OAuth v2 is the new version of the open protocol to allow secure authorization in a simple and standard method from web, mobile, and desktop applications.
To use oAuth v2, you must first register an account with the web application as you will need the sign in credentials for that application to configure the settings for the Authorization Mechanism.
How oAuth v2 Works
- The Kore.ai application redirects the user to a login dialog at the web application.
- The user authenticates.
- The web application redirects the user back to the Kore.ai application with an access token.
- The Kore.ai application validates the access token.
- The access token allows the Kore.ai application to access a protected resource at the provider, on behalf of the user.
Defining oAuth v2
To define Authorization for your bot, follow these steps:
- Open the bot for which you want to configure an Authorization profile.
- Select the Build tab from the top menu.
- From the left menus, click Configurations -> Authorization Profile

- Click Add. The New Authorization Mechanism dialog opens.
- In the Authorization Type drop-down list, select auth v2.
- In the Name field, enter the name for your authorization.
The following illustration is an example of the oAuth v2 fields that you must define to enable basic authorization for your Bot.
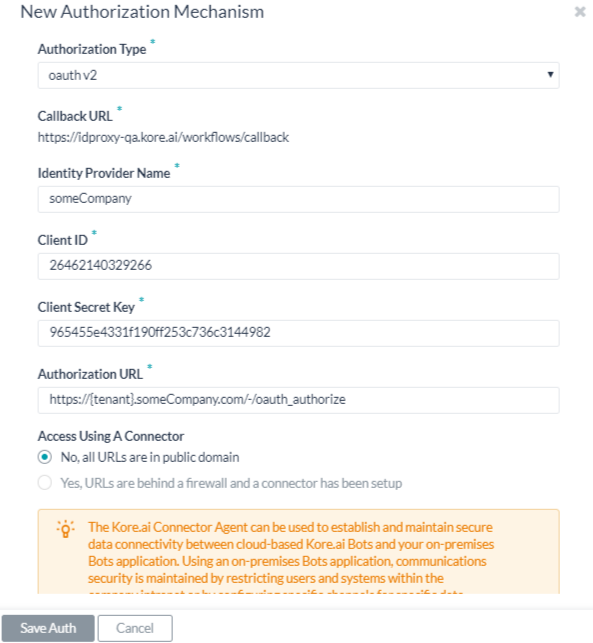
To configure oAuth v2, define the fields described in the following table.
| FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Authorization Type | Set to oAuth v2. |
| Bots Callback Link | The URL used by the web application or web service to redirect the end-user after end-user authorization is complete. This value, https://idp.kore.ai/workflows/callback/ is provided as a read-only value by the Kore.ai application when you define oAuth v2 settings. |
| Identity Provider Name | The name of the web application or web service, for example, Asana. This field is required. |
| Client ID | The ID of the Kore.ai client. |
| Client Secret Key | The value provided as the Kore.ai application authentication based on the Client ID to the web application. |
| Authorization URL | This is the URL used to obtain end-user authorization for the Kore.ai application to access the web application or web service using the access token. This field is required. You can use dynamic fields, path parameter fields, query fields, and so forth, to define the Authorization URL, for example, https://kore.someCompany.com/sap/opu/odata/sap/{{authfield1}}/?$format=json or https://{tenant}.service-now.com/api/now/v1/table/incident For more information, see Using Session and Context Variables in Tasks. |
| Access Using a Connector | Select Yes to enable access for Kore.ai Bots using the Kore.ai Connector agent. This option is only visible if a Kore.ai Connector agent is configured and enabled in your enterprise on-premises network. For more information, see Using the Kore.ai Connector. |
| Token Request URL | The URL used by the Kore.ai application to obtain an unauthorized request token. A request token is a value used by the Kore.ai application to obtain authorization from the end-user to obtain an access token. After end-user authorization, an access token can be requested by the Kore.ai application. This field is required. |
| Scope | If the Bot web service requires additional values for authorization, add one or more Key/Value pairs. For example, some Bot web services support using a scope key using read-only, write, or both as the value. |
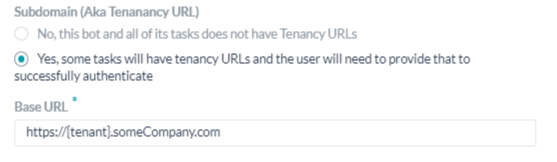
Defining Tenancy
If required, in the Subdomain section, select Yes if the base URL for a web application or user interface that uses a tenant name in the URL. For example, kore is the tenant organization for a web service using tenants at www.kore.someCompany.com.
