You can build a Knowledge Graph in a CSV or JSON file and upload it to a bot. Similarly, you can export the existing Knowledge Graph to CSV or JSON. Exporting a Knowledge Graph helps you edit it in a spreadsheet or import it to another Bot.
There is a platform restriction of a maximum of 50k FAQs spread across a maximum of 20k nodes. Import of files exceeding these numbers is rejected.
Importing Knowledge Graph
- On the left pane, click Bot Tasks > Knowledge Graph.
- You can find the Import option on the respective Knowledge Graph.
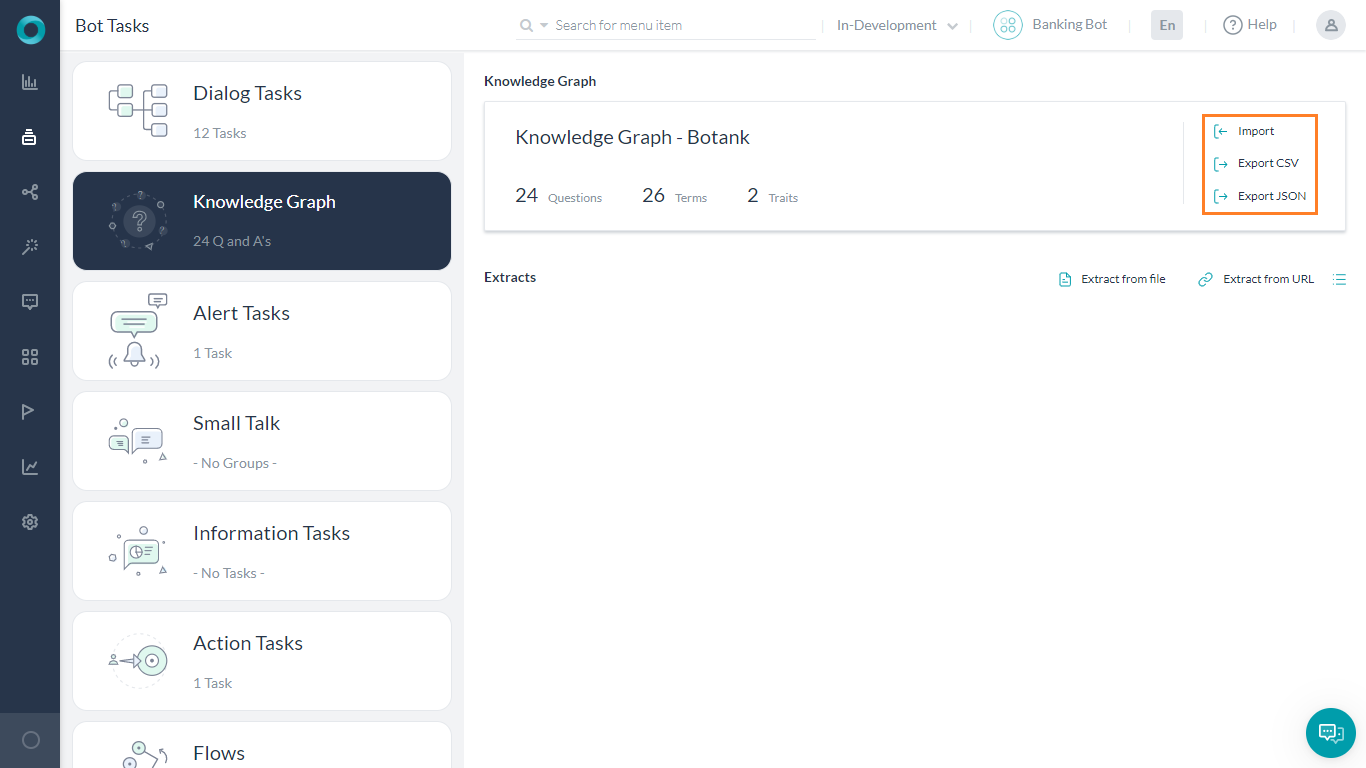
- Click Import.
- On the Import dialog box, do one of the following:
- If you are creating the Knowledge Graph from scratch, click Proceed.
