The Entity Type provides the NLP Interpreter with the expected type of data from a user utterance to enhance recognition and system performance. The Kore.ai NLP interpreter extracts the entity from the user utterance. If the user does not enter a required entity, you can define a virtual assistant Response node to prompt the user to provide the entity. For more information, refer to Working with the Confirmation Node.
You can also define entity rules to validate user input, refer here for details.
The following Entity Types are specified for an entity node.
Address
Captures addresses written in the standard US and Germany address formats. For example, 200 E Main ST Pheonix AZ 85123 USA. The complete address is captured as a string: “200 E Main ST Pheonix AZ 85123 USA.” In addition to this string, the Address entities like City, Country, and Zip Code also provide the full formatted address that has been captured.
"entities":
{
"AddressEntity": "200 E Main ST Pheonix AZ 85123 USA"
}
For other country addresses, the platform captures strings that end with a recognizable city or country name. For more details, please refer to the City entity.
Airport
Captures airport details with the following inputs:
- City name
- Airport name
- IATA code
- ICAO
- Abbreviations of US cities.
Airport details are returned as a JSON entity with the elements shown below:
"AirportEntity":
{"IATA": "LHR",
"AirportName": "London Heathrow Airport",
"City": "London",
"ICAO": "EGLL",
}
We use https://github.com/opentraveldata/opentraveldata for all the airport details.
| Input | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| City name |
Identifies the airport name from the city name in the user utterance. If the city has multiple airports, shows the list of airports to choose from. | Utterance: Flying to Los Angeles Response: The airport you entered seems to be ambiguous. Tell me the option you would like to choose. <Names of five airports in Los Angeles> |
| Airport name | Identifies the airport name from full airport name or partial name with the prominent keyword. | Utterance: Flying to Heathrow Captured: London Heathrow Airport with the necessary details in the virtual assistant. |
| IATA | Identifies airport names by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) codes. | Utterance: Flying to LHR Captured: Details of the London Heathrow Airport |
| ICAO | Identifies International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) codes. | Utterance: Flying to EGLL Captured: Details of the London Heathrow Airport |
| Abbreviations of cities | Identifies city abbreviations that are listed in www.geonames.org | Utterance: Flying to LA Response: The airport you entered seems to be ambiguous. Tell me the option you would like to choose. <Names of five airports in LA> |
Attachment (Image / File)
The user can attach a file, image, or email up to 25 MB.
"entities":
{
"AttachmentEntity": "send"
}
Note: Currently, the attachment entity is supported only for the following channels – Facebook, Twitter, Web/Mobile, and Slack.
City
The name of a city in an utterance such as What is the temperature in New York. The virtual assistant captures any city name with over 5000 population in the form of a string. We use www.geonames.org for all the city details.
"entities":
{
"CityEntity": "New York"
}
Country
Captures the name of a Country from user utterance such as What is the capital of the United States of America.
Country details are returned as a JSON entity with the elements shown below:
"CountryEntity": {
"alpha3": "USA",
"alpha2": "US",
"localName": "United States of America",
"shortName": "United States",
"numericalCode": 840
}
See here for a complete list of countries https://www.nationsonline.org/oneworld/country_code_list.htm.
| Element | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| alpha3 | The three-letter code of the country | USA, GBR, or IND |
| alpha2 | The two-letter code for the country | US, GB, or IN |
| localName | Name of the country | United States of America, United Kingdom, or India |
| shortName | Short name | United States, United Kingdom, or India |
| numericalCode | United Nations, used numerical code M49 for countries | 840, 826, or 356 |
Company Name or Organization Name
Captures the name of a company from user utterances such as the Nearest branch for Amazon. The value for Company Name is returned (Amazon) as a string. See Supported Companies list.
The company name corpus includes language-specific names. Variations of a company’s name like stock name, registered name, etc. are all mapped to a common name, thus ensuring that, for example, Amazon, Amazon.com, Amazon Inc are all recognized as a single company.
Apart from the supported companies, the virtual assistant recognizes the words starting with a capital letter and followed by these suffixes as a company type: Inc, Incorporated, Corp, Corporation, Group, Ltd, Limited, Co, Company, LP, LLP, LLLP, LLC, PLLC.
