This tutorial is an end-to-end walkthrough for setting up and running an instance of the Kore.ai Bots Web SDK which is a collection of libraries that you can use to integrate Kore.ai bots with your own web applications.
Web SDK Tutorial Overview
In this tutorial, you will install a Kore.ai sample bot, a test application to host the bot, and then a JSON Web Token (JWT) generation web service using your local host server to communicate between the bot on your local server and the Kore.ai Bots Platform.
The following list describes the general steps you will take to install and configure the Web SDK.
- Build the Bot to be integrated – For this tutorial, you will install the Travel Planning Sample bot that uses open APIs to get flight and location information, along with weather reports.
- Configure Web/Mobile Client channel – To use the Travel Planning Sample bot with the Web SDK, you must configure the bot for the Web/Mobile Client channel.
- Create a new Client App – When you configure the Web/Mobile Client channel for the Travel Planning Sample bot, you must create a client app and select the JWT signing algorithm used to generate the authentication tokens.
- Publish the bot – After you have configured the Travel Planning Sample bot, you must publish the bot which sends the bot to the Bots Admin for approval.
- Approve and Deploy the bot – In the Bots Admin Console, the published bot and tasks must be approved to deploy.
- Download and install Node.js – You will need to install Node.js used to host the JWT token generation web service for the Web SDK to communicate between the bot in the test application and the Kore.ai Bots Platform.
- Download and uncompress the test application – The test application, SDKApp is used to simulate your application that will host the Kore.ai bot as a channel on a web page using your computer local host server.
- Download and uncompress the Kore.ai Web SDK – The Web SDK contains the libraries used to communicate and run the bot in the test application using the Web/Mobile Client channel. You will need to configure settings in the index.html file for your computer.
- Start your application and view the bot in a web browser – In a Terminal window, you will start the JWT service, and then view the bot in a web browser.
Now let us see detailed step by step implementation.
Installing and Running the Kore.ai Web SDK
This section provides detailed steps on how to run a Kore.ai sample bot using the Web SDK and a test application running on your computer local host server.
To get started, you will need to build a bot to run in the test application, and then configure the bot to run in the Web/Mobile Client channel. For this tutorial, we will be installing a sample bot (see here for detailed steps)
- Log on to Bot Builder, and click the down-arrow next to the +New Bot and select Install Sample Bots.
- Hover over Travel Planning Sample, and then click Install.
- The Travel Planning Sample installed successfully message is displayed and the sample bot is added to your Bots left-hand navigation menu.
In this next section, you will define the Web/Mobile Client channel for the Travel Planning Sample bot by creating a new client app and defining channel settings. See here for a detailed explanation of the steps.
- On the bot builder menu, click App Extensions > Web/Mobile SDK.
- In the Select App drop-down list, click Create App. The Create Client App dialog is displayed.
- In the Name field, enter a name for your app, for example, My SDK Client App.
- In the JWT Signing Algorithms section, select HS256 to generate the authentication tokens.
- Click Next -> Done.
- The Web/Mobile Client Channel page is displayed with the following JWT credentials, make a note of all these details. We will be using them later in the Web SDK setup:
- Bot Name
- Bot ID
- Client ID
- Client Secret
- Click Save.
Now that the bot is created and defined for the Web/Mobile Client channel, you are ready to publish and deploy your bot.
- On the Publish tab, click Publish Now.
- On Define Deployment tab, select all tasks, and then click Next.
- On the Review & Confirm tab, click Confirm, and then in the Deploy Standard Bot dialog, click Yes.
- In the Deployment Status dialog, click Close.
After an enterprise developer publishes a bot, it must be approved and assigned to the users for use.
- Complete one of the following bot deployments in the Bots Admin Console depending if your bot Target Audience is set to Enterprise Users or General Public. Complete one of the following:
- In the Bots Admin Console, in the Bots Management module, on the Enterprise Bots page, click the Ellipses icon for the Travel Planning Sample bot that you want to deploy, and then click Manage bot tasks. The Manage Bot Tasks dialog is displayed.
- In the Bot tasks field, click the Expand
 icon to display the available and deployed tasks, select all tasks for this bot, and then click Confirm.
icon to display the available and deployed tasks, select all tasks for this bot, and then click Confirm. - In the Manage bots tasks dialog, click Confirm. The Bot status changed successfully message is displayed.
- On the Enterprise Bots page, click the Ellipses icon for theTravel Planning Sample bot that you want to assign the users to, and then click Bot & task assignments.
- The Bot & task assignments dialog is displayed. Assign the bot to your users, for all tasks, including yourself.
Now it is time to download, uncompress, install and configure the software packages required for the Web SDK and a test application to run the bot locally on your local host server.