(or) - If you have an existing Knowledge Graph, make sure to take a backup of the same to a CSV or JSON file, and then Proceed.
Note: Importing a Knowledge Graph does not update it but replaces the entire existing Knowledge Graph.
- If you are creating the Knowledge Graph from scratch, click Proceed.
- Drag and drop the file in the Import window or click Browse to locate the file.
- Click Next to begin the import.
- After the import is complete, the success message appears in a dialog box. Click Done.
- The hierarchy is displayed in the Knowledge Graph and you can edit and train the same.
Exporting Knowledge Graph
To export a Knowledge Graph, follow the below steps:
Creating a Knowledge Graph
Instead of creating the Knowledge Graph from the platform UI, you can work in your preferred editor like Spreadsheet or as a JSON file. The platform gives you the option to create a Knowledge Graph in a spreadsheet or JSON and use the same to import it into the bot.
To import, follow the below steps:
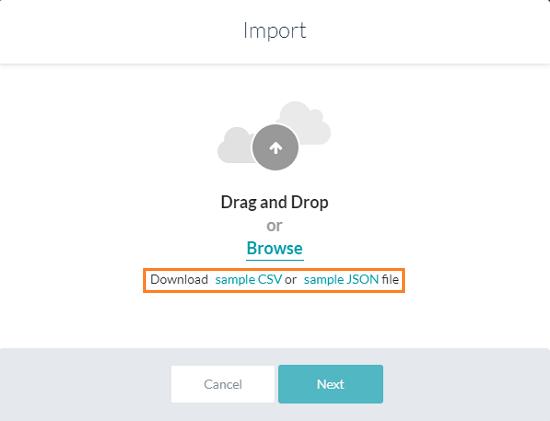
- Download sample CSV or a JSON file. You can download these sample files from a blank Knowledge Graph too.
- Edit the file by adding rows corresponding to the questions, responses, synonyms, etc.
- Import the file to your bot.
From a CSV File
You can create the Knowledge Graph using a sample spreadsheet that you can download from the bot. If you anticipate frequent changes to the Knowledge Graph, we recommend you to create it in a spreadsheet as it is easier to perform bulk updates compared to the application UI.
Follow the instructions below to build your Knowledge Graph in a spreadsheet.
Download the Sample CSV file
- On the left pane, click Bot Tasks > Knowledge Graph.
- You can find the Import option on the respective Knowledge Graph.
- You are prompted to back up the Knowledge Graph before proceeding. Choose the CSV or JSON format for the backup.
- After backup, click Proceed.
- On the corresponding dialog box, click Sample CSV. The CSV file is downloaded to your local computer.
Build the Knowledge Graph in a CSV (post v7.3)
The format for the CSV file is modified in v7.3 of the bots platform to cater for details regarding alternate answers, extended responses, and advanced responses. See below for the older format. You are strongly recommended to use the new format since the older format will be deprecated in the upcoming releases.
- The following types of entries are supported:
- Faq – The leaf level nodes with questions and answers.
- Node – For node/tags, traits, preconditions, and output context.
- Synonyms
- KG Params
- Traits
- Each of the above categories needs to be preceded by the appropriate header.
- The header helps identify the new vs old versions of the JSON file by the platform.
The following is the detailed information for each section and the content expected for each.
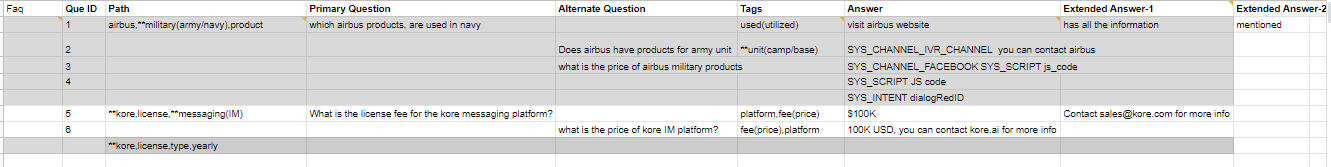
FAQ
This contains the actual questions and answers along with the alternate questions, answers, and extended answers.
Following are the column-wise details that can be given:
- Faq – Mandatory entry in the header, must be left blank in the following rows.
