Webhook channel provides a generic webhook integration to connect your bot with any external communication systems. Kore.ai platform provides standard request and response APIs to send and receive text messages. End user’s input through a voice, keypad, or any other means must be converted to plain text before it is sent to the Kore.ai platform using the request API.
NOTE: From v7.0, you can enable multiple WebHook channels to your bot. Once added, the WebHook channel will not be disabled from the channel list and you can use the same process to enable another WebHook channel with a different name. Webhook channels with the name and type mentioned (webhook ) are available in the channels filter on the dashboard and analyze section to views the metrics on the applied channel. You can apply channel-specific overrides for each of the webhook channels created/enabled – channel selection drop shows all the webhook channels created. Further, all the channels will be available for selection during the bot deployment.
Prerequisites
To enable the Webhook channel for your Kore.ai bot, you must:
- Associate App – To enable the Webhook channel for your Kore.ai bot, you must associate the channel with either an existing app in your Kore.ai account or create a new app.
- Select Integration Mode – Enable an integration mode that is supported by the channel based on your business requirement. You can copy the Webhook URL from the Configurations tab of the channel.
- Review Payload Formats – Review Payload formats to verify the integration.
To access the Bot Platform’s public APIs, the application making the API request requires authentication. Kore.ai uses the JWT (JSON Web Token) technology to handle the authentication. For a quick overview of the JWT token, refer to Introduction to JWT tokens.
Configure Webhook as a Channel
To configure webhook as a channel, follow the below steps:
- In the Bots section of the Bot Builder, click the bot to which you want to add the Webhook channel.
- On the Channels tab, click the Webhook icon. The Webhook page is displayed.
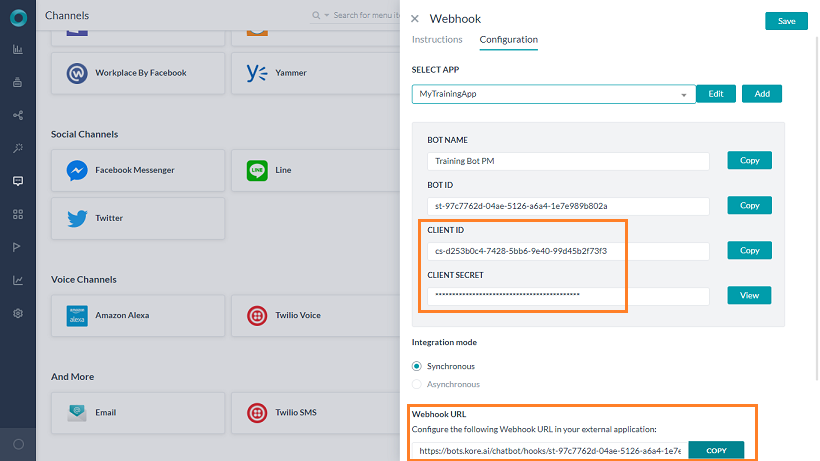
- Go to the Configurations tab of this page and associate this channel with an app.
- Enter a Name for the channel.
- You can select any of the existing Apps available in your Kore.ai account or create a new app.
- Enter a name for the app and click Create. The app is created and Client ID and Client Secret are generated. Copy the Client ID and Client Secret details.
- If you want to use JSON Web Encryption (JWE) standard, you can view the Public Key by clicking the link provided below the Client Secret field.
- Webhook channel supports both synchronous and asynchronous modes. Depending on your business needs, you can enable one of these modes in the Configurations tab.
- Synchronous mode delivers full response directly to the incoming requests. Note that, an alert can not set up a webhook on the webhook channel in synchronous mode, you can also consider using the onAlert event through BotKit, click here for details.
- Asynchronous mode defines the POST_URL of your external system and Access Token used for delivering partial or full responses. When hit, the WebHook URL receives an empty message with a 200 status code, the response message is sent to the POST_URL defined.
- Select Yes to Enable Channel.
- Save the configuration. The Webhook URL in this channel instance is created dynamically.
- Use the Webhook URL to establish integration with external communication systems. This URL is available only after enabling the channel.
After completion of these steps, a success message appears on the screen, and a channel request is sent to your Bots Admin for approval.
Notes
- The channel remains non-functional until the Bots Admin approves it.
- In the case of bot import, WebHook channels will also be imported. You must configure the channels which are created with the import, and associate the channels with an application.
- In the case of Smart Bots, if the parent has webhook channels configured, these channels will be inherited from the child bots. The channel inheritance happens to the child bot every time a new webhook channel is added to the parent and published.
WebHook API Reference
Receives plain text messages from external communication systems
- in case of single webhook configuration and in case of multi-webhook configuration for the first instance
POST {{host_url}}/chatbot/hooks/{{bot id}} - in case of multi-webhook configuration for the second instance onwards:
POST {{host_url}}/chatbot/hooks/{{bot id}}/hookInstance/{{webHookId}}
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
| host_url | Your Kore.ai Bots Platform URL. |
| bot id | The ID of the bot to which you want to post messages. You can access it from the General Settings page of the bot. |
Authorization
Invoke the API with JWT in the header with the following syntax:
Authorization: bearer {{JWT}}
Generate JWT using the following header and payload from this page.
JWT Header
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
JWT Payload
{
"appId": "{{clientId of the bot}}",
"sub" : "{{random number}}"
}
Note: JWT must be generated and signed by the secret key from the server (backend). JWT must not be generated in the browser. The Secret Key must be kept on the server.
