To define Basic Authorization for your bot, follow these steps:
- Open the bot for which you want to configure the Basic Authorization profile.
- Select the Build tab from the top menu.
- From the left menus, click Configurations -> Authorization Profile

- Click Add. The New Authorization Mechanism dialog opens.
- In the Authorization Type drop-down list, select Basic Auth.
- In the Name field, enter the name for your Basic Auth type.

Defining Tenancy
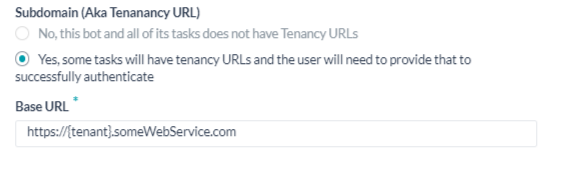
If required, in the Subdomain section, select Yes if the base URL for a web application or user interface uses a tenant name in the URL. For example, kore is the tenant organization for a web service using tenants as www.kore.someCompany.com.
In the following example configuration, the tenancy URL contains the {tenant} organization placeholder.
Adding Form Fields
If the default username and password fields do not meet your needs for authorization input, you can add custom fields displayed to the end-user by adding authorization IDP form fields. You can use these form fields. For example, if PIN code is required in the authorization process, in addition to the Username and Password form fields.
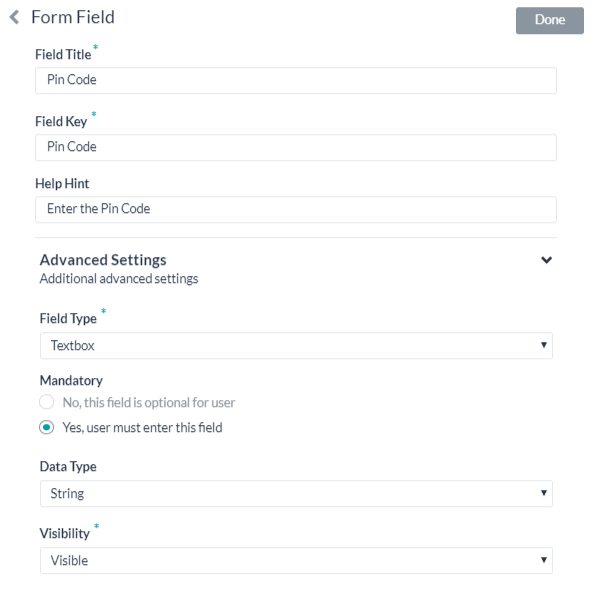
The following table describes the fields used to define an authorization IDP form field.
| FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Field Title | Specify the name of the field displayed to the end-user in the authorization dialog. |
| Field Key | The value that represents the end-user input value to the authorizing service. |
| Help Hint | The help text displayed in the field to describe what should be entered into the field. |
| Field Type | When Advanced Options is selected, specify the type of field displayed in the end-user interface to collect the user input assigned as the value for the Field Key, one of:
|
| Mandatory | When Advanced Options is selected, select if the end-user must define this field to complete the authorization. |
| Data Type | When Advanced Options is selected, specify the type of data expected as input from the end-user, for example, String. |
| Visibility | When Advanced Options is selected, specify if the authorization field should be visible, hidden, or displayed as read-only. |
Adding Authorization Fields
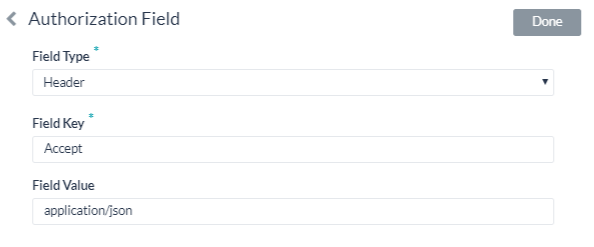
By default, authorization fields are configured as part of the header of the Bot request message. If your Bot request requires additional authorization fields or the expected authorization is not part of the header, for example, social security number or PIN, click Add in the Authorization Fields section and then define the required fields.
- In the Field Type field, you can select one of the following depending on where in the Bot request message and the type of authorization fields that are required.
- Header – The bot looks for the authorization fields in the request header.
- Payload – The bot looks for the authorization fields in the request body content.
- Query String – The bot looks for the authorization fields as a query in the request body.
- Path Param – The book looks for the authorization fields in the request URL path.
- In the Field Key field, enter the name of the field for the selected Field Type.
- In the Field Value field, enter the value for the Field Key specified.
- Click Add. The new authorization field is added in the Authorization Fields section.
To add additional authorization fields, click Add in the Authorization Fields section.
Authorization Check URL
In the Authorization Check URL field, optionally define a URL that can be used to test the authorization settings from Bot Builder before you deploy the Bot with the authorization mechanism. You can use dynamic fields, path parameter fields, query fields, and so forth, to define the test URL.
For example
https://kore.someCompany.com/sap/opu/odata/sap/{{authfield1}}/?$format=json
or
https://{tenant}.service-now.com/api/now/v1/table/incident
For more information, see Using Session and Context Variables in Tasks.