- Que ID – The question ID generated by the platform for each question.
- Path – To which the FAQ belongs
- Mandatory node names must be prefixed with ** and organizer nodes with !!
- Primary Question – The actual question user might ask: When left blank, the entry in the Answer column is considered as the alternative answer to the previous primary question.
- Alternate Question – Optional: Alternate question to the primary question if there are multiple alternate questions, they must be given in multiple rows.
- Tags – For each question or alternate question.
- Answer – Answer to the question serves as an alternate answer when the primary question field is left blank. Answer format can be:
- Plain text
- Script with SYS_SCRIPT prefix i.e.
SYS_SCRIPT <answer in javascript format> - Channel-specific formatted response when prefixed with SYS_CHANNEL_<channel-name>, the answer can be simple or in script format:
SYS_CHANNEL_<channel-name> SYS_TEXT <answer>SYS_CHANNEL_<channel-name> SYS_SCRIPT <answer in javascript format>
- Trigger a dialog then prefix with SYS_INTENT i.e.
SYS_INTENT <dialog ref id>
- Extended Answer-1: Optional to be used in case the response is lengthy.
- Extended Answer-2: Optional to be used in case the response is lengthy.
- ReferenceId – reference to any external content used as a source for this FAQ
- Display Name – the name that would be used for presenting the FAQ to the end-users in case of ambiguity.
Nodes
This section includes settings for both nodes and tags.
- Node – Mandatory entry in the header must be blank in the following rows.
- Que ID – Mandatory when specifying settings for tags, leave blank for nodes.
- Nodepath – Path for reaching the node/tag.
- Tag – Mandatory for tag settings, leave blank for node.
- Precondition – For qualifying this node/tag.
- outputcontext – Context to be populated by this node/tag.
- Traits – for this node/tag.
Synonyms
Use this section to enter the synonyms as key-value pairs.
- Synonyms – Mandatory entry in the header, must be blank in the following rows.
- Phrase – for which the synonym needs to be entered.
- Synonyms – Comma-separated values.
Use of bot synonyms in KG term identification can be enabled using the following:
- confidenceConfigs – Mandatory entry in the header, must be blank in the following rows.
- parameter – useBotSynonyms in this case
- value – true or false
KG Params
- KG Params – mandatory entry in the header, must be blank in the following rows.
- lang – Bot language code. For example, en for English.
- stopwords – Comma-separated values.
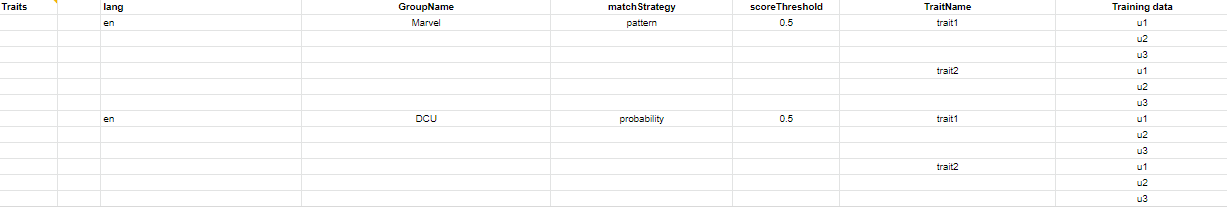
Traits
Trait related information can be specified as follows:
- Traits – Mandatory entry in the header, must be blank in the following rows.
- lang – Bot language code. For example, en for English.
- GroupName – Trait group name.
- matchStrategy – Pattern or probability (for ML-based).
- scoreThreshold – Threshold value (between 0 and 1) when the matchStrategy above is set to ML-based.
- TraitName – The name of the trait.
- Training data – Utterances for the trait.
From a JSON file
Kore.ai allows you to create the Knowledge Graph in JSON and upload it. You can download a sample JSON from the bot to understand its structure.
Follow the instructions below to build your Knowledge Graph using JSON:
Downloading the JSON sample
- On the left pane, click Bot Tasks > Knowledge Graph.
- You can find the Import option on the respective Knowledge Graph.
- You are prompted to back up the Knowledge Graph before proceeding. Choose the CSV or JSON format for the backup.
- After backup, click Proceed.
