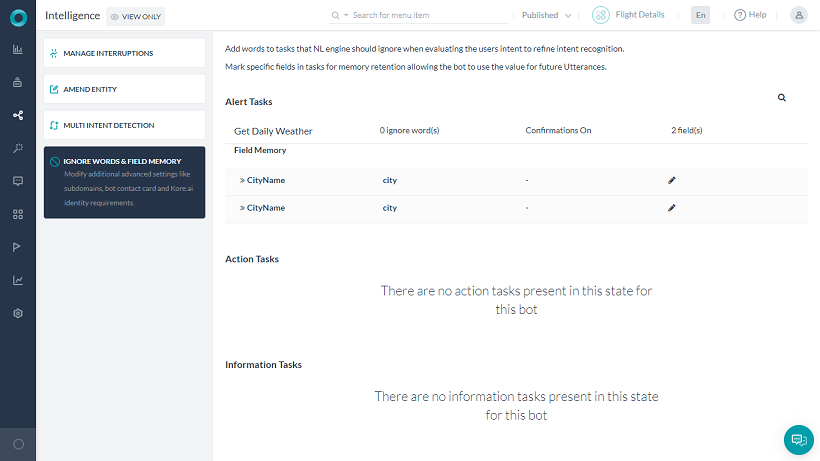
Developers can include words for the NLP engine to ignore when interpreting the user input for a task. Bots can then respond faster to user input and improve the probability of correct task recognition. The NLP engine comes pre-built with a large set of generic ignore words.
To manage this setting,
- On the left pane, click Natural Language > Intelligence.
- On the Intelligence page, click the Ignore Words & Field Memory tab.
You can edit each task to persist data for that task to pre-populate in another related task for the same bot in the Field Memory settings for each task. For example, for a theme park bot, Get Wait Times for Rides task, you can pre-populate task fields into the related task, Book a FastPass action task. You can also configure words to ignore in the user input at the task level. For example, for the 7-day Weather Forecast task, you might want days of the week, such as Monday, Tuesday, and so forth to be ignored since all weekdays are included.
Click a task name to show task fields that can be configured or edited for Field Memory and other field settings. The task fields are the parameters defined for the selected task. To define ignore words for a task,
- Hover over the task, and then click the Edit icon.
Edit a Task
To modify or add a configuration for a task,
- Hover over the name of the task, and then click Edit. The Edit Task window is displayed.
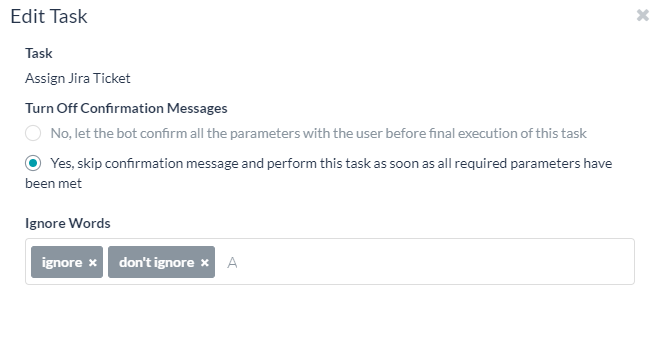
- Turn Off Confirmation Messages – Select Yes to disable confirmation of the execution of a task when using NLP. When No is selected, the user is asked to confirm the task before running it.
- Ignore Words – Enter one or more ignore words for the task name. The list of words to ignore is processed by the Bots Platform before interpreting the user input. This means the bot can respond faster to user input and provide the correct task by filtering out words that apply to many tasks but do not help to identify which task. For example, a user may input, I want to get the weather forecast for today. To return the correct task to the user, the Bots Platform interpreter only needs to recognize three words, weather, forecast, and today. The rest of the words can be ignored. The Kore.ai Bots interpreter is already defined with a set of generic ignore words, so words like I, you, want, get, etc., do not need to be defined as ignore words. If your bot uses the same words for many or all tasks, for example, your company name, you might add your company name as an ignore word.
- Click Save to save the settings and close the Edit Task window.
Define Field Memory for a Task
To add or edit Field Memory settings for a task,
- Click the Task Name to display the associated Task Fields; then click the Edit
 icon to display the Field Memory window as shown in the following illustration.
icon to display the Field Memory window as shown in the following illustration.
In the Field Memory dialog, you can specify the following options: - Entity Type – Select the type of data that the NLP interpreter should expect as input to enhance recognition and performance:
See here for entity types. - Memory User-Provided Value – Enable or disable persistence of data provided by the user for a specified time. One of:
No, do not memorize – The user’s data for this field is not persisted after the task is completed.Yes, memorize this value – The field value is persisted for the time specified in minutes. - Click Save to save the settings and close the Field Memory window.