As we have seen here, you can define filters for end-users to limits the results of an alert task to the results an end-user needs. For example, you can define a filter for the name, or account, or business. When the alert is set up by the end-user, and the filter applied, only alert messages that meet the filter specifications are displayed to the end-user.
Defining Filters
To get started with defining filters for a task, on the Settings tab, click the Expand icon in the Filters section, and then click Add as shown in the following illustration.
When you click Add, the Alert Task Filter dialog is displayed as shown in the following illustration.
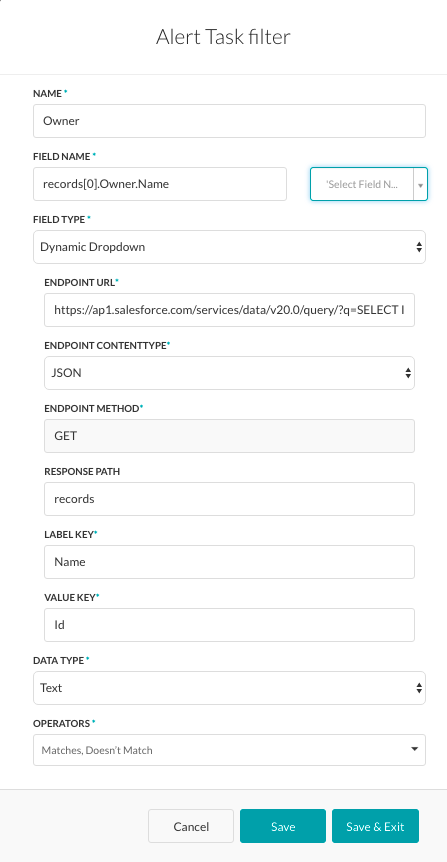
The Filter defined in the previous illustration is displayed to the end-user as a filter labeled Owner, with the Field Type set to Dynamic Dropdown to enable the end-user to select a name from a dynamically populated list of owners defined in the response payload.
Define the fields described in the following table to create a new filter for a task.
| PARAMETER NAME | DESCRIPTION |
| Name | Specify the name of the Filter displayed to the end-user in the Filters section when configuring the task, for example, Notify me only when the below user tweets. |
| Field Name | Enter the name of the field to filter the task on, or click Select Field to display a drop-down list of field names parsed from the Response Sample defined on the task API Request tab. |
| Field Type | Select the type of input field to collect the user input.
|
| Data Type | The data type for the content received from the endpoint URL. One of:
|
| Operators | Select one or more filter operations that the end-user can select to apply to the filter. Depending on the Data Type selected, one or more of the following options are available to select to display to the end-user in the filter.
|
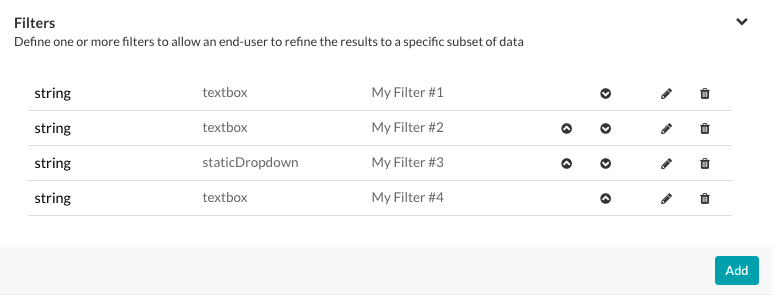
For multiple filters, you can order the filters in an order the end-user expects, shown in numerical order in the following illustration.

Use the Move Up ![]() icon and the Move Down
icon and the Move Down ![]() icon in the Actions column in the Filters section to reorder the filters if needed.
icon in the Actions column in the Filters section to reorder the filters if needed.
Click the Edit ![]() icon to modify the settings for an existing filter.
icon to modify the settings for an existing filter.
Click the Delete ![]() icon to delete an existing filter.
icon to delete an existing filter.
Warning: This operation is permanent and cannot be undone.