Response content type
application/json
Sample Request Payload Reference
payload: {
"message":{
"text" : "Hi",
"attachments" : [<array of attachment links>]
},
"from" :{
"id": <unique-id-of-sender(mandatory)>
},
"metaTags": {// metatags to be captured for this message
"userLevelTags": [<array of objects: To capture user tags>],
"sessionLevelTags": [[<array of objects: To capture session tags>]],
"messageLevelTags": [<array of objects: To capture message tags>]
},
"mergeIdentity" :<true/false>,
"preferredChannelForResponse":"<channel name>" //the channel context to be used to generate a response
}
Sample cURL
curl -X POST
{{host}}/chatbot/hooks/{{bot-id}}
//{{host_url}}/chatbot/hooks/{{bot id}}/hookInstance/{{webHookId}} in case of multi-webhook configuration
-H 'authorization: bearer {{JWT Token}}'
-H 'content-type: application/json'
-d '{ "message": {
"text": "hi" },
"from": {
"id": "1323465" },
"metaTags": {
"userLevelTags": [
{
"name": "userTag",
"value": "userTag_value"
}
],
"sessionLevelTags": [
{
"name": "sessionTag",
"value": "sessionTag_value"
}
],
"messageLevelTags": [
{
"name": "messageTag",
"value": "messageTag_value"
}
]
},
"mergeIdentity" :true,
"preferredChannelForResponse":"rtm"
}'
You can also send additional custom data from the Webhook channel by including it in the request payload. Refer below for an example. This custom data, along with the full payload, will be available as part of the “context.session.BotUserSession.lastMessage” object.
"customData": {"name":"John","age":30,"cars":
{"car1":"Ford","car2":"BMW","car3":"Fiat"}},
Synchronous Response
{
"text": [
"You have $45,000 in your Salary account.",
"Let me know if you need any other assistance"
],
"endOfTask": true,
"endReason": "Fulfilled",
"completedTaskId": "dg-eb0cc36e-06ac-5bff-8234-e4adf501a2ef",
"completedTaskName": "show balance"
}
The response contains the following details:
- text – containing the response from the bot;
- endOfTask – indicating whether the task was completed or not, values true or false
- endReason – the reason for the task completion – fulfilled, interrupted, or canceled
- completedTaskId – the id of the dialog task triggered
- completedTaskName – the name of the dialog task triggered
If the response that needs to be sent back is of a template, then the template JSON object will be included in the text array object. Refer here for more on message templates.
Asynchronous Response
When the client app sends the request to Webhook URL configured in Asynchronous mode, the platform responds back with an empty message and a status code 200.
Further, the platform sends the response to the POST_URL configured at the channel based on the request received from the client app.
Following is the format of the response sent to the POST_URL. If the response that needs to be sent back is of a template, then the template JSON object will be included in the text array object. Refer here for more on message templates.
{
"text" : "message",
"from" : "from_id",
"mergeIdentity" :<true/false>,
"endReason": "Fulfilled",
"completedTaskId": "dg-eb0cc36e-06ac-5bff-8234-e4adf501a2ef",
"completedTaskName": "show balance"
}
Handle Digital Forms
If your bot has a form that needs user input, the synchronous WebHook channel gets the complete form definition in the response and you need to send the formData in the request when interacting with the bot.
Sample Response
{
"text": [],
"form": {
"formDef": { Formdef },
"formInitialization": { FormInitialization } //if any
}
..other params if any
}
FormDef
(This is the complete Form definition which is used to render the Form)
{
"_id": "",
"refId": "",
"streamId": "st-####a#d-##fd-#b##-acab-b#f#f######",
"branding": {
"properties": []
},
"components": [
{
"_id": "fct-#f#e###d-d#b#-###a-#a##-######f###b",
"refId": "#####f##-###c-###b-##a#-da########1d",
"metaData": {
"type": "textField",
"key": "textField",
"displayName": "Text Field",
"name": "TextField0",
"placeholder": "Provide your input",
"toolTip": "",
"isVisible": true,
"required": false,
"validations": {
"validationType": "simple"
},
"validateOn": "onBlur"
},
"name": "TextField0",
"type": "textField"
},
{
"_id": "fct-#f#e###d-d#b#-###a-#a##-######f###b",
"refId": "#####f##-###c-###b-##a#-da########1d",
"metaData": {
"type": "textField",
"key": "textField",
"displayName": "Text Field",
"name": "TextField1",
"placeholder": "Provide your input",
"toolTip": "",
"isVisible": true,
"required": false,
"validations": {
"validationType": "simple"
},
"validateOn": "onBlur"
},
"name": "TextField1",
"type": "textField"
},
{
"_id": "fct-#f#e###d-d#b#-###a-#a##-######f###b",
"refId": "#####f##-###c-###b-##a#-da########1d",
"metaData": {
"key": "button",
"type": "button",
"displayName": "Submit",
"name": "Submit",
"buttonAction": "submit",
"isVisible": true,
"buttonStyle": "primary",
"sourceUrl": ""
},
"name": "Submit",
"type": "button"
}
],
"description": "regular",
"displayName": "Form 1",
"name": "firstForm",
"type": "regular",
(... few other fields)
}
FormInitialization
(This must be used for pre-filling Forms)
{
"valueMap": {
"TextField0": "input1",
"TextField1": "input2"
}
}
Sample Request
{
"session": {
"new": false
},
"message": {
"formData": {
"formId": "frm-2b2f1ae4-9a3b-5f22-8940-b6827710940f",
"data": [
{
"componentId": "fct-9f7e487d-d4b8-542a-9a77-7806819f141b",
"input": "input1"
},
{
"componentId": "fct-7aae4eae-2ce7-5d1b-8db1-bb5cfadc3342",
"input": "input2"
}
],
"meta": {}
}
},
"from": {
"id": ""
}
..others params if any
}

