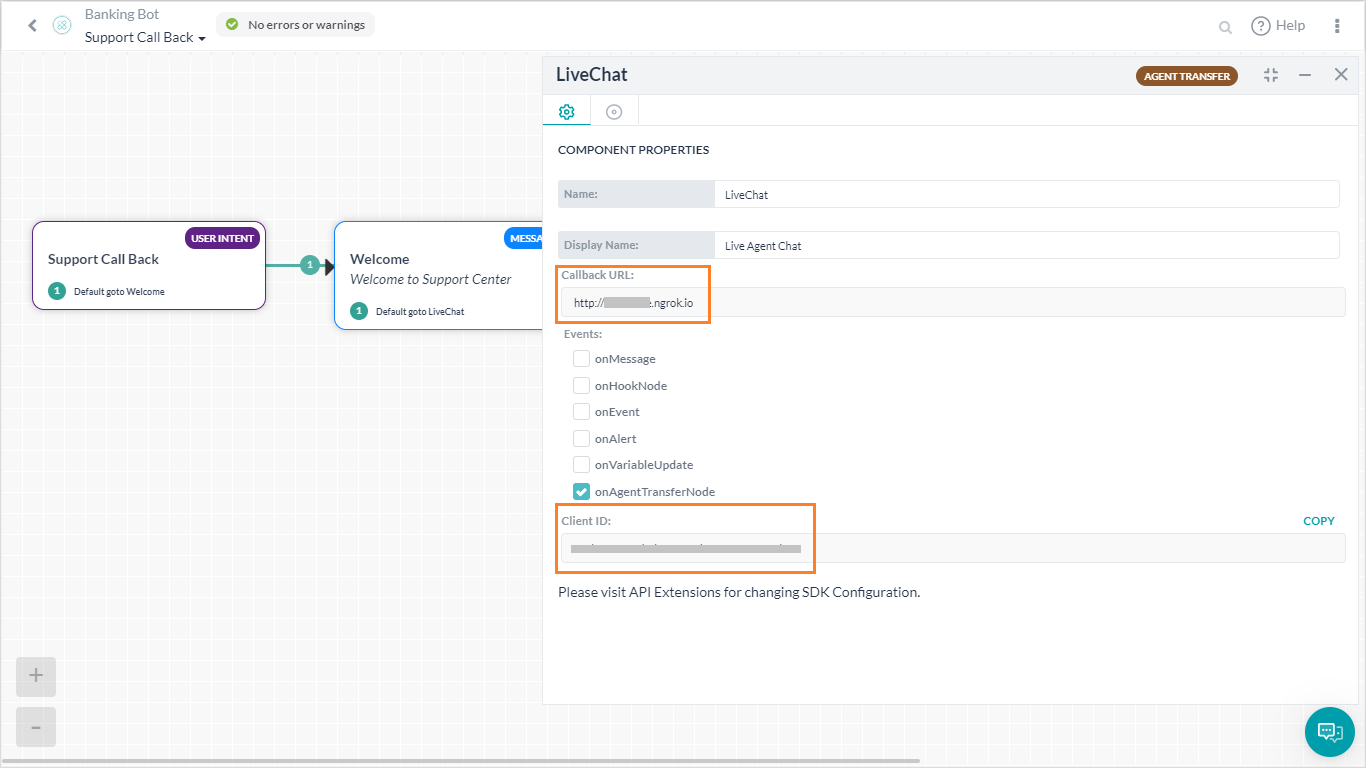
RS256 and RS512 JWT signing algorithms are not supported for Custom BotKit or Botkit. - Enter the Callback URL of your application to be invoked by BotKIt SDK events. Since we are using NGROK we will show how to obtain the callback URL:
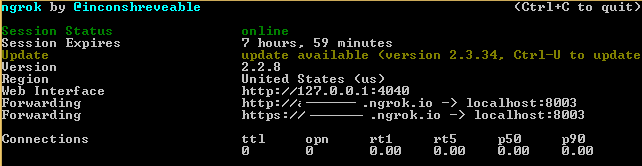
- In a Terminal Window, start ngrok to monitor port 8003 using the following command:
ngrok http 8003. - Copy ngrok forwarding URL. It will be in the format –
http://XXXXXXaa.ngrok.io.
