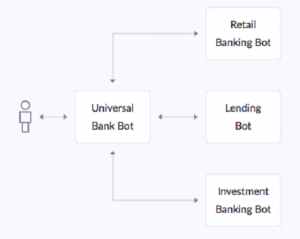
Kore.ai’s Universal Bots facilitate a scalable, modular approach to bot building by linking several standard individual bots into one.
- Modularity: Build separate bots that address domain-specific issues and then integrate them to optimally interoperate.
- Scalability: Start building bots that address key use cases and keep adding additional bots to address more use cases.
Use Case 1: Banking Bot
Banks offering various products and services to their customers may independently develop product-specific bots and incrementally launch them adding them to a common Universal Bot.
- End users would only have to converse with the Universal Bot which would identify the right bot to fulfill user’s request.
- Engineering teams can build product specific bots without impacting bots of other products.
- Release cycles of individual bots can be maintained independently so that a specific group can upgrade their bot without waiting for other groups.
Use Case 2: HR Bot
HR bots can be built incrementally by integrating various departmental bots as and when they are ready. Universal Bot could be launched with a single standard bot to answer FAQs on HR policies and can be gradually scaled up to integrate with other bots like leave management, performance reviews, benefits management etc. End users can start consuming new bot skills without the need to switch between various bots.
How it works:
- Universal bot acts as a single interface for the Bot users of an enterprise, across business lines or products or services.
- Standard bots that aim to meet a specific purpose can be built independently and then be associated with a Universal bot by linking them to the Universal Bot.
- When end users interact with Universal bot, it will perform intent recognition across all linked bots to understand user’s intent and engage appropriate bot to perform the task.
- In the case of ambiguity in identifying appropriate bot or task, a sub-dialog is initiated to obtain confirmation from the user.
- Universal bots also provide a ‘Default Dialog’ / ‘Fallback Dialog’ for gracefully handling any untrained/un-recognized requests.
- The developer can view and analyze all user interactions from within Universal bot and also train the respective bots with additional training data.
Know more about Universal Bots from here.
You can also start creating your Universal Bots by referring here.