A Script node allows you to write JavaScript code in a Dialog Task.
You can use the Script node to do the following:
- Manipulate user input parameters before executing an API call.
- Manipulate the parameters from an API response payload before continuing with the Dialog.
- Display custom error messages to the user.
- Make decisions based on complex business rules.
When you test a dialog in the Bot Builder, script node errors are displayed in the Error in Script Node dialog with the line number and column number, along with the associated Context object. You can update and test the script directly in the Error in Script Node dialog as shown in the following illustration.
Setting up a Script Node
Setting up a Script node in a Dialog task involves the following steps:
Step 1: Adding a Script Node to the Dialog Task
Step 2: Configuring the Component Properties
Note: The configurations you set up or edit in these sections reflect in all other dialog tasks that use this node
Step 3: Configuring the Connections Properties
From the node’s Connections panel you can determine which node in the dialog task to execute next. You can write the conditional statements based on the values of any Entity or Context Objects in the dialog task, or you can use intents for transitions.
To setup Component Transitions, follow these steps:
- You can select from the available nodes under the Default connections.
- To configure a conditional flow, click Add IF.
- Configure the conditional expression based on one of the following criteria:
- Entity: Compare an Entity node in the dialog with a specific value using one of these operators: Exists, equals to, greater than equals to, less than equals to, not equal to, greater than, and less than. Select the entity, operator using the respective drop-down lists, and type the number in the Value box. Example: PassengerCount (entity) greater than (operator) 5 (specified value)
- Context: Compare a context object in the dialog with a specific value using one of these operators: Exists, equals to, greater than equals to, less than equals to, not equal to, greater than, and less than. Example: Context.entity.PassengerCount (Context object) greater than (operator) 5 (specified value)
- Intent: Select an intent that should match the next user utterance.
- In the Then go to the drop-down list, select the next node to execute in the dialog flow if the conditional expression succeeds. For example, if the PassengerCount (entity) greater than (operator) 5 (specified value), Then go to Offers (sub-dialog).
- In the Else drop-down list, select the node to execute if the condition fails.
JavaScript Examples
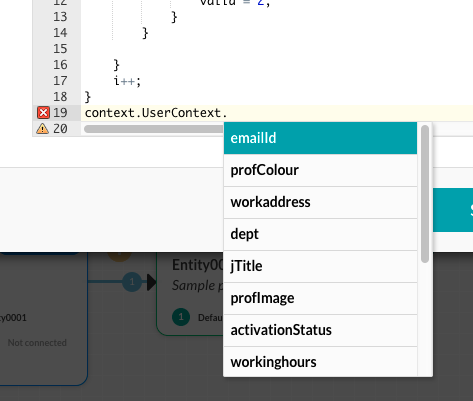
Using JavaScript, you can customize your dialog task by processing data before or after an API call or, for example, directing the dialog task flow. You can use the Context object type-ahead feature to identify and select dynamic variables as shown in the following illustration. For more information, see Context Object.
Examples 1: Manipulating Data
In JavaScript, you can fetch data from the session data using session variables. For example, you can GET the user ID using context.session.UserContext.identities, and then PUT the data into context as shown in the following example.
var x = context.session.UserContext.identities;
var isEmailFound = false;
for (var i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
if (x[i].type === "mapped") {
var identity = x[i].val;
var arr = identity.split("/");
var pattern = /^cs/i;
var result = arr[0].match(pattern);
if (result) {
isEmailFound = true;
context.UserSession.put("rtmEmail", arr[1], '20000');
}
}
}
...
For more information, see Using Session and Context Variables in Tasks.
Examples 2: Handling Conditions
The following code example returns the customer ID using a Context object variable from the Service node response body when the ID is not provided in the data.results
var data = context.getcontactsService.response.body;
if (data & amp; & amp; typeof(data.results) != 'undefined') {
context.customerID = data.results.customerId;
} else {
context.customerID = context.Usersession.customerID;
}
Examples 3: Handling Flow
The next Script node code example validates the bank transfer amount does not exceed limits for the type of account selected using Context object variables.
var valid = 0;
var i = 0;
while (context.accdata.length - i) {
if (context.accdata[i].accountType == context.entities.FromAccountName) {
if ((context.accdata[i].amount - context.entities.Amount) < 0) { valid = 3; } else { if (context.entities.Amount > context.accdata[i].transferLimit) {
valid = 0;
} else {
valid = 2;
}
}
}
i++;
}
context.canProceed = valid;