- On the corresponding dialog box, click Sample JSON. The JSON file is downloaded to your local computer.

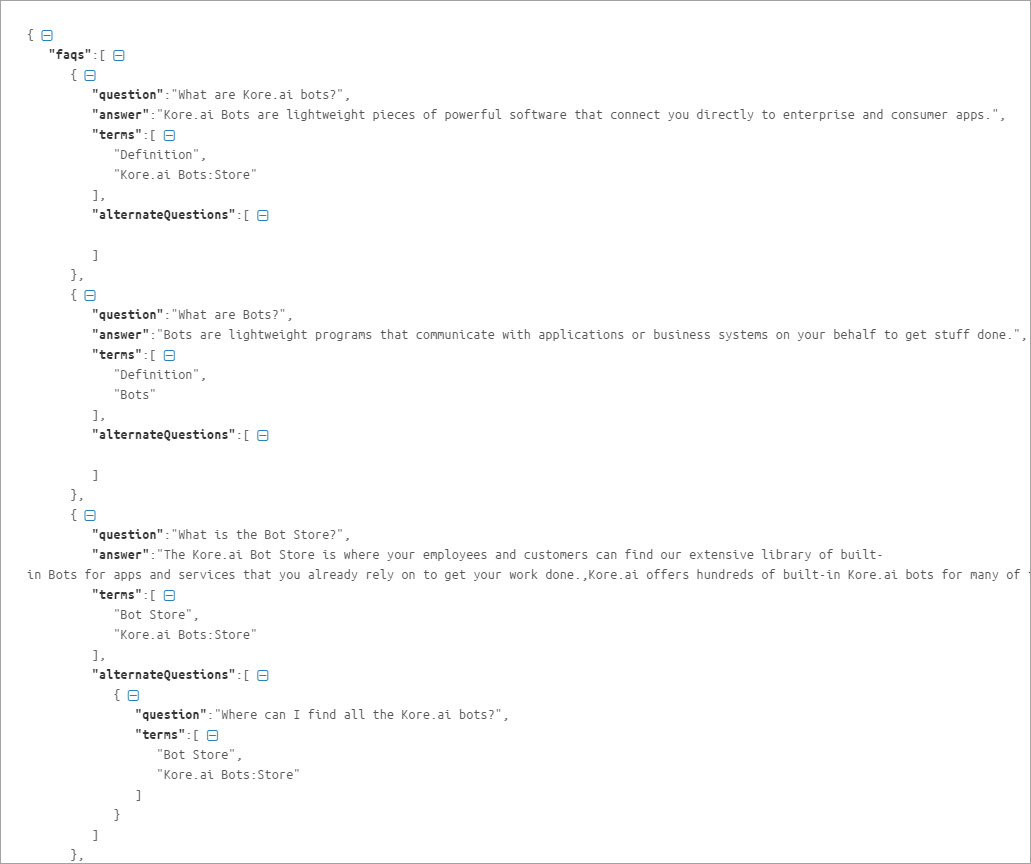
JSON Reference
| Property Name | Type | Description |
| FAQ | Array | Consists of the following:
|
| Question | String | Primary question; included in the FAQ array. |
| Answer | String | Bot response; included in the FAQ array. |
| Terms | Array | Includes the leaf node to which the question is added, and its parents up to the First-level node. |
| refId | String | Optional reference to any external content used as a source for this FAQ |
| Alternate Questions | Array | Consists of alternative question and terms. Include terms from leaf to the First-level node. |
| Synonyms | Object | Consists of arrays of terms and their synonyms. |
| Unmappedpath | Array | Consists of arrays of nodes that do not have any questions, and all their parents up to the First-level node. |
| Traits | Object | Consists of trait names as keys and an array of utterances as values. |
Building the Knowledge Graph in a CSV (before v7.3)
NOTE: This format will be deprecated in upcoming releases.
Open the downloaded Sample CSV file.
The details that you need to enter in each row of the CSV file differ based on the type of information. For example, the details you need to enter for an FAQ (Question, Answer, Nodes, Alternate Questions) differ from the details you need to enter for Synonyms (Term, Synonyms).
