Kore.ai’s Smart Bots allow enterprises to build Bots centrally and allow various teams within the enterprise to reuse and extend the Bot configurations to suit their requirements. Smart Bots expedite the bot building process by allowing new bots to inherit the configuration and tasks of pre-defined bots.
For example, a bank with operations in various countries and jurisdictions can use Smart Bots to define global standards and allow regional units to supplement with any local regulatory or customer needs.
Or a utility bot could be built to fulfill common enterprise needs like IT Help Desk, Leave Management, etc. and individual departments could inherit this utility Smart bot and supplement department specific tasks. Like, the Marketing & Sales team could subscribe to the utility Smart bot and add tasks related to prospecting by integrating with Salesforce, Hubspot, etc.
Use Case
Banking Bot – Multi-jurisdiction Operations
Banks with operations in various countries or jurisdictions can use Smart Bots to define global standards and allow regional units to supplement with any local needs of the regulators and/or customers. 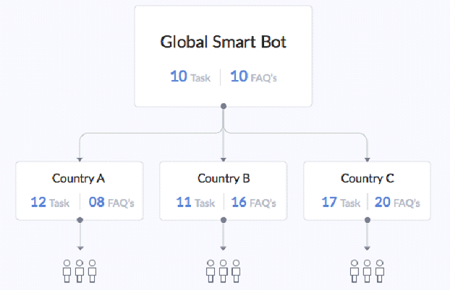
- A global team can define the minimum essentials or the mandatory tasks as a Smart bot;
- Regional units or groups can install the Smart bot to inherit the configurations and include additional tasks to meet specific local requirements;
- Upgrades to the Smart bots are automatically inherited by all regional bots;
- Regional units/groups can also selectively unlock the components to stop receiving upgrades from Smart bot.
How it works
- Smart Bots functionality is built based on the concepts of Object Inheritance Model.
- Developers of a Smart Bot can build the bot definition along with tasks and knowledge queries and publish it like any other standard bot.
- Any parameters that need to be customized locally can be exposed as variables.
- Interested teams or developers within the enterprise can build child bots by inheriting the bot definition from the Smart bot.
- Any update on the parent can automatically be passed onto all inheriting child bots.
- Developers may extend the child bot with additional tasks and knowledge queries. These extensions will not affect the parent bot or the other inheriting child bots.
- The developer of the child Bot will also have the option to selectively override the inheritance if required.
Learn how to define Smart Bots from here.
