The Kore.ai Bots Platform only accepts clients that are authorized to connect and exchange messages. You must register your SDK app with the Kore.ai Bots Platform in the Bot Builder tool and acquire client credentials. You can then use your client credentials to authorize the app and communication exchange between your user, bot, and the Bots Platform.
Securing Your SDKs
Using Kore.ai SDKs, you can create secure interactions with the Kore.ai Bots Platform.
Kore.ai SDK libraries can be embedded with web or mobile applications to make HTTPS calls and establish web socket connections with the Kore.ai Bots Platform on behalf of a user of your application chatting with a Kore.ai bot.
To establish identity and initiate a secure web session:
- Your application SDK should sign and send the identity of the user to the Kore.ai Bots Platform
- The Kore.ai Bots platform verifies the signature to establish trust with your application using:
- JSON Web Token (JWT) – Used to send the user identity to Kore.ai Bots Platform
- Bearer Token – Your application SDK exchanges the JWT for a bearer token used for subsequent calls
About JWT
Kore.ai uses the JWT (JSON Web Token) mechanism to handle the authentication.
JWT Flow
The following diagram depicts a typical JWT flow in Kore.ai Bots Platform.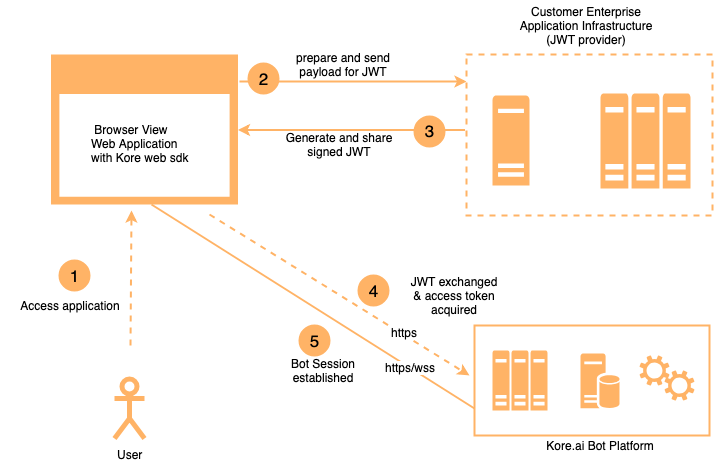
JWT Tokens
JSON Web Tokens consist of three parts separated by dots ” . ” as:
- Header
- Payload
- Signature
using the hhhhh.ppppp.sssss syntax where h represents the header, p the payload, and s representing the signature.
JWT Header
The JWT Header defines the token type, which is JWT, and the security algorithm, for example,
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
The JWT type can be one of:
- HS256 (HMAC with SHA-256) – This algorithm uses a Secret Key to sign the token. The Secret Key is generated when the app is registered in Bot Builder when defining the Web/Mobile Client channel for your bot.
- RS256 (RSA signature with SHA-256) – This is an RSA public/private key based algorithm to sign and verify the token. The client Public Key is defined when the app is registered in the Bot Builder tool on the Kore.ai Platform. The client app signs the token using a Private Key, and the Kore.ai Bots Platform verifies this token using the Public Key.
To use these JWT types for your bot, you need to register your application and select the algorithm type. For more information about using JWT, see https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519 and https://jwt.io/introduction/.
JWT Payload
The SDK client needs to assert the user by generating unique JSON Web Token using your app registration credentials created in Bot Builder when you defined the Web/Mobile Client channel for your bot and the identity of your app user.
The following example shows a sample payload used to generate the JWT.
Sample Header
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
Sample Payload
{
"iat": 1466684723,
"exp": 1466684783,
"jti": "1234", //or kore_jti
"aud": "https://idproxy.kore.ai/authorize",
"iss": "cs-xxxxxxxxxx-1234", //or kore_iss
"sub": "john.doe@achme.com", //or kore_sub
"isAnonymous": false,
"identityToMerge": "anonymoususer1@test.com" //to map anonymous user
}
The following table describes the parameters for the JWT Header and Payload.
| Parameter | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| alg |
A drop-down list of security algorithms. One of:
|
string |
| typ | The token type. For JSON Web Token, enter JWT. | string |
| iat | The date/time that the token was issued. This value should be in seconds. | integer |
| exp | The date/time that the token expires. This value should be in seconds. | integer |
|
jti or kore_jti |
A jti claim which can be used to prevent replay attacks: “The “jti” (JWT ID) claim provides a unique identifier for the JWT. The identifier value MUST be assigned in a manner that ensures that there is a negligible probability that the same value will be accidentally assigned to a different data object; if the application uses multiple issuers, collisions MUST be prevented among values produced by different issuers as well. The “jti” claim can be used to prevent the JWT from being replayed. The “jti” value is a case-sensitive string. Use of this claim is OPTIONAL.” (ref) NOTE: Use kore_jti to bypass the pre-populated value for jti with Kore specific values |
string |
| aud | The audience that the token is intended for. For Kore.ai, the audience is https://idproxy.kore.com/authorize. | string |
|
iss or kore_iss |
The ClientID of the client application. The ClientID is generated when the app is registered in the Kore.ai Bot Builder. NOTE: Use kore_iss to bypass the pre-populated value for iss with Kore specific values |
string |
|
sub or kore_sub |
The token subject which is represented by the email ID or phone number for users who are logged in the client application system. For anonymous users, the client app can generate a unique random ID and assign that ID to this field. NOTE: Use kore_sub to bypass the pre-populated value for sub with Kore specific values |
string |
| isAnonymous | When set to true, the user is an anonymous user for the client application system. Anonymous users are not persisted on the Kore.ai Platform. Default setting is false. |
boolean |
|
identityToMerge |
The anonymous Identity that needs to be merged into known user |
string |
jti Validations
In case jti claim is passed as part of the JWT payload, the platform performs the following validations:
- Expiry to be less than or equal to 1 hour: In case of failing to meet this requirement the following response is sent:
{"errors":[{"msg":"error verifying the jwt: if \"jti\" claim \"exp\" must be <= 1 hour(s)","code":401}]} - Restricts replay of XHR: The following response is sent in case of non-compliance:
{"errors":[{"msg":"error verifying the jwt: possibly a replay","code":401}]}
Hosting the JWT Generation Web Service
The Kore.ai SDK libraries and UI widgets are integrated directly into your client applications, and you will need to generate the JWT from your server.
