Emotion tones are critical indicators in understanding the attitudes and opinions of users interacting with the bots. Sentiment Management allows the developer to define and trigger events based on the user’s emotion or sentiment.
NOTE: This feature was introduced in ver 7.0.
Negative emotion scenarios like anger or disgust would typically be considered for transferring the conversation to a live agent.
The Natural Language Processing (NLP) interpreter can parse user utterances for specific words and phrases, and then provide an average tone score based on the connotation, word placement, and any added modifiers. (See here for more on Tone Analysis)
The tone or sentiment scores can be stored as context and used to drive the flow of a dialog task via conditional transition statements. You can use these scores to steer user-bot conversations or seamlessly invoke escalation to a live agent.
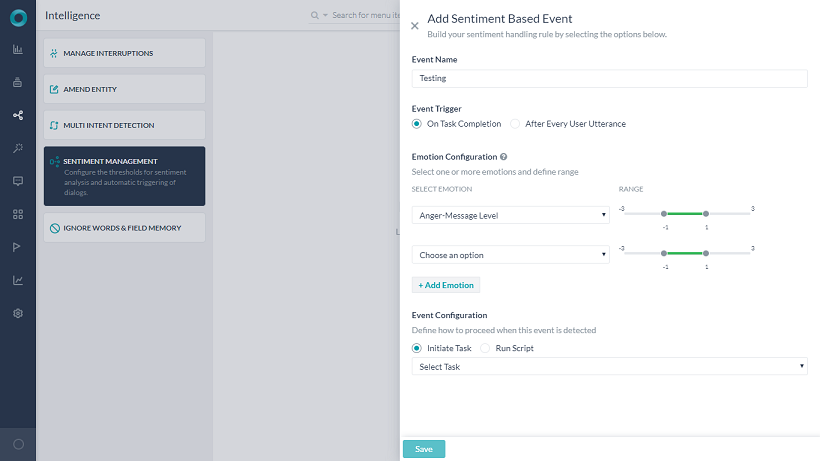
Following parameters can be configured for a sentiment event:
- Event Name – Name for the Event.
- Event Trigger – Defines how often the sentiment should be checked. It can be set to:
- On Task Completion – Sentiment will be checked only after completion of a task (dialog, action, alert and information task)
- After Every User Message – Sentiment will be checked after every message from the end user. The event will be evaluated before proceeding with the conversation using the incoming utterance.
- Emotion Configurations –
- Select the required emotions to be captured from a list of six tones – angry, disgust, fear, sad, joy, and positive.
- Select if the tone should be considered at the ‘Dialog’ level or ‘Message’ level
- Dialog level tone value is a consolidated tone value across all user messages in a conversation session.
- Message-level tone value is a tone value calculated for a given message from the user.
- Define the range to be considered for each of these tones, the range can be between -3 to +3. (See here for more on Tone Analysis)
- When multiple emotions are selected, the event will be triggered when ALL the tone rules are met. In case you want the event to be triggered when any one tone rule is met, add them as separate rules.
- Event Configuration – The result of the event trigger could be either to Run a Dialog or Run a Script.
Event Flow
Emotion tones are continuously updated whenever a message received from the users and as such the sentiment events are also continuously evaluated. When an event’s criteria are met, the platform will trigger the defined behavior.
- If the configuration used is to ‘Initiate task’, then the current task is discarded and bot switches to the new task according to the event configuration.
- Any other implicitly paused tasks will also be discarded.
- Tasks that are kept on hold using Hold & Resume settings will be resumed as per Hold & Resume configuration.
- If the dialog selected to be triggered for the sentiment event is not available for any reason, then a standard response is displayed. Refer to the standard response with the title ‘Dialog task required for conversation is not available’ for more information. (more on standard responses).
- If the configuration used is to ‘Run script’, then the platform will execute the script and continue with the task execution. In case of any errors executing the script associated with the sentiment event, then a standard response is displayed. You may refer to the standard response titled ‘Error in continuing the conversation due to incorrect bot definition’ for more information. (more on standard responses).
- In case of a conflict between a sentiment event and direct intent invocation by the user, sentiment event is given precedence.
- When tone criteria for two or more sentiment events are satisfied at the same instance, then the platform will prefer the sentiment event with the highest order of precedence used in defining the events.
Execution Flow for Universal Bots
- Events configured at universal bot will be honored over the events defined in the child bots
- If an event at universal bot is qualified, then the corresponding behavior will be triggered
- If an event at universal bot is not qualified or not defined, then the events defined for the child bot that the user is interacting with will be evaluated and triggered if qualified.
- If no child bot is being executed, then child bot events will not be evaluated.
Reset Tone
By default, sentiment values are reset at the beginning of every user conversation session.
Apart from the beginning of the conversation session, the platform resets the sentiment values (i.e. tone scores) once the associated events are triggered. The reset behavior is based on the type of event trigger:
- If a Script is run, then the values would be reset after successful execution of the script.
- In case of a Dialog task being triggered, the values are transferred to the new Dialog task’s (triggered by the sentiment event) context and reset in the original global context.