Access Using a Connector
In the Access Using a Connector section, select Yes to enable access for Kore.ai Bots using the Kore.ai Connector Agent.
The Kore.ai Connector Agent can be used to establish and maintain secure data connectivity between cloud-based Kore.ai Bots and your on-premises Bots application. Using an on-premise Bots application, communications security is maintained by restricting users and systems within the company intranet or by configuring specific channels for specific data exchange.
If your domain does not have any active Kore.ai Connectors defined, a warning message is displayed to contact the Bots Admin Console system, administrator. For more information, see Using the Kore.ai Connector in the Bots Admin Console documentation.
Click Save to save the authorization settings and close the New Authorization Mechanism dialog.
Testing the Authorization
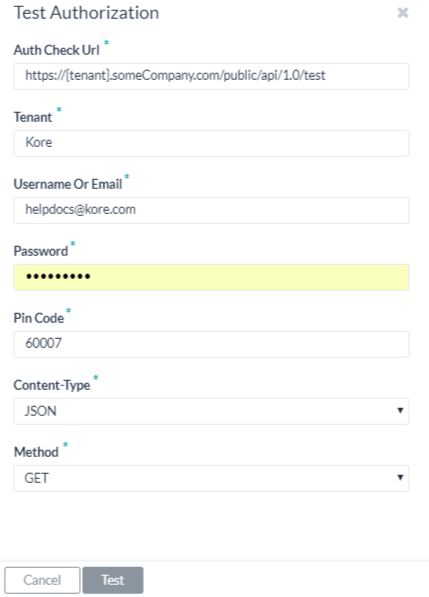
Once you save the authorization settings, you can test your authorization definition when you click Test from the Authorization Profile page.
When you click Test, the Test Authorization dialog.
To configure the Test Authorization – Basic Auth
- In the Auth Check URL field, verify or enter the URL to test the authorization configuration.
- If your bot uses subdomains, the Tenancy field is displayed and you must specify the tenant.
- Enter your User Name and Password for the web service.
- Select the content type expected for the URL in the Content-Type field.
- For testing the URL, the Method field is read-only and set to GET.
- Click Test to begin the authorization test.
When the validation of authorization is complete, the Test Authorization dialog closes and you can see the results of the validation, either success or failure, on the top-right corner of the screen.
If the authorization fails, the Auth Test Failed message is displayed along with the Headers and Response tabs.
How it all Works
When basic authorization is used for a Bot, the Kore.ai application automatically prompts the user for login credentials to access the web application or web service as shown in the following illustration.
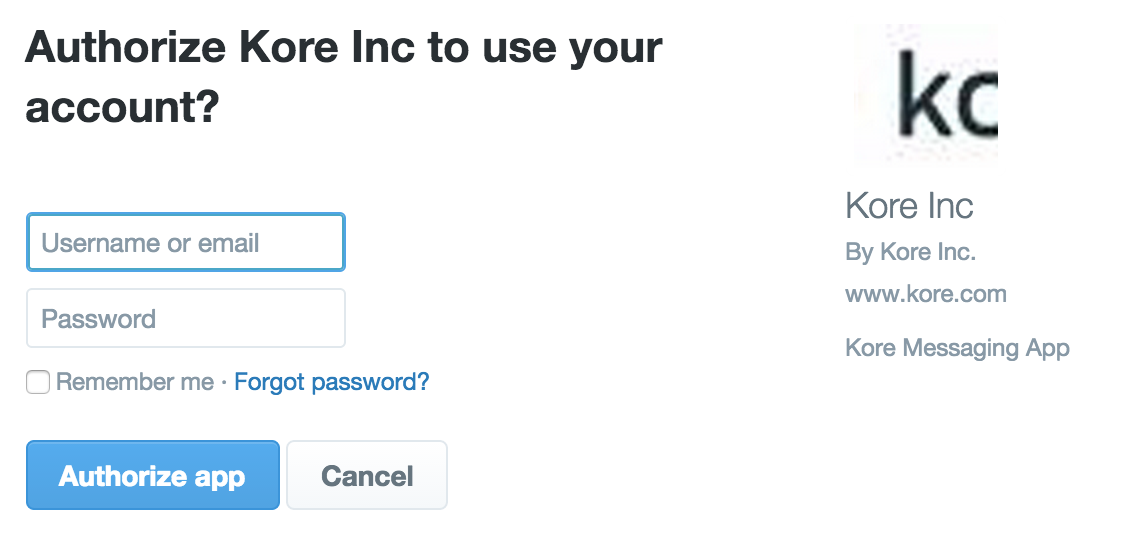
After the end-user authorizes, the settings are saved using the following naming syntax:
{{ First Name }} {{ Last Name }} {{ Bot Name }} {{ Account # }} {{ Sequence # }}
For example, John Smith’s Twitter Account #1.
The Kore.ai application can access the web application or web service for all future Bot requests using this account. In addition, the end-user can reuse the account for other tasks for the same Bot.