Kore.ai Knowledge Graph helps you turn your static FAQ text into an intelligent, personalized conversational experience. It goes beyond the usual practice of capturing FAQs in the form of flat question-answer pairs. Instead, Knowledge Collection enables you to create an ontological structure of key domain terms and associate them with context-specific questions and their alternatives, synonyms, and Machine learning-enabled classes. This Collection, when trained by the platform, generates a Knowledge Graph that enables an intelligent FAQ experience.
Knowledge Ontology
This document is intended to familiarize the reader with the terms used in building Knowledge Collection.
Terms or Nodes
Terms or Nodes are the building blocks of an ontology and they can be used to define the fundamental concepts and categories of a business domain.
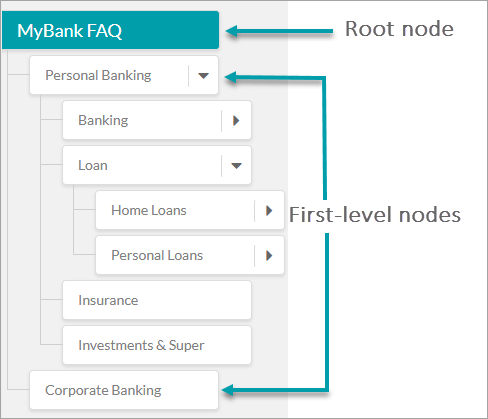
As shown in the image below, you can organize the terms on the left-hand panel of the Bot Ontology window in a hierarchical order to represent the flow of information in your organization. You can create, organize, edit, and delete terms from there.
For easier representation, we identify some special nodes using the following names:
Root Node
Root node forms the topmost term of your Bot Ontology. A Knowledge Collection consists of only one root node and all other nodes in the ontology become its child nodes. Root node takes the name of the bot by default, but you can change it later.
First-level Nodes
The immediate child nodes of the root node are known as First-level nodes. There can be any number of First-level nodes in a collection. It is recommended to keep First-level nodes to represent high-level terms such as the names of departments or functionality. Examples – Personal Banking, Online Banking, and Corporate Banking.
Leaf Node
Any node to which question-answer sets are added is called a Leaf Node, be it First-level, Parent, or Child.
Parent-Child Relationship
Depending on their position in the ontology, a node plays different roles, for example, it becomes a Parent Node when a subcategory or Child Node is added to it. A parent node is in simple terms a category that may have one or more subcategories under it, called the child nodes. Examples: Loan is the parent node of Home Loan and Personal Loan. Personal Loan can again have two child nodes: Rate and Fees, Help and Support.
Synonyms
Users would use a variety of alternatives for the terms of your ontology. Knowledge Collection allows you to add synonyms for the terms to include all possible alternative forms of the terms. Adding synonyms also reduces the need for training the bot with alternative questions.
For example, the Internet Banking node may have the following synonyms added to it: Online Banking, e-banking, E-banking, Cyberbanking, and Web banking.
When you add a synonym for a term in the Knowledge Collection, you can add them as local or global synonyms. Local synonyms apply to the term only in that particular path, whereas global synonyms apply to the term even if it appears on any other path in the ontology.
Traits
Note: From ver 7.0, Traits replace Classes of ver 6.4 and before.
A trait is a collection of typical end-user utterances that define the nature of a question when they ask for information related to a term. A trait is a common feature that can be applied to multiple terms across your Bot Ontology.
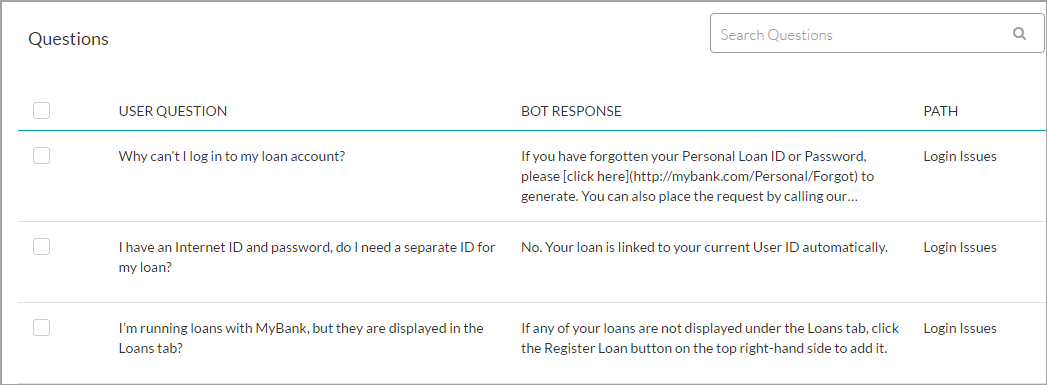
Questions and Answers
These are the actual questions associated with your business domain and their corresponding responses. The question-answer pairs must be added to relevant nodes in your bot ontology. A question may be asked differently by different users and to support this, you may associate multiple alternate forms for each question.