"entities":
{
"OrganizationEntity": "amazon"
}
Color
Captures the name of the color from a user utterance. For example, Set the status to Green. Returns a value for the Color as Green as a string. See Supported Colors list.
"entities":
{
"ColorEntity": "green"
}
Currency
Captures the amount and type of currency from the user utterance. For example, This handbag is priced at 200 dollars where 200 is the amount and USD is the currency.
This entity type recognizes:
- Full currency names (Dollar, Rupees, Indian National Rupees, Dinar)
- Currency symbols ($, S$, £)
- Standard currency abbreviations (INR, USD)
- Commonly used slang for currencies (Buck, Nickel, Dime, Quid, Loonie, Toonie, Benjamin, Jackson, Hamilton.)
"CurrencyEntity":[
{
"code": "SGD",
"amount": 20
}
Custom
Define a regular expression to validate the user input in the Regex field displayed.
For example, enter: [a-zA-Z]{3}[-]\d{4}
to return a sample response as: {"regex":"NLP-1234"}
For more information, refer to Regex Expressions.
Composite
Composite entities are used to capture multiple entity values in one entity.
For example, consider the sales inquiries for flight bookings. Typical queries can be of the form: I am interested in flying first class from Los Angeles to New York City, tomorrow. or I want to fly to NYC tomorrow</em>
As you can see, the virtual assistant typically needs to process a combination of details like flight class, departure city, destination city and travel date to respond to those queries.
These scenarios are taken care of by the Composite Entity Type. Refer here to know more about Composite Entity Types.
Date
Captures a date mention from a user utterance. For example, Book a flight on the 10th of October returns the value for Date in ISO8601 date format is YYYY-MM-DD.
The virtual assistant recognizes all possible ways and formats of dates, like:
- Formatted dates like YYYY-MM-DD, DD-MM-YYYY, DD-MM-YY, YYYY/MM/DD, DD/MM/YYYY, DD/MM/YY, YYYY.MM.DD, DD.MM.YYYY, DD.MM.YY.
- All number dates like YMD and DMY for 20180518 and 09102013.
- Formatted dates with space separators like YYYY MM DD. dd/mm yyyy, dd-mm, dd-mm-yyyy, dd-mm-yy, mm-dd, dd / mm / yyyy, dd . mm . yyyy, ddmm yyyy, mmdd.
- Named months like yyyy/dd/monthNames or yyyy-dd-monthNames or dd.monthNames.yyyy 2018/28/Dec or 2018-28-Dec or 28.Dec.2018.
- Absolute dates related to now like today, tomorrow, yesterday, tonight, this evening, this afternoon, day after tomorrow, the day before yesterday, yesterday morning, tomorrow night, tomorrow for 1 hour, 3 days ago, 24 hours ago, in 3 days, 2 months hence, this day next month last year, next June, June 26 of the year after next, in a week, 2 weeks ago, 22nd of this month, Next month this day, Next 25th, This month 30th, 27th of this month, 3rdmonth, 2nd of the month.
- Named dates like Christmas Day, Christmas Eve, Memorial Day this year, Thanksgiving 2018, last Thanksgiving, week after Thanksgiving, Passover, a day before the new year, day after Christmas.
- Relative dates from absolute like 2 more days from tomorrow, 3 days after July 4, 3 days from now, 5days from today, Need two more days, in 2 days.
- Weekdays like Saturday, coming Monday, Sunday, Saturday, next weekend, First Saturday of the upcoming year, First Sunday of the upcoming month, first Saturday of next month, First Sunday of next year.
"entities":
{
"DateEntity": "1982-04-13"
}
Date Time
Captures a date grouping along with time in a user utterance.
For example, Book a flight on the 10 th of October at 6 pm, returns the value for Date Time in ISO8601 date format as YYYYY-MM-DDThh: mm: ss.sTZD.
The virtual assistant recognizes all possible ways and formats to express date and time.
