Kore.ai bots platform provides a way to declare and use variables within the bot. These variables can be used to capture values that are commonly used by different tasks, nodes, and other bot elements
In this How-To, we will explore a scenario in a Banking Bot, where Bot Variables can be used. We will see how Global Variables can be used to pass API endpoints and change them easily when migrating from development to testing to production environments.
For details on what Bot Variables are and how they are implemented in the Kore.ai Bots platform, refer here. For a use case with Content Variables, refer here.
Problem Statement
In our Banking Bot, we have two tasks:
- Get Balance which makes a service call with a given account number to get the balance in that account
- Update Balance which makes a service call to update a given account with the specified amount.
- Both the above tasks call the same service and the service API endpoint changes for development, testing, and production environments.
- Changing the service call in both the Dialog Tasks is cumbersome and leading to errors, if the change is not done properly.
In this document, we will see how Global Variable can be used to store the API endpoint and use it for the service calls.
Pre-requisites
- Bot building knowledge
- A Banking Bot with the dialogs as mentioned below:
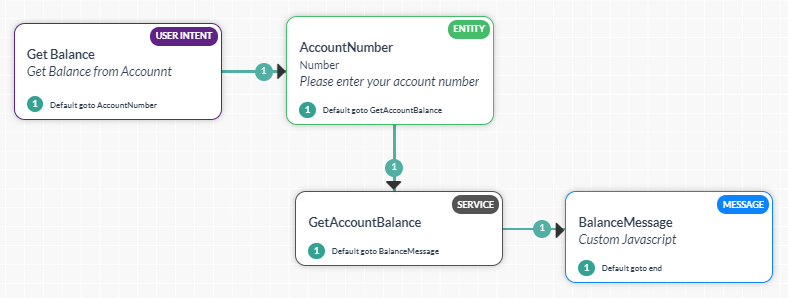
- Get Balance – Dialog task prompting the user for their Account Number and displaying the available balance in the account.