In the following example configuration, the tenancy URL contains the {tenant} organization placeholder.
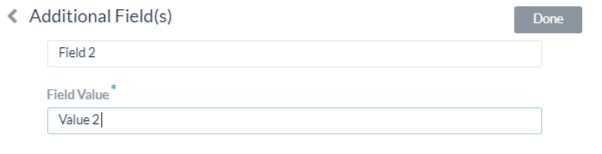
Adding Additional Fields
Click Add to open the Additional Fields dialog and then enter one or more key/value pairs that represent additional authorization input fields.
If the default username and password fields do not meet your needs for authorization input, you can add custom fields as key/value pairs that are displayed to the end-user by adding Additional Fields. You can use these fields, for example, if a PIN code is required in the authorization process, in addition to the Username and Password fields.
Additional Fields are added as shown in the following illustration.
- Field Key – The name of the custom field to specify for authorization.
- Value – The value of the custom field to specify for the authorization.
Click Add to save the Additional Field.
To add more Additional Fields, click Add in the Additional Fields section.
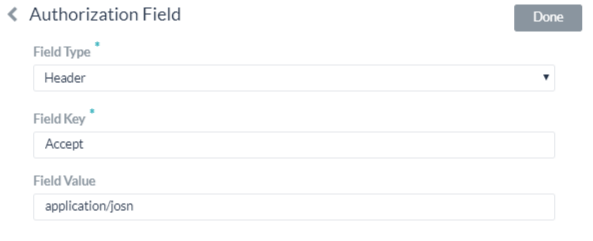
Adding Authorization Fields
By default, no authorization fields are configured as part of the header of the Bot request message. If your Bot request requires authorization fields or the expected authorization is not part of the header, for example, social security number or PIN, click Add in the Authorization Fields section and then define the fields as shown in the following illustration.
- In the Field Type field, you can select one of the following depending on where in the Bot request message and the type of authorization fields that are required.
- Header – The Bot expects the authorization fields as part of the header of the request.
- Payload – The Bot expects the authorization fields as part of the content of the body of the request.
- Query String – The Bot expects the authorization fields as a query in the body of the request.
- Path Param – The Bot expects the authorization fields as part of the URL path for the request.
- In the Field Key field, enter the name of the field for the selected Field Type.
- In the Field Value field, enter the value for the Field Key specified.
- Click Add. The new authorization field is added in the Authorization Fields section.
To add additional authorization fields, click Add in the Authorization Fields section.
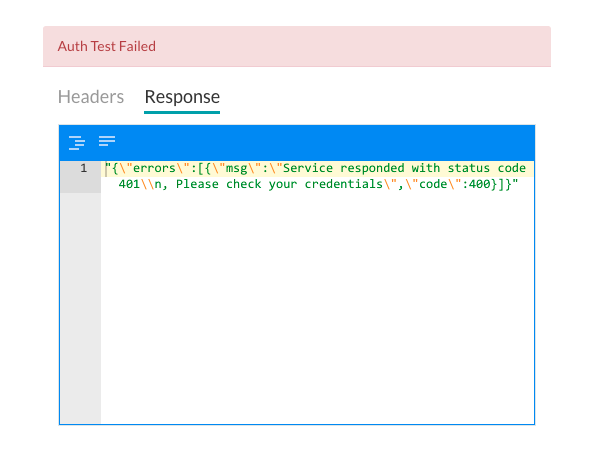
Testing the Authorization
After you save the authentication, you can test your authorization definition on the Authentication page when you click Test before continuing to develop the remain steps of your task. When you click Test, the test is executed using the authentication token URLs and the Client ID and Client Secret Key. If tenancy was defined, the Test Authorization dialog is displayed.
Click Test to begin the authorization test. When the validation of authentication is complete, the Test Authorization dialog is closed and the results of the validation, either success or failure, is displayed to the immediate right of the Test Authorization button. If the authorization fails, the Auth Test Failed message is displayed along with the Headers and Response tabs as shown in the following illustration.