"entities":
{
"DateEntity": "2017-10-10T18:00:00+05:30"
}
Date Period
Captures start date and end date from the user input. For example, Book the hotel for five days starting May 5. If the user input does not include one or both of the dates, the virtual assistant prompts the user to provide the necessary input.
Note: Unlike other entities, Date Period entities allow you to enter two sets of user and errors prompts:
- User and Error Prompt for From Date.
- User and Error Prompt for To Date.
The following table lists how the entity works in different scenarios:
| Input Type | Virtual Assistant Behaviour |
|---|---|
| Does not include both From and To dates [For example, Book hotel]. | Shows User Prompts for From Date to the user |
| Includes either From or To date [For example, Book a hotel from 15th Aug] | Shows User Prompts for From Date or User Prompts for To Date based on which is missing from the input |
| Includes implicit reference to From Date and duration [For example, Book a hotel for five days starting from Tuesday] | Determines both dates |
| Includes From Date and duration [For example, Book a hotel for five days from 15th Nov] | Determines both dates |
| Includes From Date and To Date [For example, Book a hotel from 5th to 10th] | Determines both dates |
Description
Captures statements or paragraphs of text from the user utterance. The value for Description is returned as a string and can include wild characters.
"entities":
{
"Description": "text here"
}
Captures email address from the utterance. For example, “Send an email to help@koremessenger.com” returns the value of Email as a string.
"entities":
{
"Email": "help@koremessenger.com"
}
List of Items (enumerated)
Display a list of values to the end-user. To define the list type,
- Click the Settings icon next to the List of items (enumerated) Type field.
- On the List of items (enumerated) Setup page, define one of the following list types.
- Static List
- List from Context
This feature is not fully supported in all languages Click here for details.
- Static List – Enter the Display Name, Value, and Synonyms for the key. Set up Auto-Correction value for the user inputs.
- List from Context – Define a context variable to use for this item in the following fields:
- Specify Context Variable to Use – Defines the context object type. For example, EnterpriseContext, BotContext, UserContexts, or session variables such as context.entities. Enter
context.; select a context object type. - Display Name Key – The name displayed to the end-user.
- Value Key – The key that represents the value of the item in the list.
- Synonyms Key – Enter one or more synonyms for the key (Click here for details).
- Specify Context Variable to Use – Defines the context object type. For example, EnterpriseContext, BotContext, UserContexts, or session variables such as context.entities. Enter
- Auto-Correction– Set up auto-correct thresholds for the LOV entity type so that it not only accepts exact matches but also closest utterances with small variations. For example, let us consider that a list value called Apple for which a typo such as appel is accepted based on your threshold settings. The Auto-Correction setting works in the following way:
- The virtual assistant identifies the number of letters to be changed (inserts, deletes, or replaces) in user input to match it to a value in the list.
- The number is converted to a percentage of the total number of letters in the input.
- The list value with the highest similarity is considered as input if the score is greater than or equal to the configured percentage.
Spell correction does not apply to dictionary words or alphanumeric inputs.
Post v7.1, the following keys are added to the context object for the below-mentioned usage:
- ambiguousEntityValues: This key contains values when the user input for a multi-item entity is ambiguous. Using this, you can check if any ambiguous values were identified and construct the flow to resolve the ambiguity. This key is reset if the entity is re-prompted during the dialog. The values are an array of JSON objects, each object containing title, value, and synonym.
- synonymsUsed: This key holds the synonym used to identify the item. You can use this value to personalize the virtual assistant response accordingly if needed. This key is reset if the entity is re-prompted during the dialog.

Note: The ‘Display List of Values’ option is available only for the List of Items (enum). It is NOT available for the List of Items (lookup).
List of Items (lookup)
Display a list of values to the end-user. To define the lookup list,
- Click the Settings icon next to the List of items (lookup) Type field.
- On the List of items (lookup) Setup page, define one of the following list types.
- Static List
- Remote List
This feature is not fully supported in all languages. Click here for details.
