When it comes to automating customer interactions, IVR systems have proven to be among the top choices for organizations. But if you are using an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system for your customer service, odds are you might have encountered these two issues quite often:
- Non-Intuitive Interface: IVR systems do not simply let the customers state their need. They make the users go through a plethora of menu options from which to select before finding their intent. Even if they allow users to express their intent at first go, the backend programs can only understand a limited number of phrases.
- Static Flows: IVR systems use static call flows that do not align with the nonlinear and contextual nature of human interactions. Take the following example of a customer trying to Book Flight tickets:
User: Book me a ticket to NYC IVR: Sure, for which date? User: Wait, will it rain there this Sunday? IVR: Sorry, I don’t understand the input.
Conventional IVR system leaves limited room for the users to articulate their requests beyond the rigid program flows.
Kore.ai IVR Support
Kore.ai allows you to give a conversational makeover to your IVR system. It lets you build chatbots with human-like conversation capabilities and integrate them with your existing IVR system, thus taking your organization’s customer service experience to a whole new level.
The following features enable the seamless integration of your Kore.ai Bots with your existing IVR:
- Native VXML Support: Built-in support to parse and generate W3C compliant VXML files.
- Hybrid integration: Flexibility to build use cases or dialogs on the Bots Platform, which can work in-sync with the IVR dialogs.
- Discourse Analyzer: Kore.ai’s discourse analyzer helps enterprises generate conversation flows using historical chat or call transcripts. Chat and call transcripts are analyzed using neural network-based machine learning models to identify intents and discourse patterns to fulfill a specific intent. This is an out-of-the-box feature which is in Beta state. Contact our support team if you want to try this feature.
- Granular Call Flow Support: Ability to define all the call flow elements such as grammar, prompts, retry and time-out periods. Kore.ai supports call termination handlers, allowing you to end calls or invoke dialogs in case of exceptions.
Setting Up
Setting up IVR integration involves the following three steps:
- Configure Bot Settings: Define IVR settings such as transcription options, welcome messages, standard responses and VXML properties
- Dialog Definition: Define Dialog by configuring node-specific grammar, prompts, and call flow behavior like time-out, retries.
- Channel Setup: Set up authentication, configure WebHook in your IVR system and enable channel.
Bot Settings
Step 1: IVR Settings for a Bot
As the first step of the integration, you first need to enable the IVR settings for the bot and define the Transcription options and VXML properties. These settings act as the default for the bot. You may override VXML properties defined at the bot level by defining custom values at the node level of the Dialog tasks.
To configure IVR settings for the bot
- Open the Bot for which you want to integrate the IVR.
- Select the Deploy tab from the top menu.
- From the left menu, click Channels
- Locate and click the IVR voice channel. The IVR Panel with Instructions opens.
- From the Configuration tab,
- You can use Kore.ai IVR Sandbox for testing your Bot, see below for details.
IMP: If you save the configuration after associating an app without Enabling IVR Settings, the platform will pre-populate the required settings for Sandbox. - Associate an App with the IVR channel – either by creating a new one or selecting an existing one.
- Use the WebHook URL provided in your external application.
- You can use Kore.ai IVR Sandbox for testing your Bot, see below for details.
- From the Voice Call Properties tab set the configurations.
If you have enabled IVR Sandbox, the following settings are required by the platform. These will be pre-populated if you do not enable the IVR settings. In case you have enabled the settings, ensure the values are the same as given below, sandbox may not respond as expected if you use different values:
– Enable Transcription set to Yes,
– transcription engine source set to builtin:speech/transcribe,
– IVR Data Extraction Key set to userinput,
– ASR Confidence Threshold Key set to userinput.confidence,
– ASR Threshold Confidence set to 50 - (Optional) To enable an external transcription engine, under Enable Transcription, select Yes.
- On enabling the transcription engine, a text box appears for entering the source of the transcription engine.