- To download and install node.js on your computer, go to https://nodejs.org/en/download/, and then select your OS as .pkg for Mac, and .msi for Windows.
- In a Terminal window, run the
node -vcommand to verify installation and version, for example,v6.10.2. - Locate the SDKApp/sdk folder of your web server hosting the app where you want to integrate the Kore bot. For this tutorial, to download the test application and JWT web service, click SDKApp, and unzip it.
- To download the Kore.ai Web SDK, go to https://github.com/Koredotcom/web-kore-sdk, and then click Download. Extract all files to the …/SDKApp/sdk folder mentioned in step above. Check for the release compatibility from the release notes.
- From the Bot Builder Web/Mobile Client Channel page on the Channels menu, copy the following (as mentioned in step 8 above):
- clientSecret
- clientId
- Bot Name
- For ver7.2 of the platform, the Web SDK repo structure has undergone a major change. The steps would vary based on which repo you are using.
- Follow this step for latest Web SDK file downloaded after ver7.2 of the platform i.e. after Feb 2020.
- Open the index.html file from the …/SDKApp/sdk/UI folder using a text editor. Update the following lines to add the path to the UI folder:
<script src="libs/jquery.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery.tmpl.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery-ui.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link href="libs/jquery-ui.min.css" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<script src="chatWindow.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link href="chatWindow.css" rel="stylesheet"></link> - Open the kore-config.js and update the botOptions parameters botInfo, clientId and clientSecret, and your email id as userIdentity.
“clientSecret”: “{client secret}” $.ajax({ url: “http://localhost:3000/api/users/getJWT”, //this is sample url of a localhost. //This should include the url where you are hosting the bot. botOptions.userIdentity = ‘ ‘; // Provide users email id here botOptions.clientId= "{client id} "; // secure client-id _botOptions.botInfo= {name:"{bot name}","id":"{bot id"}; // Kore bot name is case sensitive })The JWTUrl refers to the location where your app (where you want the Kore.ai Bot to be integrated) is hosted. For this tutorial, we are using the JWT server (as setup in step 19) and hence using the same here.
- Ensure that in kore-config.js you set the audience for your bot. Choose one of the following:
"isAnonymous": < false >;if bot is deployed for the enterprise users, and then setbotOptions.userIdentity = '< Your email ID >';
– or –"isAnonymous": < true >;if bot is deployed for Consumer Use
- Open the index.html file from the …/SDKApp/sdk/UI folder using a text editor. Update the following lines to add the path to the UI folder:
- This step is valid for older Web SDK file downloaded before ver7.2 of the platform i.e. before Feb 2020
- Open the index.html file from the …/SDKApp/sdk/UI folder using a text editor:
- Update the following lines to add the path to the UI folder:
<script src="libs/jquery.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery.tmpl.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="libs/jquery-ui.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link href="libs/jquery-ui.min.css" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<script src="chatWindow.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<link href="chatWindow.css" rel="stylesheet"></link> - Update the following parameters to run as local host
“clientSecret”: “{client secret}” $.ajax({ url: “http://localhost:3000/api/users/getJWT”, //this is sample url of a local host. //This should include the url where you are hosting the bot. botOptions.userIdentity = ‘ ‘; // Provide users email id here botOptions.clientId= "{client id} "; // secure client-id _botOptions.botInfo= {name:"{bot name}","id":"{bot id"}; // Kore bot name is case sensitive })Note: The URL mentioned in the above code snippet, refers to the location where your app (where you want the Kore.ai Bot to be integrated) is hosted. For this tutorial, we are using the JWT server (as setup i step 18) and hence using the same here.
- Choose one of the following:
"isAnonymous": < false >;if bot is deployed for the enterprise users, and then setbotOptions.userIdentity = '< Your email ID >';
– or –"isAnonymous": < true >;if bot is deployed for Consumer Use
- Update the following lines to add the path to the UI folder:
- Open the index.html file from the …/SDKApp/sdk/UI folder using a text editor:
- Follow this step for latest Web SDK file downloaded after ver7.2 of the platform i.e. after Feb 2020.
- Save your changes.
You are ready to start the JWT token generation service and access the test application with the configured Web SDK in your local web browser. - Go to home directory
cd SDKApp - Install dependencies using the following command
npm install
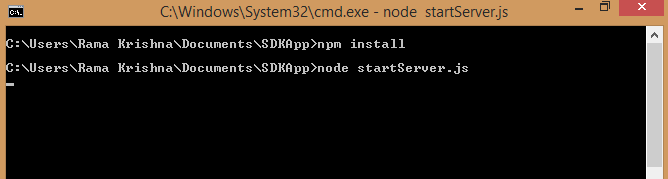
- Start SDKApp
node startServer.js - Access the application in any browser using localhost:3000
Passing data via webSDK
You can pass additional information of the user accessing the channel by adding the custom data at botInfo inside the index.html file.
botOptions.botInfo = {name: "Banking Bot",
"_id": "<bot_id>",
customData: "value"
};
Details like phone number, address, or location, etc., are examples of data that can be passed inside the customData.
customData can be accessed from lastMessage under the BotUserSession of the context object. This data will be specific to the user using webSDK and will last for the user session.