Static List: Use Static List to define the entity values as one of the following list types:
- JSON tab – Enter a list of key/value pairs and synonyms (Click here for more). For example:
[{ "title": "United States", "value": "US", "synonyms": ["united states", "USA", "US", "U.S.A", "America"] }, { "title": "John F. Kennedy International Airport", "value": "JFK", "synonyms": ["John F. Kennedy International Airport", "New York International Airport", "JFK"] } ] - Editor tab – Enter the Display Name, Value, and Synonyms for the key.
- Upload File – Click Upload File to locate a JSON formatted file list or a .csv file formatted list of key/value pairs. For example,

Post v7.1, the following keys are added to the context object for the below-mentioned usage:
- ambiguousEntityValues: This key contains values when the user input for a multi-item entity is ambiguous. Using this, you can check if any ambiguous values were identified and construct the flow to resolve the ambiguity. This key is reset if the entity is re-prompted during the dialog. The values are an array of JSON objects, each object containing title, value, and synonym.
- synonymsUsed: This key holds the synonym used to identify the item. You can use this value to personalize the virtual assistant response accordingly if needed. This key is reset if the entity is re-prompted during the dialog.
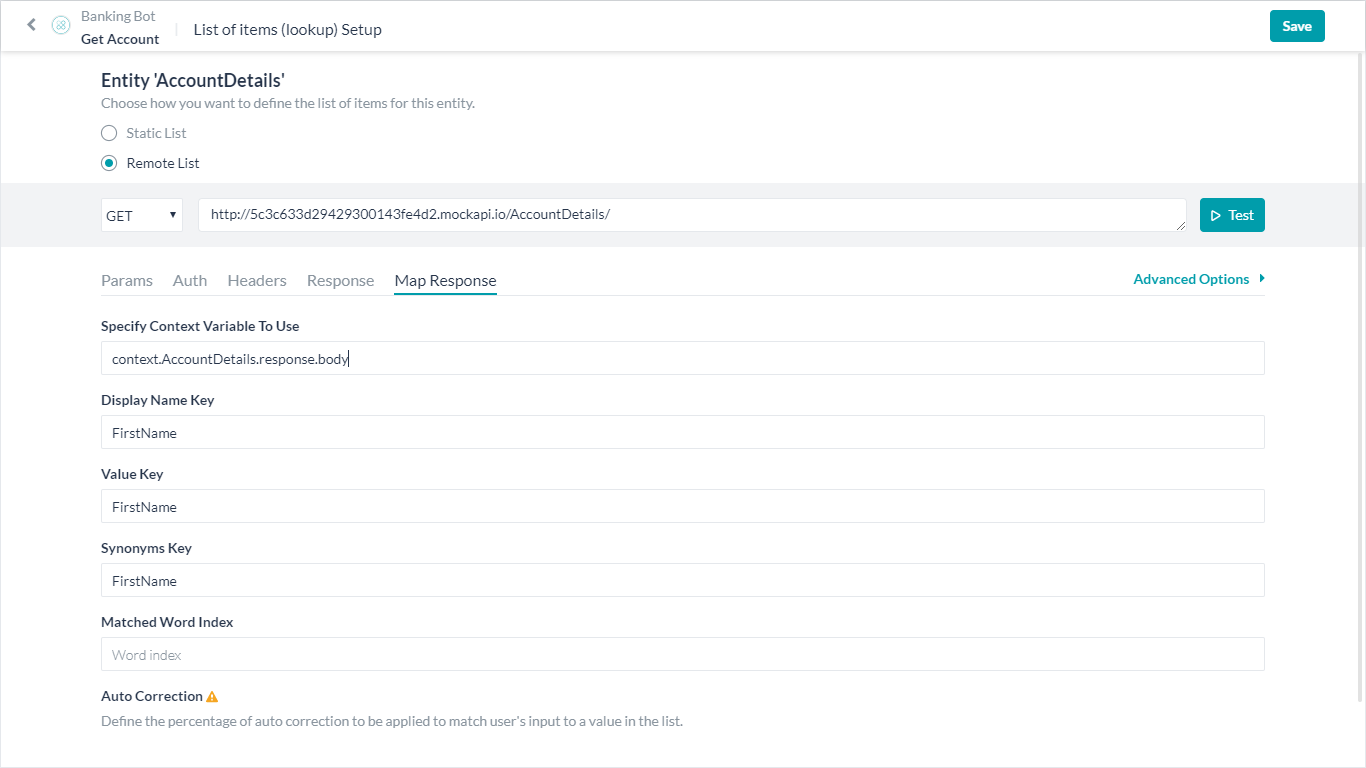
Remote List
Remote List is used when the entity extraction needs to be done by an external service due to security restrictions or any other reasons. This can also be used to handle large data.