 .
. - Use this forwarding URL as the call-back URL and save.
Note: The forwarding URL changes whenever the ngrok is restarted. Make sure you make the changes to the callback URL every time ngrok is restarted.
- In a Terminal Window, start ngrok to monitor port 8003 using the following command:
- The agent transfer is configured at the dialog level. You can open the dialog task and open the agent transfer node to see that the configuration is saved, as shown below. You can select the Events required (see below for details).
 .
. - Install any live agent software e.g. Livechat, Liveperson, Concentrix, Vayusphere, etc., depending on your enterprise requirement and license availability. Since we are using LiveChat, we will should you how to obtain the license details needed for Agent Transfer:
- Sign in to your LiveChat account.
- Go to Settings from the left navigation and select the chat link.
- Copy the URL and note the license code. If the URL is
https://lc.chat/now/104xx297/and then the license code is104xx297.
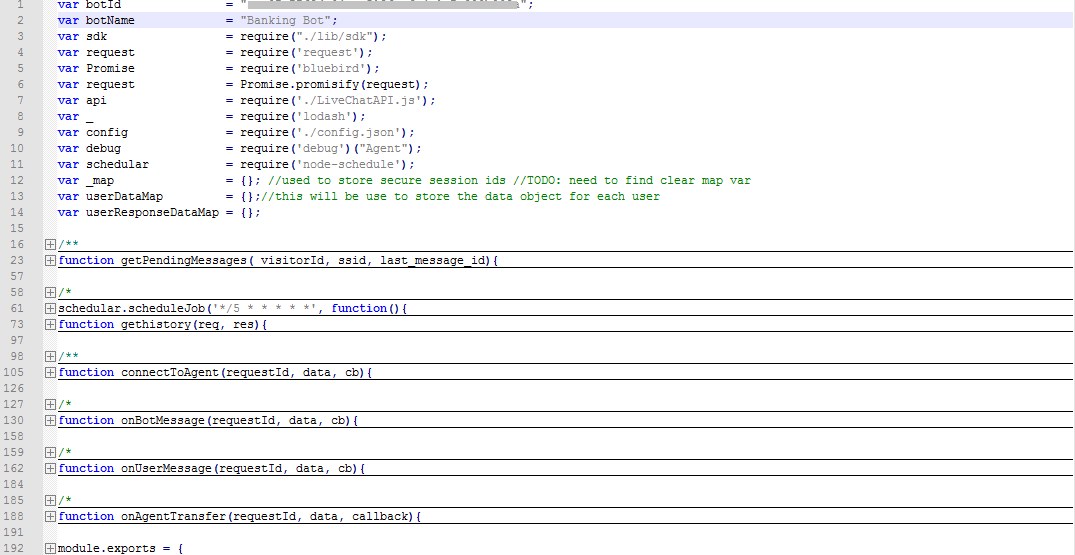
- Open the downloaded BotKit SDK folder and do the following:
- Edit
livechatapi.js:- Give the respective botId and botName of your bot, which you have copied earlier.
- This JS file contains 3 APIs of Kore – Initialization, Send Message and Get Message. If required, any new APIs written for human agent transfer should be put in here.
Example: If connection closing is required, then close connection API written needs to go into livechatapi.js.
 .
.
- Edit
config.json.- Client ID and Client Secret key, respective server ports running, and liveagent license of the third-party server goes here.
- Client Id, Client Secret can be copied from Events and Extensions – Agent Transfer.
- ngrok forwarding url can be copied from ngrok running instance. It is the call-back URL. This should be the URL entry.
- Liveagentlicense is the code given in the chatlink of livechat.
- Edit
LiveChat.js. - Edit app.js.
- Edit
Execution
- Open a terminal window and run the BotKit SDK by entering the command:
node app.js. - Please make sure to install all the missing modules to run the server successfully without any errors as shown below.
