As seen here, alert tasks only reach out to a web service for data when the Bot makes a request. For each task, you need to define when, and how often the web service is queried for data for an alert message. You can define the scheduling options presented to the end-user when the task is set up, as well as the default schedule for the task.
Configuring the Schedule for a Task
You need to configure the default settings for how often the task runs to request data from your web service. This topic describes how to configure the recurrence for a task.
To get started with defining the schedule to run a task, on the Settings tab, click the Expand icon in the Schedule section as shown in the following illustration.
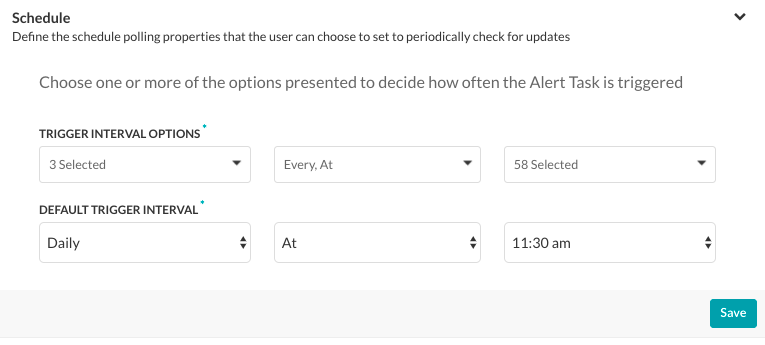
To configure the schedule for your task, you must define the Trigger Interval Options, and then the Default Trigger Interval. The Default Trigger Interval is the elapsed time between the last task request and the next automated task request.
To set the options displayed to the end-user, in the Trigger Interval Options section:
- In the first field, select one or more of Daily, Weekday, Weekend, individual days of the week or Select All, and then click OK.
- In the second field, select one or more of Every, At, or Select All, and then click OK.
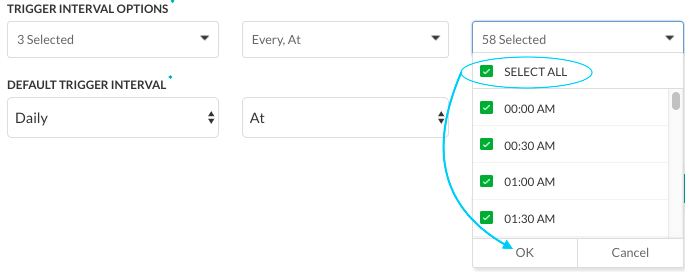
- In the third field, select one or more of the available 5-minute intervals or 30-minute time slots (based on whether the second field is Every or At), or Select All, and then click OK.
In the following illustration, the Default Trigger Interval settings of Daily At < any 30-minute interval >.