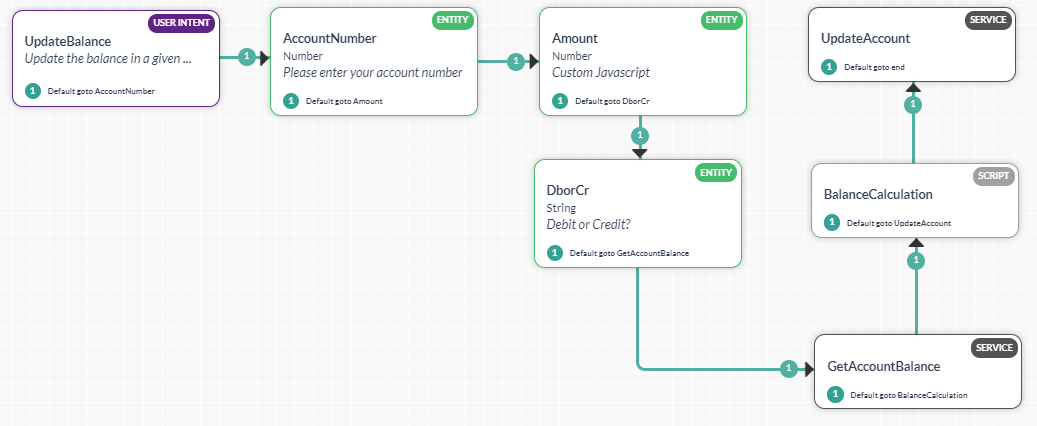
- Update Account – Dialog task prompting the user for Account Number that needs to be updated, the Amount to be updated and whether the amount needs to be credited or debited and updating the Account balance accordingly.
- Get Balance – Dialog task prompting the user for their Account Number and displaying the available balance in the account.
Implementation
Declaring a Global Variable to hold the API endpoint will help the transition easier and faster.
- Open the Banking Bot.
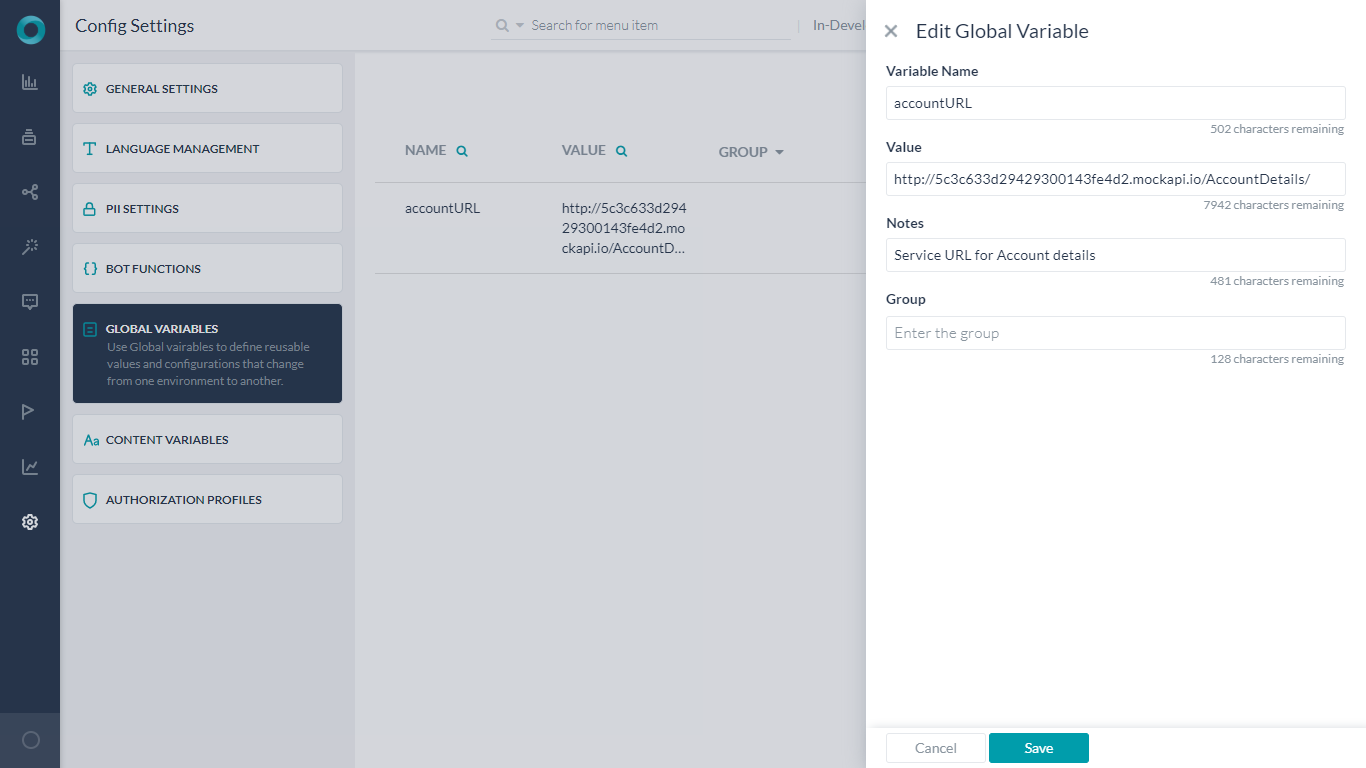
- From Settings -> Config Settings select Global Variables section.
- Click Add Global Variable to open the corresponding window.
- Enter Variable Name, and Variable Value. For this use case were are calling the Variable accountURL, and for value we are entering the Service API call endpoint.
- Save.
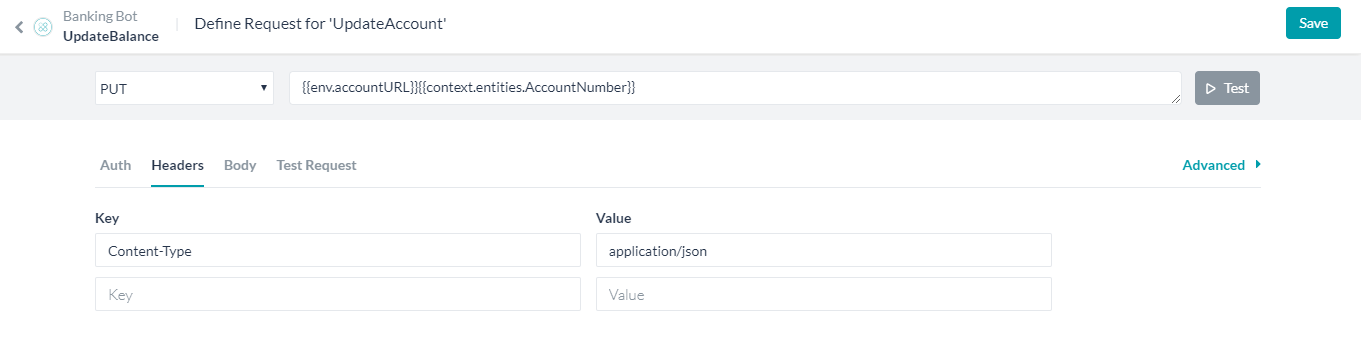
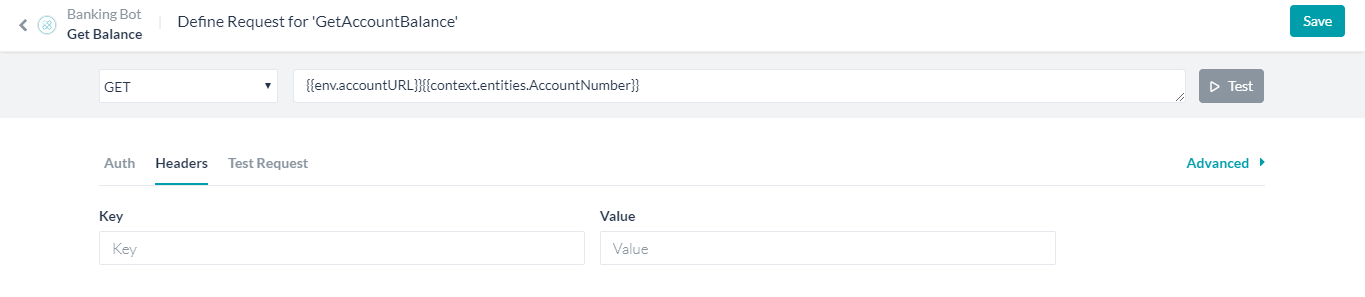
- Now open the Get Balance Dialog Task.
- Select the GetAccountBalance Service Node.
- Click Edit Request under the Request Definition
- Replace the request URL with the Global Variable created above. using the
envprefix followed by any parameters needed. In this case:
{{env.accountURL}}{{context.entities.AccountNumber}}
- Repeat for Update Balance Dialog Task.
- Now when you Export and Import the Bot to another environment, all you need to worry about is to change the value of the Global Variable and the changes will be effective in both the Dialog Tasks.