- For the Web SDK, the SDK libraries are run from the user’s browser.
- For mobile SDKs, the SDK libraries are run from a user’s mobile phone.
You need to host the JWT generation as a REST web service for security because the Client Secret or RSA Private Key is required for JWT generation and should not be hosted at the client application. You can make the REST web service directly available to SDK libraries or have your application call the JWT generation web service at the backend to make the JWT available to the SDK libraries.
When making the JWT generation web service available to the SDK libraries, you should keep the Client ID, Client Secret, and any key expiration logic on the server-side and expect only the user ID from the client.
There are several open-source libraries available to generate JWT, for example,
- NodeJS – https://github.com/auth0/node-jsonwebtoken
- Java – https://github.com/auth0/java-jwt
- .Net – https://github.com/jwt-dotnet/jwt
To generate credentials for your clients, you must register your client app in the Bot Builder tool. For more information, see SDK App Registration.
You can also try out our tutorial using a Kore.ai sample bot, a test application, and configuring your localhost server for JWT generation. For more information, see the Kore.ai Web SDK Tutorial.
JSON Web Encryption (JWE)
JWT is used to send user identity in a secure form by signing the payload using the Secret Key(HS-256 algorithm) or RSA Private Key(RS-256 algorithm). There can be a requirement to send additional user data along with user identity in JWT and make them available in the dialog execution context. This additional data may be sensitive information. Hence we need to send in encrypted form. JWE(JSON Web Encryption) is an IETF standard, which provides a way to send the JWT in an encrypted form.
Generating JWE
JWE token has five parts:
- Header,
- JWE Encrypted Key (CEK),
- Initialization Vector,
- Cipher Text, and
- Authentication Tag
Header
Header part can have the following attributes:
- alg: defines the algorithm for content key wrapping
Following algorithms are supported:
-
- RSA-OAEP,
- RSA1_5
- enc: defines the algorithm for content encryption
Following algorithms are supported for content encryption:- A128CBC-HS256
- A128GCM
- A256GCM
- kid: Key Id of Kore Platform’s public key. This will be displayed when you enable JWE bot builder
- typ: This will have JWT as a value since the wrapped content is JWT
Below is the decoded sample JWE header:
{
"alg": "RSA-OAEP",
"enc": "A128CBC-HS256",
"kid": "k-ffb4hty69-750a-44af-91c1-de0bvcf6a",
"typ": "JWT"
}
JWE Encrypted Key (CEK)
A symmetric key is generated to encrypt the payload using the algorithm specified in “enc” field of the header. This key is encrypted using Kore.ai Public Key using the algorithm specified in “alg” field of the header.
Initialization Vector
This is used in the encryption of the payload (JWT).
Cipher Text
This contains encrypted JWT payload. This is encrypted using the algorithm specified in “enc” field of the header using the initialization vector.
Authentication Tag
The Authentication tag is generated when authenticated encryption is performed using the algorithm specified in “enc” field of the header. This is used during decryption to ensure integrity.
Kore.ai public key will be displayed in JWK format when you enable JWE option while creating an SDK app. You can use this in your client library to generate JWE.
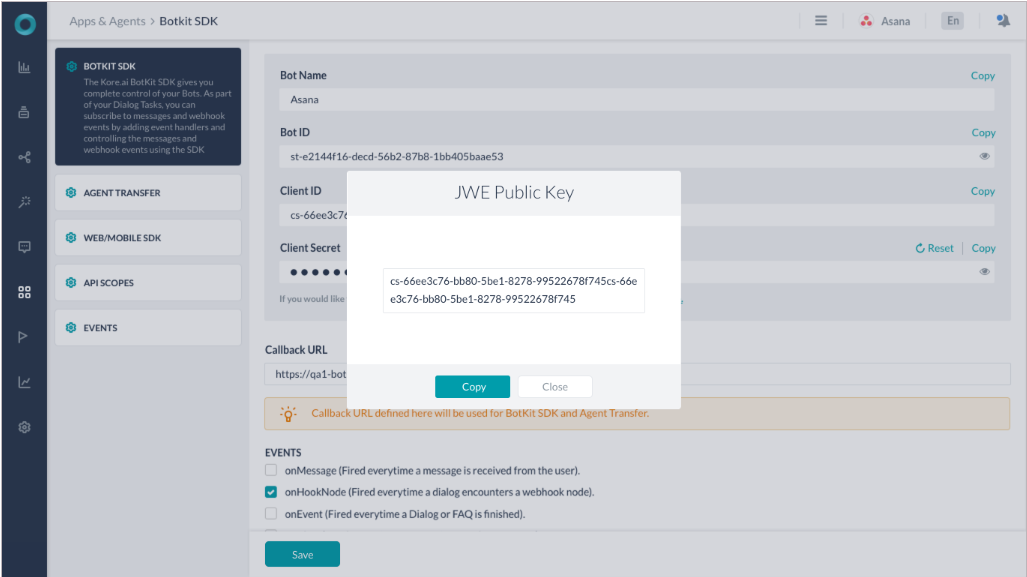
For more information about JWE, refer to https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7516.