For example, if error “method url-template, node-schedule are missing” is shown, then install the above modules using the command.
npm install <module-name>for windows andsudo npm install <module-name>for mac. - ngrok and node.js server will be running in different terminals.
- When a user initiates the chat from the bot, the bot transfers the call to an agent and sends a message to the user.
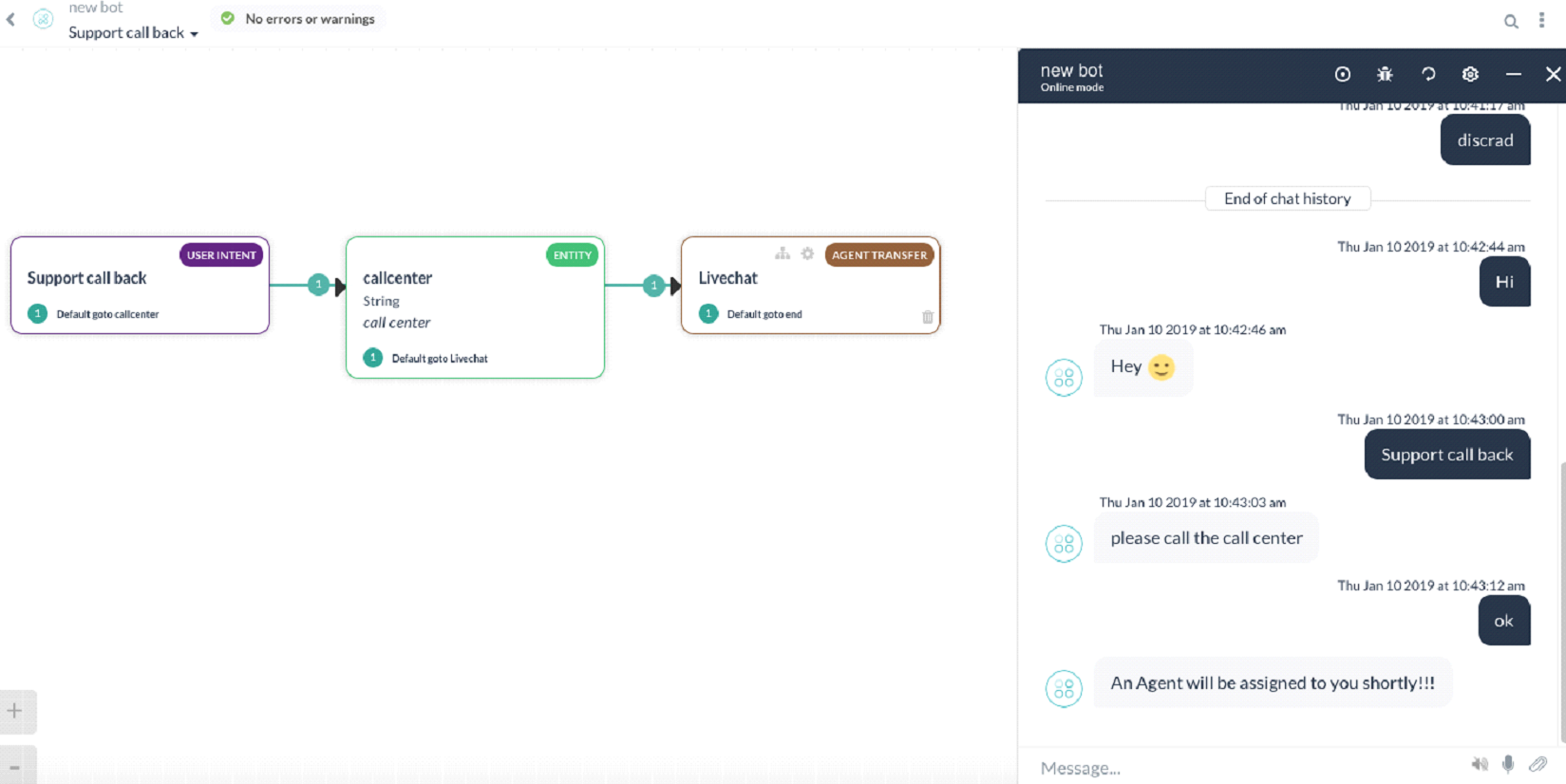
- Agent receives a notification about this on the livechat.