The bot interprets the data present in each row of the CSV file, depending on the information type specified in Column # 1 of the row. Below are the valid entries for Column#1 of the CSV file, which represent the different information types:
- faq: Represents a primary or alternate question in the Knowlege Graph.
- unmappedpath: Represents nodes with no questions associated with them.
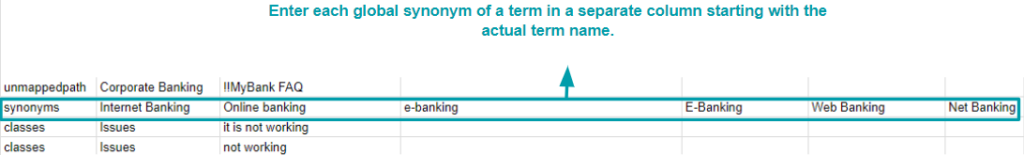
- synonyms: Represents global synonyms for terms.
- classes: Represents the trait names and their associated utterances.
Important Notes
You cannot import or export the following bot elements using a CSV or spreadsheet.
- Alternative Responses: While the spreadsheet support entering alternative questions for an FAQ, you cannot enter alternative responses in the spreadsheet and import them into the bot.
- Split Responses: You cannot enter or import FAQ responses that are split into multiple consecutive messages.
- Advanced Responses: The CSV import does not support responses written in the advanced mode using JavaScript.
The following sections provide the remaining details that you must fill in for each information type:
FAQ
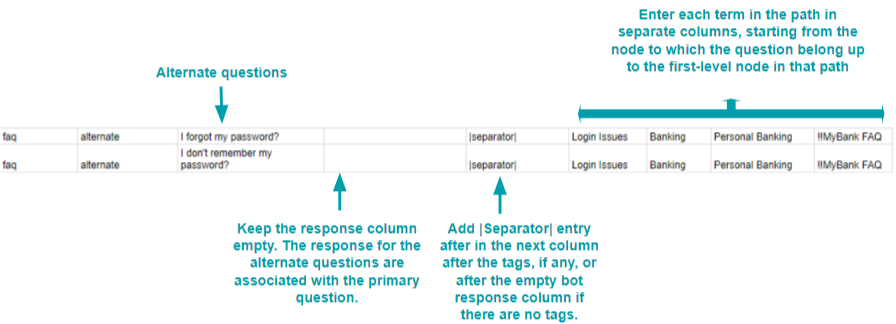
Primary Question
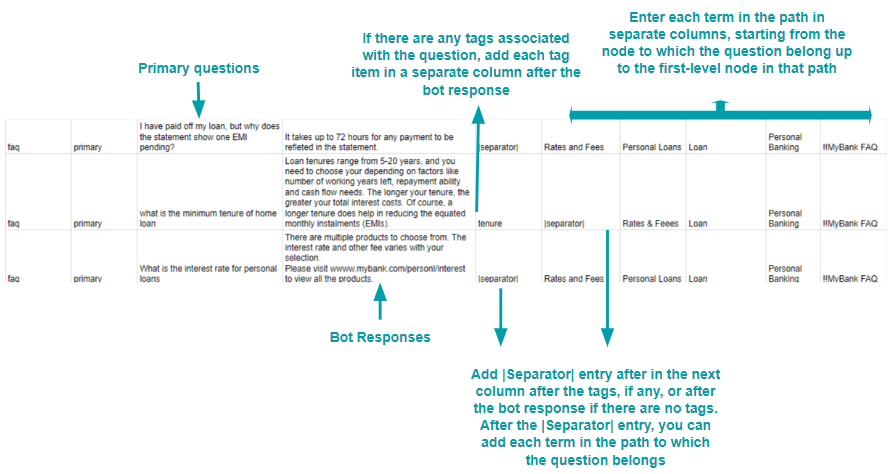
Note: Enter the names of all the parent nodes in separate columns until you reach the First-level node in the path.
Alternate Questions
Terms/Tags
- Mandatory tags and terms can be prefixed with **
- Organizer tags and terms can be prefixed with !!
Unmappedpath
Unmappedpath refers to nodes for which no question is added.

Global Synonyms
Path Synonyms
Traits
<tag/term-name>:<class-name>>