Note: Bots Platform supports all UniMRCP-encoded voice-to-text services. Only if you select the Enable Transcription option for the bot, the platform allows you to do away with defining grammar during configuring IVR settings for any node (described in Step 2).
- Enter the details to complete the setup, see here for details.

- On enabling the transcription engine, a text box appears for entering the source of the transcription engine.
- Once you have enabled the IVR channel, we recommend configuring the Telephony Welcome Event for IVR Settings. This would play a welcome message for users when they connect to the Bot via the IVR channel.
For this:- Under the Build tab, select Intelligence -> Event configure Telephony Welcome Event
- Click the Use Voice Call Properties button to open the voice settings section.
- Under the Initial Prompts text box, enter the message that needs to be played when the user connects to the Bot.
- For details regarding other configuration fields, refer to the Configuring voice call properties for a Node section.
Sandbox Configuration
Note: This option was introduced in ver 7.1 of the platform. It is not available for on-prem installation.
Kore.ai offers an IVR Sandbox environment to instantly launch your bot for interactions over voice calls. This is particularly useful when a working IVR system is not feasible or available for testing your Bot over a voice channel. IVR Sandbox is an optional integration and it can coexist with your custom IVR integration.
Enabling this option will give you a Phone Number, Pin, and Secret. You can call your bot by using the phone number and PIN allocated for your bot to develop and test the bot with your teams. On receiving the valid Pin and Secret you will be connected to the Bot for interactions.
Once enabled you can access the IVR Sandbox interaction details by selecting the Test button on hover over the IVR icon from the channels page.
Limitations
- The platform supports only a limited number of concurrent lines hence calls to your bots via IVR Sandbox may not be responded to at times.
- We strongly recommend you use IVR Sandbox only for serving internal testing purposes and not for the end-users of your bots as there might be some functional limitations.
Channel Settings
Step 3: Setting Up IVR Channel for the Bot
After configuring IVR Settings at both the Bot and the Dialog levels, you should configure IVR Channel for the bot. IVR channel provides a generic integration to connect bots with IVR systems. Kore.ai platform generates required VXML files to be exchanged as part of bot interaction with the end user via the IVR systems.
Enabling IVR Channel and Associating an APP
Kore.ai Bots require a JWT token to authenticate the incoming requests from IVR. For generating JWT token, you should associate an app with the bot. You can select any of the existing Apps available in your Kore.ai account or create a new app.
- Hover over the side navigation panel of the bot and click Channels.
- On the Channels page, click IVR. The IVR Channel Instructions page opens.
- Click the Configuration tab.
- From the Select App drop-down list, select an existing App. If you do not have any app to associate the bot with, click Add.
- Copy the following:
- WebHook URL: For calling the bot from IVR.
- Client Secret: To generate JWT token that must be appended to the WebHook URL.
- Select Yes for Enable Channel.
Generating JWT Token
- Refer here to get the JWT token, click here
- JWT has to be passed in the IVR hook URL as value for the query parameter “token”:
https://bots.kore.ai/ivr/hooks/{{botId}}?token={{JWT}}
The token can also be passed as the body parameter.
Calling Bot from IVR Call flow
You can pass data to the bot from the IVR call flow using VXML <subdialog> as shown in the picture below. The subdialog src should be Webhook URL with JWT Token which takes the following parameters as Input
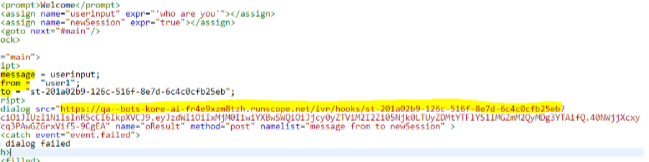
- message : Message from User
- from: Unique User’s Identity Ex: Phone Number
- to: Bot Stream Id
The endOfConversation variable should be processed from the data returned from the sub-dialog. If the value is set to true, it indicates that the dialog execution (conversation) is complete. It can be a triggering point to end the call with the user.


