Communication has been the essence of life from the beginning of times. With the evolution of technology, mode, and style of communication have also evolved.
In the early days, conversations were restricted to verbal and textual interaction between humans. These interactions are usually guided by emotions, context, and awareness of the previous conversation. With the advent of computers, interactions have now expanded to include machines i.e. human-machine interactions. The transition from a command-based interface to a Graphical User Interface (GUI) to a Conversational User Interface (CUI) was natural, need-based and this transition made the communication easier.
With CUI, came chatbots that interact with users in a natural language. Further enhancements using Artificial Intelligence and NLP capabilities enabled a chatbot to understand user utterance in the natural language; derive the task from the user utterance as well as extract the information required to successfully execute the task.
AI-driven, NLP-based chatbots and voice assistants are the latest in technology and a must for all businesses these days.

What are Conversational Bots?
A Conversational Bot or Chatbot is a virtual assistant that acts as an intelligent intermediary between people, digital systems, and internet-enabled things. It replaces the traditional Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) of an application or website with a Conversational User Interface. It is a paradigm shift from the earlier communications achieved either by entering syntax-specific commands or clicking icons.
Chatbots are designed to chat with users through a combination of natural language-based conversations. Responses come in the form of buttons, calendars, or other widgets that accelerate the speed with which a user can respond.
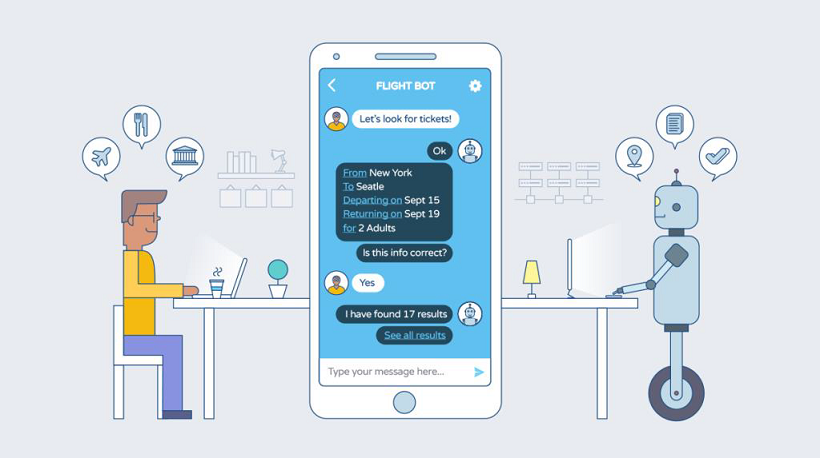
AI-powered messaging solutions or Conversational Bots serves as the stepping stone to the future. A Conversational Bot is an automated computer program skilled in digital media communication. It communicates through intelligent virtual agents, organizations’ apps and websites, social media platforms, and messenger platforms. Users can interact with such bots using voice or text to access information, complete tasks, and execute transactions.
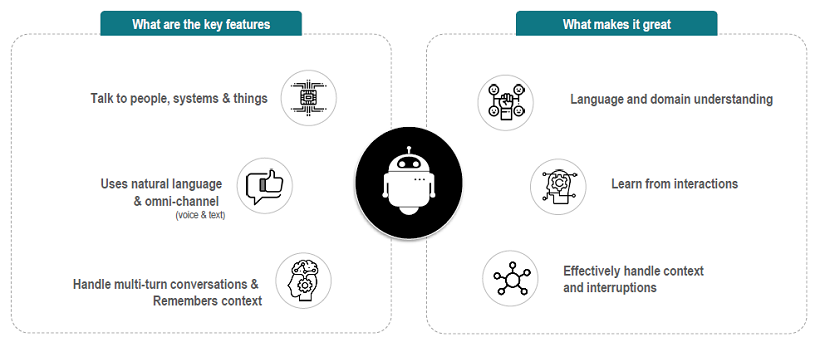
So what makes the Conversational Bot so special? This in a nutshell:
What are Intents & Entities?
A Conversational Bot faces three challenges:
- Intent Detection – Understanding what the user wants.
- Entity Extraction – Extracting the required information from the user to accomplish what the user wants.
- Dialog Flow/Conversation – Accomplishing the user wants.
Whatever the user says is considered as an Utterance. It is the task of the Conversational Bot to extract from this user utterance, the intent, and entities essential to carry a conversation. For example, let us consider the following user utterance: I want to fly to London this weekend.
An Intent is the user’s intention. It usually comes in the form of a verb or noun within the user utterance. From the above user utterance, a Conversational Bot understands the user intent as want to fly and triggers the corresponding dialog task.
Entities are a collection of data or information that the Bot requires to complete the task as identified in the user intent. There can be multiple entities in various formats that are required by the Bot. These can be a part of user utterance or the Bot needs to prompt the user for the entity values. For example, in the above user utterance, London, and this weekend form the values for the entities Destination and Travel Date respectively. As you can notice, the Source entity value is missing and the Bot needs to prompt the user for the same.
As seen, an Entity can be of any type like location, date, time, person, etc,.

How to Build Intelligent Bots?
Bots are not smart by default. They are made capable of showing some level of artificial intelligence by leveraging technologies like machine learning, big data, natural language processing, etc. A chatbot is intelligent when it is aware of user needs, understands the user’s perspective or context, and responds according to the user’s mood or emotion. Its intelligence gives the chatbot the ability to handle any scenario of a conversation with ease.
The key for a Conversational Bot to understand humans is; its ability to identify the human intentions, extract relevant information from the user utterance and map the relevant action/task against that utterance. NLP (Natural Language Processing) is the science of extracting the intention (Intent) of text and relevant information (Entity) from the text.
Managing dialogs to keep track of multiple conversation threads, remembering the context, and responding to the user tone or sentiment provides the much-needed humane touch to the conversation and at the same time serving the user with accurate and appropriate responses.
Another aspect that helps build an intelligent Bot is having a Knowledge Base. This gives the Bot an ability to respond to frequently asked questions that return static responses. Building Knowledge Collection is an attempt to represent entities, ideas, and events with all their interdependent properties and relations according to a system of categories. This structured categorization of data helps the Bot to answer user queries effectively and with ease.