Like standard bots, you can enable more than one language for universal bots, but the functionality is completely different.
When you enable a new language for a standard bot, you need to upload language packs consisting of the entire bot definitions. Whereas to enable a new language for a universal bot, you just need to set up the corresponding default dialog.
Universal bots do not obtain the enabled languages of the linked bots. You must enable default and additional languages for the universal bot. When user utterances are made in an enabled language, the universal bot routes it to only those linked bot tasks that have the same language enabled. For example, if German is enabled for the universal bot and a user utters in German, the NLP engine looks for all the linked bot tasks that support German and sends the utterance only to those tasks.
Before you Begin
This article assumes that you understand the fundamentals of multi-language bots in Kore.ai and therefore focuses on the aspects specific to the universal bots. For the fundamentals of multi-language bots in the Bots Builder, refer to Building Multi-Language Bots.
Enable Language
Follow these steps to enable an additional language for a universal bot:
- Open the universal bot for which you want to configure new channels.
- Hover over the gear icon on the left navigation panel and click Settings -> Config Settings.
- Below the General Settings tab, click Language Management.
- On the Language Management window, click Enable next to the language you want to.
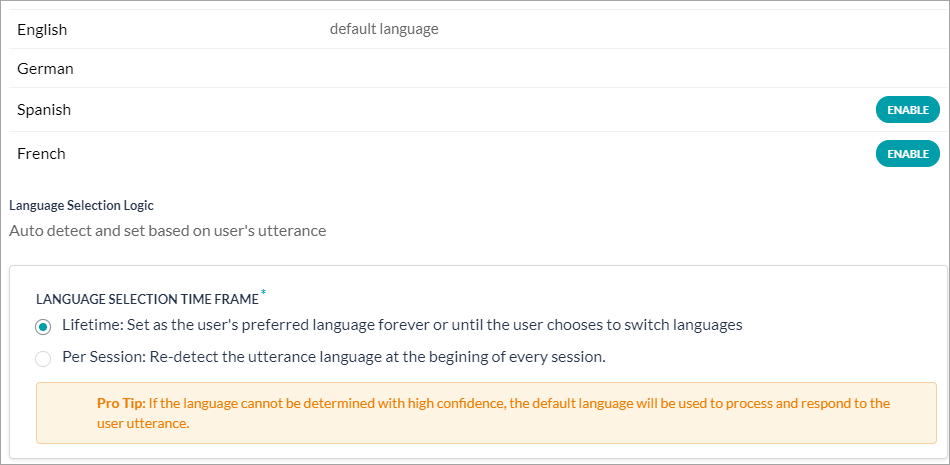 Note: If a language is already enabled, you won’t be able to see the Enable button for that language.
Note: If a language is already enabled, you won’t be able to see the Enable button for that language. - Under the Language Selection Time Frame (scroll down to view this option) select one of these options:
- Lifetime: The auto-detected language or the language preference selected by the user will be set as the user’s preferred language.
- Per Session: Detects the user’s language at the beginning of every session and responds accordingly.
Note: If the language cannot be determined with high confidence, bot requests the users to select their preferred language. The default language is used to communicate with the user during language preference selection.
- Click Save.
Customizing Default Dialog
If the Kore.ai NLP engine cannot recognize the user intent, the universal bot responds to the users with the default dialog. You must create language-specific versions of the default dialog for each enabled language so that such bot responses go in the users’ preferred language. Otherwise, the universal bot responds applies the default bot language regardless of the user’s preferred language.
Follow these steps to open the language-specific default dialog:
- Open the universal bot whose language-specific default dialog you want to change.
- On the top-right side of the bot window, click the name of current bot language, and select any of the enabled languages. It switches the bot language as per your selection.

Once you switch the language, go to the Default Dialog of the bot and make the necessary changes as explained in the Customizing the Default Dialog article.