The steps involved are as follows:
- Define the Service Call: You can set up a service call similar to how a service node is currently set up. You can set headers, body (for POST), etc,. (Click here for more).
The external service invoked must have a provision to accept and handle the user utterance data that the platform populates. Thecontext.inputDataobject with the following fields is used for that purpose:- input – An array containing the list of inputs received from the user for the current dialog.
- usedUp – Index form of words that are already used for other entities or intents. The format is x-y-z where
- x represents the sentence/utterance index (0 till n).
- y represents the start index of the used up word within the x utterance.
- z represents the end index of the used up word.
- sentenceindex-x-x represents no used up words in that sentence.
- If multiple words are used-up in a single sentence, these should be entered as comma-separated values.
- isMultiItem – Flag should be set if multiple values are expected from the service call.
"inputData": { "input": [ "get account" ], "usedUp": [ "0-x-x" ], "isMultiItem": false }
- Map Response: You can map a response from the service call with the following fields:
- The context variable that holds the response data from the service call. This must be in an array format.
- Display Key Name – Name used to refer to this field; this name is used when interacting with the user. For example, in a disambiguation scenario. This can be accessed using
{{context.entities.<entity-name>.title}}. - Value Key – The field name in the response body from the service call that holds the value, the entity is assigned this value. This can be accessed using
{{context.entities.<entity-name>.value}}. - Synonyms Key – The field containing the synonyms for this field, if any. This is the value that the user refers to. For example, in response to the disambiguation question. This can be accessed using
{{context.entities.<entity-name>.synonym}}. - Matched Word Index – To indicate the words in the inputData that were used for entity extraction (in the same format as the usedUp value in the context.inputData object). This is used by the platform to mark the word as used in the user utterance.
Flow: The platform will:
- Populate the
context.inputDatawith the values mentioned above. - Make the service call to fetch the entity values passing the values as configured in the service call.
- Use the values returned as per Response Mapping:
- If a single value is returned by the remote system, then that value is assigned to the entity.
- If multiple values are returned by the remote system, the platform extracts the entity from this list.
- If a match is found, it is assigned to the entity.
- If no match is found, the user is presented with a list of values to choose from. If the user input matches with any of the items in the list, then it is assigned to the entity. If the user input does not match any of the items, then the input is updated in the context object and another call to the remote service is initiated.
- If one or more matches are found, then it is considered ambiguous and the user is presented with the choices. If the user input matches with any of the items in the list, then it is assigned to the entity. If the user input does not match any of the items, then the input is updated in the context object and another call to the remote service is initiated.
- If the entity is marked as a multi-item entity, then the list of values returned from the remote server is re-evaluated and all valid (valid as per entity type) list items are assigned as values for the entity. Invalid list items are discarded.
- Handle the following exceptions:
- In case the response from the service call is empty or not in the expected format, the User Prompt settings for the entity are used to prompt the user for input.
- In case of ambiguity, for example, when the service returns multiple values when one is expected, the user is prompted to choose one from the list of values returned by the service.
Location
Captures the location details of a city or state from a user utterance.
For example, in Bellagio, Las Vegas the entity captures the location details of Las Vegas. The entity returns the location of the object with address and coordinates as a JSON response.
"Location":
{
"formatted_address": "Las Vegas, NV, USA",
"lat": 36.1699412,
"lng": -115.1398296
}
Number
Captures a number from a user utterance. For example, Book a room for 16 people. In this example, the value 16 is returned as the number.
The virtual assistants platform recognizes the spelled-out numbers and also standard abbreviations such as 1M. A consecutive number of words are combined into one number. For example, one two three becomes 123.