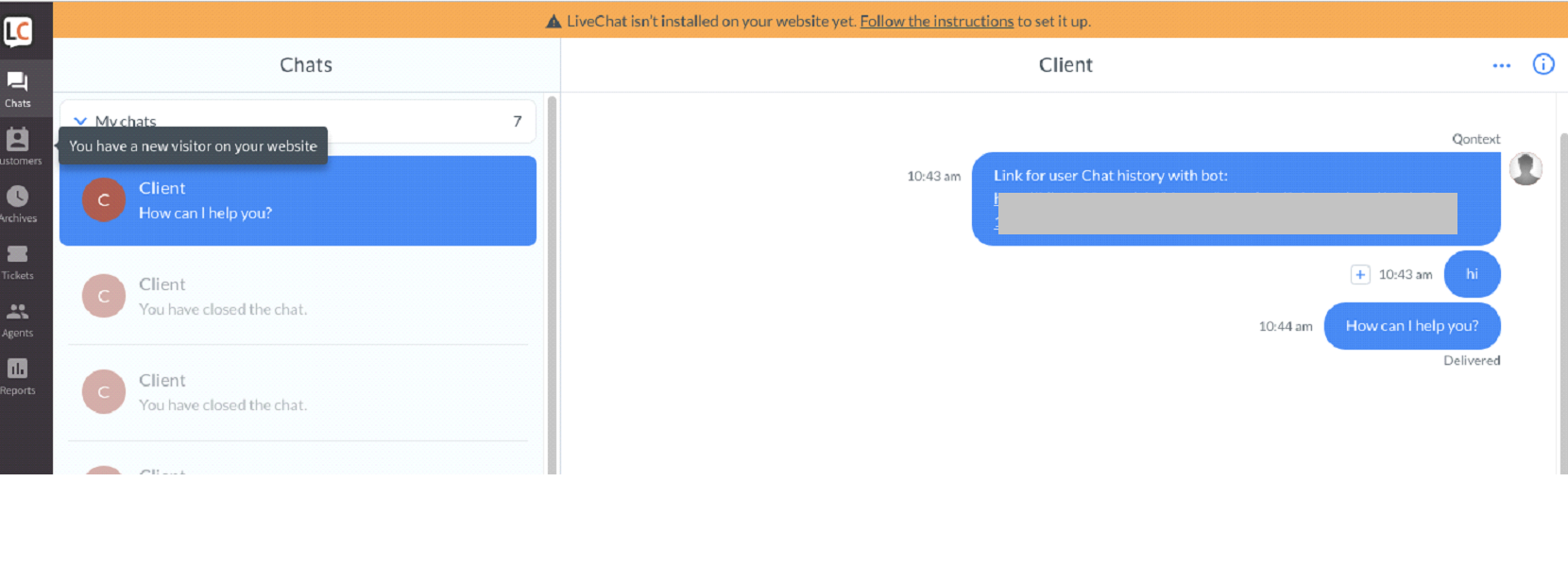
- Now, the connection between the agent and the user has been established, and the conversation continues.

Events
Note: The events and methods required for sending messages from User, bot, and transferring to Agent are outlined in LiveChat.JS.
- on_user_message event is triggered when a user sends a message. This message is sent to the bot using the sendBotMessage method.
- on_bot_message is triggered when bot sends a message. This message is sent to the user using the SendUserMessage method.
- on_agent_transfer event is triggered when the service agentTransfer node is triggered in bot. This event connects to the agent using the connectToAgent method, which internally calls the initChat API.
- gethistory method gives the chat history of the user with the bot to the transferred agent.
- scheduleJob is run for every 5 secs, and it polls for the pending messages from the Agent, which internally calls the getPendingMessages.
- getPendingMessages gets all the pending messages from Agent and delivers it to the User.
- chat_closed gets triggered when the agent closes the chat with the user.