In natural conversations, it is very common that a user provides background/relevant information while describing a specific scenario. Traits are specific entities, attributes, or details that the users express in their conversations. The utterance may not directly convey any specific intent, but the traits present in the utterance are used in driving the intent detection and bot conversation flows.
For example, the utterance my card is being rejected and am on a business trip expresses two traits card decline and emergency. In this scenario, the utterance does not convey any direct intent, or at best it is used to trigger the unblock card flow. However, the presence of emergency trait is used to directly assign the conversation to a human agent.
Traits feature of the Bots platform is aimed at identifying such characteristics present in user utterances and use them for intent detection and in customizing the bot definition using these characteristics.
Use Case
Book a Flight bot might have an added requirement to book a flight based on the cost preference.
User utterance: I am looking for a low-cost option to London must result in ordering the available flights and picking the lowest-priced ticket.
This can be achieved by:
- Adding a Trait Type called Travel Class with Trait Economy trained with the utterance low cost.
- Adding a Rule for book flight to be triggered in the presence of Economy Trait.
- Add transition condition in case Trait Economy is present in the context.
Configuration
Configuring Traits involves:
- Trait Definition
- Trait Association Rules
- Trait Detection
Trait Definition
To define Traits, under the Build top menu option, from the left menu, click Natural Language –> Training and select the Traits tab.
Following are the key features to be considered while defining Traits:
- Trait Type is a collection of related traits like Travel Class in the above example.
- Trait Type can be ML Based or Pattern Based. Each trait of a trait type can be trained using words, phrases, utterances, or patterns based on the type. Manage Trait Type allows you to define the training configuration. See below for ML-based trait configuration.

- A Trait Type can have one or more Traits.

- Traits names should be unique in a group. But traits with the same name can be present in multiple groups.
- For ML-based Traits, you can define the words, phrases, or utterances that identify the trait. One trait per trait type is detected for ML-based trait types.
- For Pattern-based Traits, you can define the patterns associated with the given trait. There is a possibility of multiple traits getting detected for pattern-based trait types. Ordering of Traits within the Trait Type signifies the importance of a trait in a trait type and detects only one trait.
- Once added, Train the bot for the Traits to be detected from user utterances.

Notes:
- You can add language-specific traits in the case of multi-lingual bots.
- When a trait name is modified, ensure that all the rules defined using that trait are corrected. This has to be done manually, the platform will not take care of it.
- The trait name must be unique in a group.
- Traits with the same name can be present in multiple groups, but distinguishing them in trait rules or trait detection results is difficult.
Traits – ML Model
When choosing to train traits using the ML model, by default, the n-gram model is used. An n-gram is the contiguous sequence of words used from training sentences to train the model. But this might not be effective when the corpus is very less or when the training sentences, in general, contain fewer words.
From v8.0 of the platform, an option is included to skip or use the n-gram model. Further, the option to parameterize the n-gram algorithm is included.
- When the n-gram option is selected, you can configure the n-gram Sequence Length by setting the maximum value of the n-gram. It is set to 1 by default and can be configured to any integer value between 1 and 5.
- When skip-gram is selected, you can configure
- Sequence Length specifying the number of words to be included in a non-consecutive sequence. It is set to 2 by default and it can take any integer value between 2 and 4.
- Maximum Skip Distance for the number of words that can be skipped to form a non-consecutive sequence of words. This value is set to 1 by default and can take any integer value from 1 to 3.
NOTE: While the settings are same for all languages (in case of multilingual bot), for some languages like Chinese and Korean sequence of characters form grams and for other (Latin-based) languages are word grams.
Trait Association Rules
Trait Rules define Dialog Execution and Knowledge Graph Intent detection.
Dialog Execution
Intent detection or Dialog execution is achieved using traits, along with the ML utterances and patterns. To achieve this, intent must be associated with the required traits by adding Rules.
There are multiple ways to add rules:
- From the Traits section using the Add New Rule link.

- From the Intent Node using the Rules section under the NLP Properties.
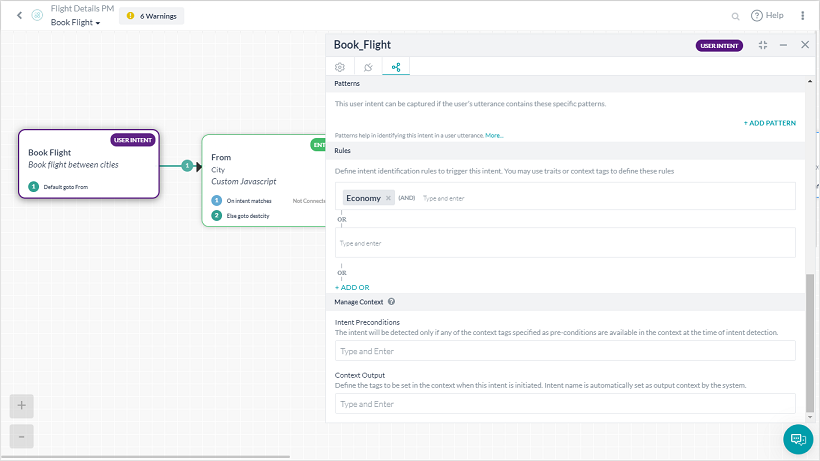
- From the Rules tab for a given Intent.

Each rule can have one or more conditions with AND as the operator. Multiple trait rules can be defined for a given intent and the intent is considered as a definite match if any one of the rules matches.
Knowledge Graph Intents
Knowledge Graph can also be part of the discovery process using Traits. For this, each term or node can be associated with a trait. A given term can be associated with a single Trait.
Trait Detection
Only one trait from a group (trait type) will be detected and is considered as a definite match.
Traits detected are included in the context object. The context is populated with unique traits identified (without reference to trait type). This information can be used in:
- Intent identification
- Dialog transition
- Entity population
- bot definitions
Batch Testing reports also include information about traits detected as do the Find Intent API.
Intent Detection
The Ranking and Resolver gets input from the three NL engines and Traits to analyze and come up with the possible/definitive matches.
- The intent is considered as a definite match only if all the traits (one in the case of Knowledge Graph) present in a trait rule are detected.
- NL Analysis includes information on traits detected and the NLP Flow shows the information about traits detected.

Dialog Transition
Conversation Flow is controlled using Traits. For a Dialog, Connection Rules are defined using the Trait Context. This is done from the Connection tab under the Properties Panel for the Dialog.
The Traits Context is accessed using context.traits. It returns an array of all traits matching the intent, hence the condition to be used is contains.