Note: The maximum number of digits allowed is 18.
"entities":
{
"NumberEntity": 16
}
Person Name
Captures the full name of a person from a user utterance.
For example, Send an email to John Smith, where John Smith is identified as Person Name.
The Kore.ai virtual assistant platform assumes that the first word in the user utterance with capital letters as the first name along and the next two words in camel case as a part of the name.
For example, if the user utterance is I want to talk to John Smith, it recognizes John Smith as the name. If the utterance is I want to talk to John smith immediately it recognizes only John as the name.
"entities":
{
"PersonName": "John Smith"
}
Percentage
Captures the percentage value from a user utterance.
For example, The chance of rain today is more than 60 percent, where 60 is the percentage and is returned as a float value of 0.6 in a range of (0.0-1.0). It supports the percent, percentage, and the % sign.
"entities":
{
"PercentageEntity": 0.6
}
Phone Number
Captures the standard 3-digit to 12-digit phone number(s) from a user utterance.
For example, Please call 4075551212, the value for the Phone Number is 4075551212 and is returned as a number. The virtual assistant now extracts the correct phone number when provided in a non-standard format like (407)-407-4077 or 407.407.4077 without prompting the user to enter the phone number in the correct format. This is applicable to all the Phone Number based entities by default.
"entities":
{
"PhoneNumber": "+4075551212"
}
Support for Phone Numbers in Arabic
The Platform now supports phone numbers in the Arabic language, where the virtual assistant identifies the Arabic number given in words from the user utterance (text) and converts it to the relevant digit.
For example:
The input أربعة صفر سبعة. أربعة صفر سبعة. أربعة صفر سبعة سبعة is converted to 407 407 407 where “.” is identified as a separator.
Quantity
Captures the quantity in an utterance with the following details from the user utterance:
- Type of quantity (length, area, volume, etc.).
- Unit of measurement (kilometers, square kilometer, cubic meter, etc.).
- The amount (100, 500, 1.5, etc.).
When you select the Quantity entity type, you also need to select a unit type for the quantity and the default measure.
For example, for capturing volumes, select Volume as the Unity Type and Milliliters as the Default Unit. So, if a user utterance is Add 500 ml of water, the following JSON is returned:
"Quantity":
{
"unit": "millilitre",
"amount": 500,
"type": "volume",
"source": "500 ml"
}
The virtual assistants platform identifies all these quantities and unites along with the standard abbreviations, codes, and symbols.
| Type | Units |
|---|---|
| Length |
|
| Area |
|
| Volume |
|
| Time |
|
| Speed |
|
| Pressure |
|
| Energy |
|
| Memory |
|
| Weight |
|
| Angle |
|
| Age |
|
| Temperature |
|
String
Works identical to the Description entity type but limited to one sentence.
There won’t be any validations done on the user utterance for string entities unless trained. Hence this entity type is used as a last resort when your requirement is not met with any of the platform supported entity types.
Time
Capture time in a user utterance. For example, Set my alarm for 6 am, return the value of Time in ISO 8601 time format as hh:mm:ss.sZD.
It recognizes the following denotations:
-
- am, a.m., AM, pm, p.m., PM, P.M.
- Numbers spelled out. For example, Six AM.
- Morning and evening. For example, Six in the evening.
"entities":
{
"TimeEntity": "T06:00:00+05:30"
}
Time Zone
A time zone. Eastern Standard Time converts the timezone into GMT and stores the resulting value. For example, if you type EST, it is stored as -6:00. The virtual assistants platform recognizes the standard time zones.
"entities":
{
"TimeZoneEntity": "-06:00"
}
URL
Captures a web URL from the utterance. The virtual assistant recognizes all standard formats of URLs. For example, Visit our website: www.kore.ai. The value for the URL is returned as a string.
"entities":
{
"URLEntity": "www.kore.ai"
}
Zip Code
Captures a US zip code from the user utterance. For example, What is the weather for 32746? The value for Zip Code is 32746 and is returned as a string.
"entities":
{
"ZipcodeEntity": "32746"
}