Multiple values can also be added to the customData in the index.html file as key-value pairs:
botOptions.botInfo = {name:"<bot_name>",
"_id":"<bot_id",
customData:{"name":"John",
"age":30,
"cars": {"car1":"Ford",
"car2":"BMW",
"car3":"Fiat"
}
}
};
Passing Mapped Identities
The Web/Mobile SDKs support the passing of mapped identities of the users when they switch from one identity to another while interacting with the bot. This process allows the users to continue any ongoing conversation initiated using a previous identity.
For example, a user may have started the conversation with the bot using an anonymous or randomly generated identity. After exchanging a few messages, the user may become an authenticated or known user by logging into your website or any application. At this point, the user’s known identity can be passed to the bot from the SDK as part of the ‘JWT Grant API’ call using the parameter identityToMerge. The Platform uses this information to merge the user identities and allows the user to resume an ongoing conversation using the new known identity.
{
"iat": 1611810186883,
"exp": 1611813786.883,
"aud": "https://idproxy.kore.com/authorize",
"iss": "cs-d3042d3e-7da4-55da-a94d-783349270cc0",
"sub": "knowuser1@test.com",
"isAnonymous": "false",
"identityToMerge": "anonymoususer1@test.com"
}
The following scenarios describe the bot behavior when dealing with the new identity and merged identity:
- When both the new and merged identities are not present in the system, then the new identity is created and a new conversation is started using new identity
- When the new identity is present but the merged identity is not present in the system, then the conversation is started or continued (in case of an active session) using new identity
- When the merged identity is present but the new identity is not present in the system, then the new identity is created and the conversation is continued using the new identity. All references to the merged identity are replaced with the new identity and the merged identity is removed.
- When both the merged identity and the new identity are present in the system and the new identity does not have an active session, then the conversation is continued using the new identity. All references to the merged identity are replaced with the new identity and the merged identity is removed.
- When both the merged identity and the new identity are present in the system and both have an active session, then the merged identity’s conversation is continued using the new identity. All references to the merged identity are replaced with the new identity and the merged identity is removed. The active session of the new identity is marked as “Drop-off” and closed
Due to the above-mentioned behavior in the user identity following changes can be seen:
- Analytics and Chat History will be updated associating all the sessions related to the merged identity with the new identity
- The sessions data is updated replacing the merged identity with the new identity
- The Billing Session tracking merged identity’s conversation will be marked as new identity
Custom Meta Tags via webSDK
With the release of ver8.0 of the platform, you can directly add Custom Meta Tags from all supported internal channels (Web SDK/IVR / IVRVoice / Webhook channels). You can define Session, User, and Message level meta-tags. These tags will be added to the Conversation Session as soon as it is created.
botOptions.botInfo = {name:"<bot_name>", "_id":"<bot_id",
customData :{"name":"John"},
"metaTags": {
"messageLevelTags": [{ "name": "tag1", value: "message"}],
"sessionLevelTags": [{ "name": "tag2", value: "session"}],
"userLevelTags": [{ "name": "tag3", value: "user"}]
}
};
Some commonly encountered errors
- A wrong URL is given in index.html, users see a 404 error. Double check the URL. URL changes depending on whether you are hosting the bot on your own web SDK or on Kore’s web SDK. If its Kore web SDK, then the URL is
http://demo.kore.net:3000/users/sts 7.
If you are hosting on your in-house web SDK, then provide the respective URL. - missing/Invalid jwt.sub(): This error occurs for enterprise Bots, when the user’s email id is not given in the index.html file. Provide users identity as shown below in index.html
botOptions.userIdentity = ‘x@gmail.com’;// Provide users email id here. - Not found: User sees this error when either wrong clientID or no clientID is given. Check the correct ClientID from Bot – API Extensions option
botOptions.clientId = “{clientID}”; // secure client-id - error verifying the jwt: the Wrong clientSecret is given in index.html: Check the correct clientSecret you get from Bot – API Extensions option
“clientSecret”: "{clientSecret}” //provide clientSecret here
After you install and test the Web SDK using the test application and your local host server, you can use the same concept to install and configure the Web SDK in your own enterprise application. You will just need to reconfigure the file paths and URLs in the index.html file of the Web SDK to point to your website and servers, and configure a Kore.ai bot for the Web/Mobile Client channel with JWT credentials for your enterprise.

